
DANGERS > WEATHER
Weather
🛈 Info:
? Questions:

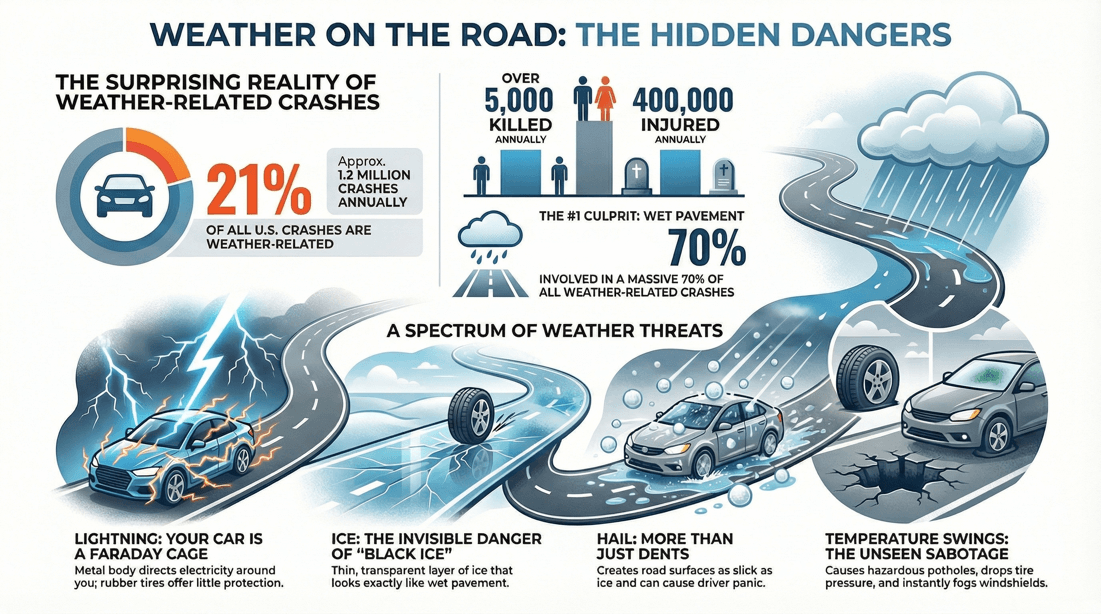
🛈 Statistics on weather-related accidents
United States:
On average, there are approximately 5,891,000 vehicle crashes each year in the U.S. About 21% of these (1,235,000) are weather-related. Weather-related crashes result in over 5,000 fatalities and nearly 418,000 injuries annually .
Rain: Rain is the most common weather-related factor in crashes, accounting for 46% of weather-related crashes. Wet Pavement: Wet pavement contributes to 70% of weather-related crashes. Snow/Sleet: Snow or sleet is responsible for 17% of weather-related crashes. Icy Pavement: Icy roads contribute to 13% of weather-related crashes. Fog: Fog is a factor in 3% of weather-related crashes .
Weather-related crashes are more frequent during the winter months, with December, January, and February seeing the highest numbers due to snow, sleet, and icy conditions.
Global Statistics:
Europe: In Europe, weather-related crashes account for a significant percentage of road accidents. For example, in the UK, about 9% of road accidents are attributed to adverse weather conditions such as rain, fog, and ice. Canada: In Canada, winter weather conditions are a major contributor to road accidents. Approximately 30% of all crashes occur on icy or snowy roads during the winter months. Australia: In Australia, wet weather contributes to about 10% of road accidents, with rain being the primary factor.
Impact on Road Safety:
Visibility: Reduced visibility due to rain, snow, fog, or dust storms significantly increases the risk of accidents. Poor visibility can lead to longer reaction times and difficulty in identifying hazards. Road Conditions: Adverse weather conditions can create hazardous road surfaces. Wet, icy, or snow-covered roads reduce traction, leading to a higher likelihood of skidding and loss of control. Driver Behavior: Drivers often fail to adjust their driving behavior appropriately for adverse weather conditions. This includes not reducing speed, maintaining safe following distances, or using headlights properly.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations:
Weather Forecasts: Stay informed about weather conditions by regularly checking forecasts before traveling. Adjust travel plans if severe weather is expected. Vehicle Maintenance: Ensure your vehicle is prepared for adverse weather conditions. This includes checking tire tread and pressure, ensuring windshield wipers are functional, and using appropriate fluids for the season. Safe Driving Practices: Reduce speed, increase following distances, and use headlights appropriately in adverse weather. Avoid sudden maneuvers and be cautious on bridges and overpasses, which may freeze before other road surfaces. Driver Training: Enhance driver education to emphasize the importance of adjusting driving behavior in different weather conditions. Provide practical training for driving in snow, ice, and heavy rain.
🛈 How weather affects traffic
Reduced Visibility:
Rain, Fog, Snow, and Dust: These conditions can drastically reduce visibility, making it difficult for drivers to see other vehicles, road signs, and hazards. This often leads to slower driving speeds and increased stopping distances. Glare from Sunlight: Low sun angles, especially during sunrise and sunset, can cause glare that temporarily blinds drivers, increasing the risk of accidents.
Road Surface Conditions:
Wet Roads: Rain can create slippery conditions, reducing tire traction and increasing the risk of hydroplaning. Wet roads can also obscure lane markings and road edges. Snow and Ice: Snow and ice significantly reduce traction, leading to longer stopping distances and a higher likelihood of skidding. Black ice is particularly dangerous because it is nearly invisible and extremely slippery. Standing Water: Heavy rain can cause flooding and standing water on roads, which can stall vehicles and create hazardous driving conditions.
Traffic Flow Disruptions:
Congestion: Adverse weather conditions often cause drivers to reduce their speed, leading to slower traffic flow and increased congestion. This is especially true during peak travel times. Accidents: Weather-related accidents can block lanes and cause traffic jams. Emergency response to these accidents can further disrupt traffic flow. Road Closures: Severe weather conditions such as heavy snow, flooding, or high winds can lead to road closures, forcing drivers to seek alternative routes and causing additional congestion on those roads.
Vehicle Performance:
Engine Performance: Cold weather can affect engine performance, making vehicles harder to start and reducing fuel efficiency. Tire Pressure: Temperature fluctuations can cause tire pressure to vary, affecting vehicle handling and safety. Battery Life: Extremely cold or hot weather can reduce battery efficiency and lifespan, increasing the likelihood of vehicle breakdowns.
Driver Behavior:
Cautious Driving: Adverse weather conditions typically cause drivers to be more cautious, which can mean slower speeds and more careful maneuvers. Stress and Fatigue: Driving in challenging weather conditions can increase driver stress and fatigue, potentially leading to slower reaction times and poor decision-making.
Seasonal Impacts:
Winter Weather: Snow, ice, and cold temperatures can lead to significant disruptions in traffic flow, particularly in regions not accustomed to such conditions. Summer Heat: High temperatures can cause road surfaces to become soft and rut, especially asphalt roads. Heat can also increase the risk of tire blowouts and vehicle overheating.
Mitigation Measures:
Weather Forecasting and Alerts: Utilize weather forecasts and alerts to plan travel routes and times, avoiding severe weather when possible. Road Treatments: Use salt, sand, and de-icing chemicals to improve traction on snowy and icy roads. Ensure proper drainage to reduce standing water. Vehicle Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain vehicle components, including tires, brakes, wipers, and lights, to ensure they are in good working condition. Driver Education: Educate drivers on how to adjust their driving behavior in different weather conditions, emphasizing the importance of reduced speeds, increased following distances, and cautious maneuvers. Infrastructure Improvements: Invest in infrastructure that can better withstand extreme weather conditions, such as improved drainage systems, better road materials, and more effective traffic management systems.
? Is a car safe during lightning?
How a Car Protects You from Lightning:
When lightning strikes a car, the electric charge travels along the metal exterior of the vehicle and then to the ground, rather than passing through the interior where the occupants are. This effect is due to the conductive properties of the metal body of the car, which distributes the electrical charge around the outside of the vehicle.
While rubber tires do not conduct electricity, they play a minimal role in protecting the car. The main protection comes from the car's metal frame. The tires slightly elevate the car, which helps to ensure that the charge dissipates into the ground more effectively.
Precautions to Take During a Lightning Storm in a Car:
Stay Inside: Remain inside the vehicle during the storm. Avoid touching metal parts of the car, such as door handles, gear shifts, and the radio. Avoid Using Electronics: Avoid using electronic devices connected to the car’s electrical system, such as the radio or charging ports, as these can conduct electricity if lightning strikes. Pull Over Safely: If possible, pull over to the side of the road to avoid driving during the storm. Turn off the engine and keep your hands in your lap. Keep Windows Closed: Keep the windows closed to minimize the risk of lightning entering the car.
Misconceptions:
Convertible Cars: Convertible cars with fabric or plastic tops do not provide the same level of protection as cars with a metal roof. It is safer to seek shelter in a hard-top vehicle or building. Tires and Lightning: Contrary to popular belief, the rubber tires do not significantly contribute to your protection from lightning. It is the metal shell of the car that acts as a Faraday cage.
Additional Safety Tips:
Avoid High Ground: Avoid parking your car in high or open areas, such as hilltops or near tall trees, as these are more likely to be struck by lightning. Seek Alternative Shelter: If you have access to a well-constructed building, it may be safer to seek shelter indoors until the storm passes.
? How does hail impact road safety?
Reduced Traction:
Slippery Roads: Hail can create slippery road surfaces, similar to ice, leading to a higher risk of skidding and loss of vehicle control. Hydroplaning: Hail can accumulate and mix with rain, creating slushy conditions that increase the likelihood of hydroplaning.
Visibility Issues:
Reduced Visibility: Heavy hail can severely reduce visibility, making it difficult to see other vehicles, road signs, and the road itself. Windshield Damage: Hail can crack or shatter windshields, further impairing visibility and potentially causing injury from broken glass.
Vehicle Damage:
Body Damage: Hailstones can dent the body of the car, causing significant cosmetic damage and potentially damaging essential components like lights and mirrors. Mechanical Issues: Severe hail can damage mechanical parts, such as side mirrors, windows, and even the engine if it penetrates the hood.
Driver Behavior:
Panic and Overreaction: Sudden hailstorms can cause panic among drivers, leading to abrupt braking, swerving, or other sudden maneuvers that increase the risk of accidents. Distraction: The noise and visual impact of hail hitting the vehicle can distract drivers from focusing on the road.
Safety Tips for Driving in Hail:
Slow Down: Reduce your speed to maintain better control of the vehicle and increase stopping distances. Increase Following Distance: Leave more space between your vehicle and the one in front to allow for longer stopping distances and to react to sudden maneuvers. Use Headlights: Turn on your headlights to improve visibility for yourself and others. Find Shelter: If possible, seek shelter under a bridge, overpass, or covered parking area to wait out the hailstorm. Pull Over Safely: If visibility is severely reduced or the hail is very intense, pull over to a safe location with your hazard lights on until the storm passes. Avoid Sudden Movements: Make gradual movements with the steering wheel, accelerator, and brakes to prevent skidding. Check for Damage: After the storm, inspect your vehicle for damage, especially to the windshield and lights, before continuing your journey.
? How do temperature fluctuations affect road safety?
Pavement Conditions:
Freeze-Thaw Cycles: Repeated freezing and thawing can cause the pavement to expand and contract, leading to the formation of potholes and cracks. These road defects can pose hazards to vehicles, potentially causing damage or loss of control. Black Ice: Sudden temperature drops can lead to the formation of black ice, a thin, nearly invisible layer of ice on the road surface. Black ice is extremely slippery and can catch drivers off guard, leading to skidding and accidents.
Vehicle Performance:
Tire Pressure: Temperature fluctuations can cause tire pressure to change. Cold temperatures can lead to under-inflation, while warm temperatures can cause over-inflation. Both conditions can affect tire grip and handling, increasing the risk of accidents. Fluid Levels: Temperature changes can affect the levels and viscosity of various vehicle fluids, such as engine oil, coolant, and windshield washer fluid. Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure these fluids function correctly in varying temperatures.
Driver Behavior:
Adaptation Time: Rapid changes in temperature can require drivers to adjust their driving behavior quickly. For example, a sudden drop in temperature may necessitate slower speeds and increased following distances due to icy conditions. Visibility: Temperature fluctuations can cause fogging on the inside of the windshield and windows. Drivers need to use defrosters and adjust ventilation settings to maintain clear visibility.
Seasonal Changes:
Spring Thaw: As temperatures rise in the spring, snow and ice melt, potentially causing flooding and creating slick, wet road surfaces. Drivers need to be cautious of both standing water and the remnants of winter road treatments (like sand and salt) that can reduce traction. Autumn Leaves: In the fall, temperature fluctuations can cause leaves to fall onto the road. Wet leaves can be as slippery as ice and pose a hazard to drivers.
Road Treatments:
Salt and Sand: In colder climates, roads are often treated with salt and sand to improve traction and melt ice. However, these treatments can be less effective during rapid temperature changes and can create additional hazards if not properly cleared.
Safety Tips for Dealing with Temperature Fluctuations:
Regular Maintenance: Ensure your vehicle is well-maintained and prepared for varying temperatures. Check tire pressure, fluid levels, and battery health regularly. Drive Cautiously: Adjust your driving speed and increase following distances when temperatures fluctuate, especially if there is a risk of ice or road defects. Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and road condition reports to stay aware of potential hazards caused by temperature changes. Use Appropriate Tires: Consider using winter tires in colder months and all-season tires during transitional periods. Winter tires provide better traction on snow and ice, while all-season tires perform well in moderate conditions. Prepare for Visibility Issues: Keep your windshield washer fluid topped up and ensure your defrosters are working correctly to prevent fogging and maintain clear visibility. Avoid Sudden Movements: Make gradual changes to steering, acceleration, and braking to maintain control on potentially slick surfaces.