
Visibility (View)
💡 Tips:
☠️ Alert:
? Questions:
⮟ What role do headlights and taillights play in improving visibility to others? ⮟ How can I tell if another driver sees me when I'm approaching an intersection or making a turn? ⮟ How do large vehicles (like trucks and SUVs) impact visibility for smaller vehicles? ⮟ How can I improve my visibility when merging or changing lanes? ⮟ Can lane markings or road design impact my visibility of other motorists? ⮟ What are the safety concerns regarding motorcycle visibility on the road? ⮟ How do I know if I'm visible to other drivers in poor weather conditions? ⮟ How does weather (e.g., fog, rain, snow) affect visibility between drivers?

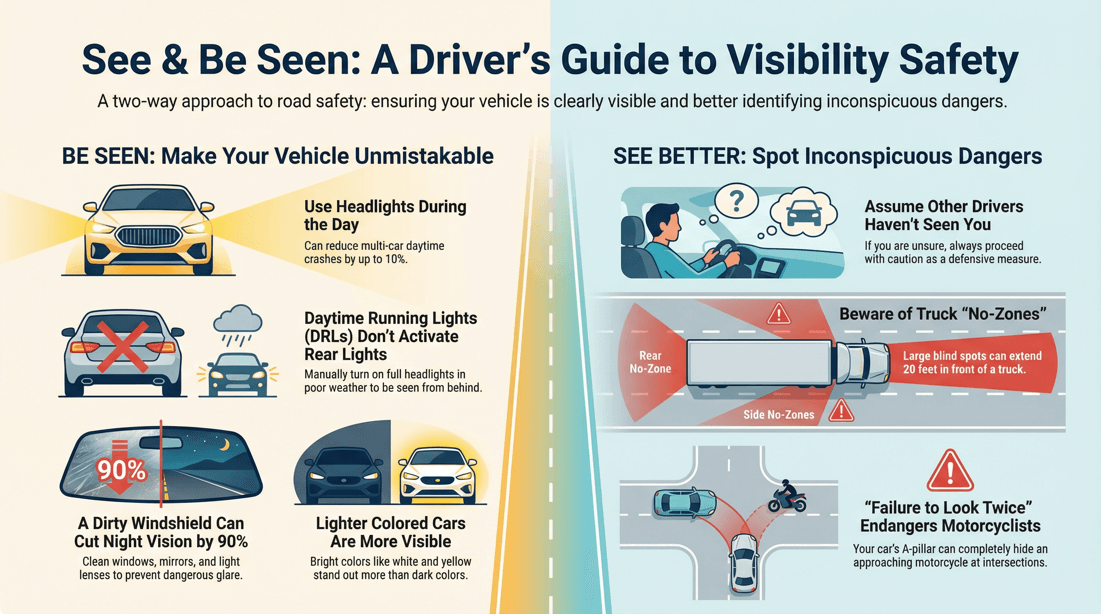
💡 Tips to improve your visibility to others on the road
Use Your Lights Properly
Headlights : Always use your headlights during low-light conditions, such as dawn, dusk, rain, fog, or snow, even if it’s not dark. This makes your vehicle more visible to others. Daytime Running Lights (DRLs) : Ensure your vehicle’s daytime running lights are functioning properly, as they improve visibility during daylight hours. Tail Lights : Make sure your tail lights are in working order so vehicles behind you can see you, especially when it’s dark or during poor weather conditions. Fog Lights : If your vehicle has fog lights, use them in foggy conditions to increase your visibility without blinding other drivers.
Signal Early and Clearly
Turn Signals : Use your turn signals well in advance of any turns or lane changes to alert other drivers of your intentions. This gives them time to adjust accordingly. Hazard Lights : Use hazard lights when you are pulled over, in an emergency, or moving at an unusually slow speed due to a breakdown.
Maintain Clean Windows and Mirrors
Windshield : Keep your windshield clean, inside and out, to prevent glare and improve your own visibility, which in turn helps others see you more clearly. Rear and Side Windows : Dirty or fogged-up windows reduce your visibility to others, so regularly clean them and use defogging systems when needed. Mirrors : Regularly clean and adjust your side and rearview mirrors to ensure that you have optimal visibility around your vehicle.
Keep Your Vehicle Visible
Lights in Poor Weather : Turn on your headlights in rainy, snowy, or foggy conditions, even during the daytime, to increase your visibility to other road users. Brake Lights : Ensure that your brake lights are functioning properly and are not obscured by dirt or debris. Reflectors : If you drive at night or in areas with limited street lighting, make sure your reflectors are intact to improve visibility.
Consider Vehicle Color
Bright or Light Colors : Vehicles painted in bright or light colors like white, yellow, or silver are more visible on the road, especially in low-light conditions. Reflective Decals : Adding reflective decals or stickers can increase your vehicle’s visibility at night.
Avoid Obstructions
Clear the Roof and Windows : Don’t place objects on the roof of your vehicle or block your windows with cargo. This allows other drivers to see your vehicle from all angles. Keep Interior Lighting Minimal : Bright interior lights can create glare and make it difficult for other drivers to see you.
Use Your Horn When Necessary
Alert Other Drivers : If you feel another driver hasn’t seen you, use your horn briefly to make them aware of your presence, especially when approaching blind spots or intersections.
Check Your Tires
Tire Maintenance : Properly maintained tires ensure better road grip, which prevents skidding and makes your vehicle more predictable to other drivers.
Avoid Excessive Tints
Legal Tint Levels : Avoid dark window tints that exceed legal limits, as they reduce your visibility to other road users, particularly at night.
Stay Out of Blind Spots
Avoid Blind Spots : Be mindful of large vehicles like trucks and buses, as they have larger blind spots. Position your vehicle where you can be seen clearly in their mirrors.
Use Proper Following Distance
Don’t Tailgate : Keep a safe following distance to ensure that the vehicle in front can see you in their rearview mirror.
☠️ Inconspicuous dangers on the road
Black Ice
What It Is : A thin, nearly invisible layer of ice that forms on the road, often in shaded areas or bridges. Danger : It is extremely slippery, making it difficult for vehicles to stop or maintain control, especially at normal driving speeds.
Potholes
What It Is : Road depressions caused by wear and tear, often filled with water or covered by shadows, making them hard to detect. Danger : Potholes can damage tires, wheels, and suspension systems. Sudden encounters with deep potholes can cause loss of control or even accidents.
Debris on the Road
What It Is : Small objects like nails, tire fragments, or rocks that may be hard to see until you are too close. Danger : Debris can cause tire blowouts, damage to the undercarriage, or force sudden swerving, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
Hidden Pedestrians or Cyclists
What It Is : Pedestrians or cyclists who may be difficult to see due to poor lighting, dark clothing, or obstructions like parked vehicles. Danger : Drivers may not see them until the last moment, leading to potential accidents, especially at crosswalks or in urban areas.
Unmarked or Faded Road Markings
What It Is : Road markings, such as lane dividers, crosswalks, or stop lines, that have worn away or are not clearly visible. Danger : Lack of clear markings can cause confusion, especially at intersections or in areas with heavy traffic, leading to misjudgments and accidents.
Low Shoulders
What It Is : Sections of the road where the shoulder is lower than the road surface, often unmarked or poorly maintained. Danger : A vehicle that drifts onto a low shoulder can lose control as the driver tries to re-enter the road, potentially leading to rollovers or crashes.
Glare from the Sun
What It Is : Bright sunlight that obscures a driver’s vision, often occurring during sunrise or sunset when the sun is low on the horizon. Danger : Glare can make it difficult to see traffic lights, pedestrians, or other vehicles, increasing the likelihood of collisions.
Sudden Changes in Speed Limits
What It Is : Unexpected changes in speed limits, often in construction zones, school zones, or rural areas, without sufficient warning. Danger : Drivers may fail to slow down in time, potentially causing accidents or receiving traffic citations.
Road Shoulder Drop-Offs
What It Is : Areas where the edge of the pavement drops off sharply into gravel or grass, making it difficult to regain control if a vehicle veers off the road. Danger : Sudden drop-offs can cause a vehicle to skid or overturn when trying to return to the road surface.
Misleading Road Curvature
What It Is : Curves in the road that appear gentle but are sharper than anticipated, especially when visibility is limited. Danger : Misjudging the curve can lead to drifting out of the lane or running off the road.
Poorly Lit or Hidden Driveways
What It Is : Driveways that are not clearly marked or illuminated, particularly in rural or suburban areas. Danger : Drivers may not anticipate vehicles entering or exiting these hidden driveways, leading to collisions.
Animals Crossing the Road
What It Is : Wildlife or domesticated animals suddenly crossing the road, particularly in rural areas or during dusk and dawn. Danger : Swerving to avoid animals can result in loss of control or collisions with other vehicles. Hitting larger animals, like deer, can cause significant damage and injury.
Inadequate Drainage and Standing Water
What It Is : Areas of the road that collect standing water due to poor drainage after rainfall. Danger : Driving through standing water can cause hydroplaning, making it difficult to steer or stop, and can also hide potholes.
Road Construction Zone Hazards
What It Is : Uneven road surfaces, sudden lane shifts, or debris in construction zones that may not be clearly marked. Danger : Construction zones are often chaotic and can have hidden dangers like sharp objects, sudden drops, or unexpected detours that lead to confusion or accidents.
Overgrown Vegetation
What It Is : Trees, bushes, or tall grass that obscure road signs, intersections, or oncoming traffic. Danger : Obscured road signs or intersections can lead to missed turns, running stop signs, or failure to yield, resulting in accidents.
Narrow Bridges or Underpasses
What It Is : Bridges or underpasses that are narrower than the approaching roadway, often with inadequate signage. Danger : Larger vehicles or vehicles with trailers may struggle to navigate these areas, leading to sideswipe accidents or getting stuck.
Weather-Related Optical Illusions
What It Is : Heat waves, rain, or fog can create optical illusions, such as the road appearing to be wet when it’s dry or distorting the appearance of vehicles ahead. Danger : These illusions can lead to poor judgments regarding speed, distance, or road conditions.
Worn or Missing Reflectors
What It Is : Reflectors that have been damaged, removed, or covered by debris, reducing nighttime visibility of lanes or barriers. Danger : Reduced visibility can make it difficult to stay in the correct lane or avoid obstacles, especially in dark or rural areas.
? How can I make my vehicle more visible to other drivers?
Use Your Lights Effectively
Headlights : Use your headlights whenever visibility is low, such as during fog, rain, snow, or dusk. Even during the day, headlights make your vehicle more noticeable to others. Daytime Running Lights (DRLs) : If your vehicle has DRLs, ensure they are functioning correctly. They help increase your visibility during daylight hours. Brake Lights : Ensure your brake lights are in good working order. They alert drivers behind you when you're slowing down or stopping. Fog Lights : In foggy conditions, use your fog lights to cut through the haze without blinding other drivers.
Keep Your Vehicle Clean
Clean Windows and Mirrors : Dirt or grime on your windows, mirrors, or lights can obscure your vehicle and reduce its visibility to other drivers. Regularly clean them for maximum visibility. Headlight and Taillight Lenses : Dirt and debris can cloud your headlights and taillights, reducing their brightness. Clean them frequently, especially after driving in bad weather.
Avoid Dark or Excessive Window Tinting
Legal Tinting : Keep your window tinting within legal limits to ensure that your vehicle's interior remains visible to others, especially at night. Excessive tinting can make it harder for others to see you and for you to see them.
Consider Vehicle Color
Bright or Light Colors : Vehicles in bright or light colors, such as white, silver, or yellow, are more visible on the road, especially in dim lighting or poor weather. If you’re choosing a new vehicle or repainting your car, consider selecting a color that stands out.
Use Reflective Materials
Reflective Decals or Stickers : Adding reflective stickers or decals to your vehicle, especially around the rear and sides, can improve visibility at night. These reflect headlights, making your car easier to spot. License Plate Frames : Reflective license plate frames can also increase your visibility in low light.
Signal Early and Clearly
Turn Signals : Always use your turn signals early and clearly before changing lanes or turning. This helps alert other drivers to your intentions and makes your vehicle more noticeable. Hazard Lights : Use your hazard lights when necessary, such as if you're slowing down unexpectedly, pulled over, or driving in extreme weather conditions.
Maintain Proper Distance from Other Vehicles
Keep a Safe Following Distance : Maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle in front of you gives other drivers more room to see your vehicle and react to your actions. Tailgating reduces visibility for everyone involved. Avoid Blind Spots : Be aware of other drivers’ blind spots, especially around larger vehicles. Position your vehicle where other drivers can see you in their mirrors.
Use High-Visibility Features
Running Lights : Keep running lights or additional lights active if your vehicle is equipped with them. These lights are often found on larger vehicles like trucks and SUVs. Additional Reflectors : Adding additional reflectors to the sides and rear of your vehicle can help others see you better at night, especially if your vehicle is dark-colored or in an area with limited street lighting.
Regularly Check Your Lights
Light Maintenance : Make sure all lights, including turn signals, brake lights, and headlights, are functioning properly. Replace any burnt-out bulbs immediately.
Be Mindful of Vehicle Modifications
Suspension and Lift Kits : Be cautious with modifications that raise your vehicle, as they can make it harder for other drivers to see your lights and signals. Ensure that any modifications still comply with safety standards for visibility.
? What role do headlights and taillights play in improving visibility to others?
Headlights
Improving Visibility in Low-Light Conditions : Headlights make your vehicle visible to other drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians during the night, dusk, dawn, or in poor weather conditions like fog, rain, or snow. They help you see the road ahead, but more importantly, they help others see you. Illuminating the Road Ahead : Headlights allow you to see obstacles, road signs, and other vehicles on the road, giving you enough time to react safely. This is especially important in low-light conditions. Daytime Running Lights (DRLs) : Some vehicles are equipped with DRLs, which are headlights that automatically stay on during the day. DRLs help make your vehicle more visible to oncoming traffic, even in bright daylight, reducing the risk of accidents. Signaling to Other Drivers : Flashing your headlights can be used as a signal to other drivers. For example, you can flash them to indicate that you are yielding the right of way or to warn them of potential dangers, such as an upcoming hazard on the road.
Taillights
Making Your Vehicle Visible from Behind : Taillights are illuminated whenever your headlights are on, ensuring that drivers behind you can see your vehicle in low-light conditions, such as at night or in fog, rain, or snow. Indicating Stopping or Slowing Down : Brake lights, which are part of the taillight system, activate when you press the brake pedal, signaling to the drivers behind you that you are slowing down or stopping. This helps prevent rear-end collisions. Communicating Lane Changes and Turns : Your taillights contain turn signals that flash to indicate your intention to change lanes or make a turn. This gives other drivers time to adjust their speed or position, helping to avoid accidents. Providing Rear Visibility in Bad Weather : In adverse weather conditions, like fog or heavy rain, taillights ensure that your vehicle remains visible to vehicles approaching from behind. This is especially important when visibility is reduced, as drivers may not be able to see your vehicle until they are very close.
Fog Lights
Enhancing Visibility in Foggy Conditions : Some vehicles are equipped with fog lights, which are designed to cut through dense fog without reflecting too much light back into the driver's eyes. They are positioned lower on the vehicle to light up the road close to the vehicle, improving both your visibility and making your vehicle more visible to others.
Hazard Lights
Alerting Other Drivers of Emergencies : Hazard lights, which are activated by both the front headlights and rear taillights flashing, are used to warn other drivers that your vehicle is stopped or moving unusually slowly due to an emergency, such as a breakdown. They help make your vehicle more visible when you are in a vulnerable position.
Turn Signals and Brake Lights
Signaling Intentions : The flashing of your turn signals in the taillights informs other drivers of your intention to change lanes, make a turn, or exit a parking space. This improves communication on the road and helps prevent accidents. Brake Lights as Warnings : Bright brake lights signal to drivers behind you that you're reducing speed or coming to a stop. This gives them time to react accordingly, reducing the likelihood of rear-end collisions.
Light Position and Brightness
Proper Positioning : Headlights and taillights are placed at the front and rear of the vehicle to create visibility in both directions. The height and angle of the lights are designed to optimize visibility while preventing glare that could blind oncoming drivers. Maintaining Brightness : Over time, headlight lenses can become cloudy or dirty, and bulbs can lose their brightness. Regular maintenance ensures that your headlights and taillights are operating at full brightness, improving visibility for both you and other drivers.
Key Takeaways
Headlights and taillights ensure that your vehicle is visible to others in all lighting and weather conditions. They enhance safety by allowing other drivers to see your vehicle from a distance and by clearly signaling your actions (e.g., stopping, turning, lane changes). Proper use and maintenance of these lights are essential to maximize their effectiveness and reduce the risk of accidents.
? How does vehicle color affect visibility on the road?
Bright and Light Colors (e.g., White, Silver, Yellow)
High Visibility in Most Conditions : Vehicles with bright or light colors are generally easier to see, especially in low-light conditions, overcast weather, and at night. Colors like white, silver, and yellow reflect more light, making the vehicle stand out against the darker backdrop of the road. Daytime Visibility : These colors are also more visible during daylight, as they reflect sunlight more effectively, making the vehicle easier to notice from a distance. Safety Benefits : Research suggests that light-colored vehicles, such as white and silver, are less likely to be involved in accidents because they are more visible to other road users, particularly in poor weather conditions or at dusk and dawn.
Dark Colors (e.g., Black, Dark Blue, Dark Gray)
Lower Visibility in Low-Light Conditions : Dark-colored vehicles can blend into the background, particularly at night, in bad weather, or in shaded areas like tunnels or tree-lined roads. This makes it more difficult for other drivers to see them from a distance. Increased Risk at Night : Black and other dark-colored vehicles are harder to spot at night, especially if the vehicle's lights are not functioning properly or if it is parked without proper illumination. Heat Absorption : Dark colors absorb more heat from the sun, which doesn’t directly affect visibility but can make the vehicle hotter in sunny climates, potentially affecting comfort and safety over time.
Medium Colors (e.g., Red, Blue, Green)
Mixed Visibility : Medium colors offer a balance in visibility. Colors like red and blue can be quite visible in daylight but may be harder to see in low light or bad weather compared to lighter colors. Visibility varies depending on the brightness of the shade. Psychological Impact : Bright red cars, for instance, can attract attention due to their boldness and visibility in daylight, but deeper shades of red may lose their impact in darker conditions.
Neutral Colors (e.g., Gray, Beige, Tan)
Subdued Visibility : Neutral-colored vehicles like gray, beige, or tan may blend into the road or the environment, particularly in overcast weather, fog, or dusk. These colors are not as bright as white or yellow, nor as dark as black, so their visibility is somewhat compromised in less-than-ideal conditions. More Challenging to Spot in Certain Weather : In foggy or rainy weather, these neutral colors can blend into the road and the surroundings, making them less noticeable to other drivers.
Unique Colors (e.g., Bright Green, Orange, Neon Colors)
High Visibility : Bright or neon colors like lime green, orange, or neon shades are often highly visible, even in low light or poor weather conditions. These colors stand out on the road, drawing attention quickly. Attention-Grabbing : These colors can make your vehicle more noticeable in traffic and reduce the risk of accidents, as they are easy to spot from a distance.
Factors That Influence Visibility Based on Vehicle Color
Lighting Conditions : Bright-colored vehicles are more visible in low-light conditions such as fog, rain, or nighttime, while dark-colored vehicles tend to blend into the background. Weather : Light-colored vehicles are easier to see in bad weather conditions like snow or rain, whereas dark-colored vehicles can disappear against dark skies or during nighttime storms. Surroundings : In urban environments with a lot of shadows, dark-colored vehicles can become harder to spot, while in bright, open areas, light-colored cars are more noticeable. In rural or wooded areas, bright or medium colors may stand out more against the green or brown backdrop. Accident Risk : Studies have shown that vehicles in lighter colors like white and silver tend to be involved in fewer accidents, as they are easier to detect in various conditions.
Key Takeaways
Lighter colors (white, silver, yellow) generally enhance visibility in both day and night, reducing the risk of accidents. Darker colors (black, dark blue, dark gray) are harder to see in low-light or bad weather conditions, increasing the chance of being overlooked by other drivers. Bright, unique colors (orange, lime green) provide excellent visibility and can make your vehicle stand out, improving safety. Consider your driving environment and typical conditions when choosing a vehicle color to maximize your visibility and safety on the road.
? How can I tell if another driver sees me when I'm approaching an intersection or making a turn?
Look for Eye Contact
Eye Contact : If the driver of the other vehicle makes direct eye contact with you, there's a good chance they are aware of your presence. This is especially important at intersections or when merging. Head Movement : Even if you can’t see their eyes clearly, the driver’s head movement toward your direction can be a sign that they have noticed you.
Observe Their Vehicle Movements
Slowing Down : If the other driver begins to slow down as they approach the intersection, it likely indicates that they have seen you and are preparing to yield or stop. Yielding or Stopping : When a driver stops or yields appropriately at a stop sign, traffic light, or yield sign, it is a good sign they have acknowledged your vehicle and are waiting for you to pass or complete your turn. Proper Positioning : Watch how the driver positions their vehicle. If they maintain their lane and avoid encroaching on yours, it’s a sign they are aware of your presence and are driving cautiously.
Use Your Turn Signals Clearly
Signal Early : Ensure you use your turn signals early and clearly before making a turn or changing lanes. This alerts the other driver to your intentions and increases the likelihood they will notice you. Hazard Lights : In certain situations, such as when making an unexpected or difficult turn, you can use your hazard lights to make your vehicle more noticeable.
Pay Attention to Traffic Flow
Watch Surrounding Traffic : If other vehicles in your vicinity are reacting to your presence—such as by braking, slowing down, or adjusting their lane position—it’s likely that they see you and are anticipating your next move. Driver Hesitation : Sometimes, hesitation in another driver's movements (e.g., lingering at an intersection) could indicate uncertainty about your actions, but it may also mean they are waiting for you to complete your turn or pass through safely.
Use Your Horn Sparingly and Effectively
Short Honk for Attention : If you are uncertain whether another driver sees you, a brief tap on the horn can alert them to your presence. This is especially useful if the driver seems distracted or is encroaching on your right-of-way. Avoid Aggressive Honking : While a short honk can improve safety, avoid aggressive or prolonged honking, as this can escalate tension on the road and cause confusion.
Consider the Driver’s Body Language
Aggressive or Erratic Driving : If a driver is moving aggressively or erratically (e.g., speeding up or cutting lanes without signaling), they may not be paying attention to other vehicles, including yours. Exercise caution and avoid assuming that such drivers have seen you. Distracted Driving : If you notice the other driver is distracted (e.g., looking at their phone, talking to passengers, or fiddling with controls), it’s likely they haven’t noticed you. In this case, proceed with extra caution and give them more space.
Make Yourself More Visible
Headlights : In low-light conditions or bad weather, make sure your headlights are on to increase your visibility to others. Positioning : Avoid staying in another driver’s blind spots when approaching an intersection or preparing to turn. Move to a position where your vehicle is more noticeable.
Wait for Cues at Intersections
Driver Gestures : Sometimes, other drivers will wave you through an intersection or signal with a hand gesture to indicate that they’ve seen you and are yielding. Make sure the situation is safe before proceeding. Traffic Signals and Right-of-Way : Always follow traffic signals and right-of-way rules. Even if you think the other driver has seen you, proceed with caution when making a turn or crossing an intersection.
Monitor Your Own Blind Spots
Check Your Mirrors : Before making a turn or changing lanes, check your mirrors and blind spots to ensure you are aware of all surrounding traffic. Don’t rely solely on others to see you; ensure you’ve cleared the area before proceeding.
Assume the Worst in Uncertain Situations
Defensive Driving : If you're unsure whether another driver has seen you, assume that they haven't. Proceed cautiously and be prepared to stop or take evasive action if necessary.
Key Takeaways
Look for eye contact or head movement as an indication that another driver has seen you. Observe the other vehicle's movements—slowing down, stopping, or positioning in the lane can indicate awareness. Signal clearly and early to ensure your intentions are known. Use your horn sparingly to alert distracted drivers to your presence. Stay visible by keeping your lights on and avoiding blind spots, especially in challenging conditions.
? How do large vehicles (like trucks and SUVs) impact visibility for smaller vehicles?
Blocking Visibility of the Road Ahead
Obstructed View : Due to their height and size, large vehicles can block the view of the road ahead for smaller vehicles. If you're driving behind or beside a truck or SUV, you may not be able to see traffic signals, road signs, or potential hazards until it's too late to react. Reduced Reaction Time : Because your view of the road is limited, you might not notice sudden stops, obstacles, or changes in traffic flow as early as you would if you had a clearer line of sight, reducing the time available to react.
Creating Blind Spots for Smaller Vehicles
Larger Blind Spots : Trucks and SUVs have significantly larger blind spots compared to smaller vehicles. These "no zones" exist at the front, rear, and sides of the vehicle, making it difficult for the drivers of these large vehicles to see smaller cars in adjacent lanes. Risk of Being Overlooked : If a smaller vehicle is in the blind spot of a truck or SUV, the larger vehicle's driver may not see the smaller car when changing lanes or turning, increasing the risk of a collision.
Difficulty with Lane Changes and Merging
Blocking Mirrors : When smaller vehicles attempt to change lanes or merge near large trucks or SUVs, the larger vehicle may block the view in their side and rearview mirrors, making it difficult for the smaller vehicle driver to judge the position and speed of other cars. Hiding Other Vehicles : Large vehicles can hide other cars, motorcycles, or cyclists from view, especially when merging onto highways or making lane changes. A smaller vehicle may not see a car in the next lane because it’s blocked by the larger vehicle.
Impact on Peripheral Vision
Reduced Field of View : When driving next to or between large vehicles, a smaller car’s field of view is diminished. This can be particularly dangerous at intersections, roundabouts, or when approaching traffic lights, where the smaller vehicle’s driver may not have a full view of cross traffic or pedestrians. Difficulties at Intersections : Large vehicles can obstruct the view of oncoming traffic or vehicles coming from side streets, making it harder for smaller car drivers to judge when it’s safe to proceed.
Challenges in Parking Lots
Obscured Sight Lines : In parking lots, large trucks and SUVs can obscure the view for drivers of smaller vehicles trying to back out of parking spaces or navigate through the lot. This can lead to fender-benders or accidents if drivers are unable to see oncoming traffic. Parking Next to Larger Vehicles : When parked next to a large vehicle, it can be difficult to see approaching cars or pedestrians when pulling out, increasing the chances of an accident.
Increased Risk of Rear-End Collisions
High Bumpers : Many trucks and SUVs have higher bumpers than smaller cars. In a rear-end collision, the smaller vehicle may slide under the larger vehicle’s bumper, leading to more severe damage and injury. This is particularly dangerous when following too closely or when the larger vehicle stops suddenly.
Impairing Nighttime Visibility
Brighter, Higher Lights : Trucks and SUVs have headlights that are positioned higher than those on smaller cars. This can cause issues at night or in poor weather conditions, as the lights from large vehicles can shine directly into the windows or mirrors of smaller vehicles, impairing visibility. Blinding Glare : This glare can be blinding, making it difficult for smaller vehicle drivers to see the road ahead clearly, judge distances, or react to obstacles.
Challenges in Turns and Intersections
Obstructed Line of Sight During Turns : When a large vehicle is making a turn at an intersection, it can block the view of smaller vehicles, making it difficult to see cross traffic, pedestrians, or other hazards. Wider Turning Radius : Large vehicles require more space to turn, and if a smaller car is too close, it may be at risk of getting sideswiped or being forced off the road.
Psychological Impact on Drivers of Smaller Vehicles
Intimidation and Anxiety : Large vehicles can intimidate drivers of smaller cars, especially on highways or in heavy traffic. This may cause the driver of the smaller vehicle to overreact or become overly cautious, leading to mistakes or unsafe driving practices. Pressure to Speed Up or Move Over : Some drivers of smaller vehicles feel pressured to speed up or change lanes quickly when a large truck or SUV is tailgating them, which can lead to risky maneuvers and accidents.
Tips for Handling Visibility Challenges with Large Vehicles
Increase Following Distance : Give large vehicles more space, especially when following them. This provides better visibility and more time to react to sudden stops. Avoid Staying in Blind Spots : Stay out of the blind spots of trucks and SUVs whenever possible. If you can’t see the driver’s mirrors, they likely can’t see you. Use Your Headlights : Make sure your headlights are on in poor visibility conditions, such as rain, fog, or at dusk, to ensure the large vehicle driver can see you. Be Patient and Cautious : Don’t try to rush around large vehicles, especially in tight spaces or at intersections. Exercise patience and caution, and wait for a clear opportunity to pass safely.
? How can I improve my visibility when merging or changing lanes?
Adjust Your Mirrors Properly
Side Mirrors : Adjust your side mirrors so you just barely see the edge of your own vehicle. This will minimize blind spots by extending your field of view outward. Rearview Mirror : Ensure the rearview mirror gives you a clear, unobstructed view of the road directly behind you. Adjust it so you can see as much of the rear window as possible. Blind Spot Mirrors : Consider adding blind spot mirrors or convex mirrors to your side mirrors. These small, stick-on mirrors can help you see areas that traditional mirrors may not cover.
Check Your Blind Spots
Always Look Over Your Shoulder : Even with well-adjusted mirrors, you still have blind spots. Always perform a quick shoulder check before merging or changing lanes to make sure no vehicles are in those areas. Use Your Mirrors First : Look into your mirrors first to get a general sense of traffic, then turn your head to check the blind spots.
Signal Your Intentions Early
Use Your Turn Signals : Signal well in advance of your intended lane change or merge. This alerts other drivers to your intentions and gives them time to adjust their speed or position, reducing the risk of collisions. Give Others Time to React : Signaling early helps ensure that other drivers see you and can accommodate your lane change or merge.
Position Yourself for Maximum Visibility
Stay in a Visible Position : Avoid driving in another vehicle’s blind spot, especially near large vehicles like trucks or SUVs. Stay in a position where other drivers can see you in their mirrors. Be Mindful of Your Positioning in Heavy Traffic : In heavy traffic, try to anticipate the movements of other vehicles, and avoid sudden maneuvers. Gradually position your vehicle in a way that maximizes your view of the road and allows other drivers to see you.
Increase Your Following Distance
Give Yourself More Space : Maintaining a safe following distance from the vehicle in front of you gives you more time to react and ensures that you have a better view of the road ahead. This is particularly important when merging onto highways or changing lanes at higher speeds. Improved Reaction Time : More space also gives you extra time to react if another driver suddenly brakes or changes lanes in front of you.
Use Technology to Assist with Visibility
Blind Spot Monitoring : Many modern vehicles are equipped with blind spot monitoring systems that alert you when another vehicle is in your blind spot. While these systems are helpful, don’t rely on them completely—always check your blind spots manually. Lane Departure Warning : If your vehicle has lane departure warning technology, use it to help you stay in your lane and avoid unintentional lane changes, which can help improve overall safety.
Anticipate the Behavior of Other Drivers
Watch for Indicators : Pay attention to the signals and positioning of other vehicles. If you notice a vehicle drifting toward your lane or signaling a lane change, be prepared to adjust your speed or lane position. Look for Gaps in Traffic : When merging, find gaps in traffic early and adjust your speed to match the flow of traffic. Don’t force your way in—wait for an appropriate opportunity.
Be Aware of Your Surroundings
360-Degree Awareness : Constantly scan your surroundings to be aware of the vehicles around you. This includes monitoring the traffic ahead, behind, and to your sides. Check Multiple Lanes : When preparing to merge or change lanes, be aware of the traffic not just in the lane you’re moving into but also in the lanes beyond it.
Use Headlights and Turn Signals Appropriately
Daytime Running Lights : Keep your headlights on, even during the day, to increase your vehicle’s visibility to others. Hazard Lights : If visibility is especially poor (e.g., heavy rain or fog), consider using your hazard lights when making a lane change or merge to ensure that other drivers see you.
Stay Calm and Confident
Avoid Abrupt Maneuvers : Sudden lane changes or merges can catch other drivers off guard. Plan your moves in advance, and merge or change lanes smoothly. Stay Patient : If traffic is heavy or the situation seems unsafe, wait for a better opportunity to merge or change lanes. Avoid rushing or forcing your way into traffic.
? Can lane markings or road design impact my visibility of other motorists?
How Lane Markings Affect Visibility:
Faded or Missing Markings: Worn-out or faded lane markings can make it difficult to determine lane boundaries, especially in low-light conditions or during inclement weather. This can lead to confusion about lane positions and increase the risk of accidents. Reflective Markings: Reflective or high-contrast lane markings improve visibility at night or during rain, making it easier to stay in your lane and see where other vehicles are positioned.
Wide Lane Markings: Wider lane markings are easier to see, especially from a distance or at night. They help drivers maintain proper lane discipline and reduce the likelihood of unintended lane changes. Dashed vs. Solid Lines: Dashed lines indicate where lane changes are permitted, while solid lines usually indicate that changing lanes is discouraged or prohibited. Misinterpreting these lines due to poor visibility can lead to dangerous lane changes.
Curves and Corners: On curved roads, lane markings guide the driver through the turn. Poorly visible or misaligned markings can cause drivers to misjudge the curve, leading to lane drift or collisions with oncoming traffic.
How Road Design Affects Visibility:
Hills and Dips: Roads with significant elevation changes, such as hills or dips, can obstruct your view of vehicles ahead. Cresting a hill, for instance, may temporarily block your view of the road ahead, and descending can cause vehicles behind you to be temporarily out of sight. Blind Spots on Inclines: When approaching the crest of a hill, oncoming vehicles or obstacles may be hidden from view, making it difficult to react in time.
Sharp Curves: Sharp bends in the road can create blind spots where oncoming traffic or obstacles may not be visible until you're very close to them. Proper signage and well-marked lanes are crucial in these areas to guide drivers safely. Visibility around Bends: Road design that includes clear sightlines around curves can help improve visibility, reducing the risk of head-on collisions or other accidents.
Obstructed Views: Intersections with poor visibility due to trees, buildings, or other obstructions can make it difficult to see cross traffic. This is particularly dangerous at uncontrolled intersections where drivers must judge the right-of-way. Offset Intersections: In areas with offset or skewed intersections, lane markings and signs are critical for guiding drivers and reducing confusion, which can otherwise lead to accidents.
Merging Lanes: Poorly marked or designed merge lanes can create confusion and increase the likelihood of sideswipe accidents. Clear lane markings and signs are essential for guiding drivers through merges safely. Exit Ramps: Road design that involves abrupt or poorly marked exits can catch drivers off guard, leading to sudden lane changes or missed exits, both of which can cause accidents.
Poor Road Conditions: Potholes, uneven surfaces, and poor drainage can lead to standing water or road debris, which can be obscured by poor visibility. This can cause drivers to swerve unexpectedly, leading to collisions. Wet or Icy Roads: When roads are wet or icy, lane markings can become difficult to see, and the road surface can become reflective, further reducing visibility.
Safety Tips to Enhance Visibility:
Stay Alert and Drive Defensively: Be aware of your surroundings and anticipate potential visibility issues, such as blind spots around curves or obstacles at intersections. Use Headlights Appropriately: Use your headlights, including low beams or fog lights in poor visibility conditions, to increase your visibility to other motorists and help you see lane markings more clearly. Reduce Speed in Poor Visibility: Slow down when visibility is compromised by road design, such as in sharp curves, over hills, or at poorly marked intersections. Keep Your Windshield Clean: A clean windshield reduces glare and improves your ability to see lane markings and other vehicles. Follow Road Signs and Markings: Pay close attention to road signs, especially those indicating curves, elevation changes, or intersections. These signs often provide critical information that helps compensate for visibility limitations. Be Cautious in Unfamiliar Areas: In areas where you’re unfamiliar with the road design, exercise extra caution, as visibility issues may arise unexpectedly.
Conclusion:
? What are the safety concerns regarding motorcycle visibility on the road?
Smaller Profile and Reduced Visibility:
Size and Shape: Motorcycles have a smaller profile than cars or trucks, making them harder to see, especially in a driver’s peripheral vision or in blind spots. This reduced visibility increases the risk of collisions, particularly when cars change lanes or turn. Obscured by Other Vehicles: Motorcycles can easily be obscured by larger vehicles, such as trucks or SUVs, particularly in heavy traffic. This makes it difficult for other drivers to notice them when merging or turning.
Vulnerability in Blind Spots:
Lane Changes: Motorcycles are more likely to be in a car’s blind spot due to their smaller size. Drivers may not see a motorcycle when they check their mirrors, leading to dangerous lane-change situations. Blind Spot Awareness: Motorcyclists need to be aware of this risk and should avoid riding in other vehicles' blind spots whenever possible, especially on multi-lane roads or highways.
Lack of Visibility at Intersections:
High-Risk Areas: Intersections are particularly dangerous for motorcyclists because they are often less visible when approaching or crossing an intersection. Drivers may fail to notice an oncoming motorcycle when making left turns, leading to collisions. Obscured by A-Pillars: The A-pillars (the vertical supports on either side of a car's windshield) can create blind spots that may obscure a motorcycle from a driver's view, especially when the motorcycle is coming from the side or directly ahead.
Poor Weather Conditions:
Reduced Visibility: Weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow can further reduce a motorcycle’s visibility on the road. The smaller size and lack of external lighting compared to cars can make motorcycles almost invisible in poor weather. Increased Risk of Collisions: In such conditions, other drivers may not notice a motorcycle until it is too late to react, leading to an increased risk of accidents.
Limited Lighting:
Headlights and Taillights: Motorcycles generally have fewer lights than cars, which can make them less noticeable, especially at night or in low-light conditions. This is compounded if a motorcycle’s lights are not properly maintained. Turn Signals and Brake Lights: The small size of motorcycle turn signals and brake lights can make them harder to see, especially if they are not functioning correctly or if the motorcyclist is using hand signals that are unfamiliar to other drivers.
Lane Splitting and Filtering:
Lane Splitting: When motorcycles ride between lanes of slow-moving or stopped traffic, they can be difficult for drivers to see, especially if drivers are not accustomed to lane-splitting behaviors. This can lead to accidents if a car unexpectedly changes lanes or opens a door. Filtering at Intersections: Motorcycles moving to the front of traffic at red lights (filtering) may not be anticipated by other drivers, increasing the risk of a collision when the light turns green.
Driver Distraction and Inattention:
Distracted Driving: Drivers who are distracted (e.g., by phones, GPS, or passengers) are less likely to notice motorcycles on the road. The smaller size of motorcycles makes them more vulnerable to being overlooked by distracted drivers. Failure to Look Twice: Many accidents involving motorcycles occur because drivers fail to look twice before turning or changing lanes. Motorcyclists may be missed on the first glance due to their smaller size.
Road Design and Lighting:
Poor Road Design: Some road designs may inadvertently reduce motorcycle visibility, such as poorly lit areas, sharp curves, or intersections with limited sightlines. Lack of Adequate Lighting: Inadequate street lighting can make it difficult for drivers to see motorcycles, especially on rural roads or poorly lit urban areas.
Safety Tips for Motorcyclists:
Wear High-Visibility Gear: Use bright colors, reflective clothing, and helmets to increase your visibility to other drivers. Consider adding reflective strips to your bike and gear. Use Your Lights: Keep your headlights on at all times, even during the day. Use additional lighting, such as auxiliary lights or LED strips, to increase visibility. Positioning on the Road: Ride in a position where you are most visible to other drivers, typically in the center or left portion of the lane. Avoid lingering in blind spots. Signal Clearly: Use your turn signals well in advance and consider hand signals to ensure other drivers see your intentions. Make eye contact with drivers when possible to confirm they’ve seen you. Anticipate and React: Assume that other drivers may not see you and be prepared to take evasive action. Slow down at intersections, check your surroundings frequently, and be ready to brake or swerve if necessary. Stay Out of Blind Spots: Avoid riding directly next to vehicles, especially large trucks or SUVs, and be aware of the blind spots of other drivers. Be Extra Cautious in Poor Conditions: In adverse weather or low-light conditions, reduce your speed, increase following distance, and use all available lights to make yourself as visible as possible.
Safety Tips for Drivers:
Check Mirrors and Blind Spots: Always check your mirrors and blind spots twice before changing lanes, turning, or merging to ensure there are no motorcycles in your path. Give Motorcycles Space: Allow extra following distance when driving behind a motorcycle. Motorcycles can stop more quickly than cars, and giving them space helps prevent rear-end collisions. Be Cautious at Intersections: Look out for motorcycles when turning or crossing intersections. Be especially mindful of left turns, as these are common scenarios for motorcycle accidents. Avoid Distractions: Stay focused on the road and avoid distractions. A moment of inattention can lead to missing a motorcycle in your vicinity. Use Headlights Appropriately: Keep your headlights on during poor visibility conditions to increase your ability to see motorcycles and help motorcyclists see you.
? How can I improve my visibility when driving at night?
Use Proper Lighting:
Headlights: Ensure your headlights are clean, properly aligned, and in good working condition. Misaligned or dim headlights can significantly reduce your ability to see the road. High Beams: Use your high beams when driving on rural roads or poorly lit areas, but remember to dim them when approaching other vehicles to avoid blinding other drivers. Fog Lights: If your vehicle is equipped with fog lights, use them in foggy conditions to improve your visibility of the road immediately in front of you.
Keep Your Windshield and Mirrors Clean:
Clean Inside and Out: Dirt, smudges, and streaks on your windshield can cause glare and reduce visibility. Clean your windshield, windows, and mirrors regularly, both inside and outside. Defogging: Use your defroster and air conditioning to keep the interior of your windshield clear of condensation, which can obscure your vision.
Adjust Interior Lighting:
Dim Dashboard Lights: Bright dashboard lights can cause reflections on your windshield and reduce your night vision. Adjust the brightness to a lower setting that still allows you to see your controls clearly without causing glare. Avoid Using Cabin Lights: Turn off interior lights when driving at night, as they can create reflections on the windshield and distract your eyes.
Wear Anti-Reflective Glasses:
Night Vision Glasses: If you wear prescription glasses, consider getting lenses with an anti-reflective coating, which reduces glare from oncoming headlights and streetlights. Avoid Tinted Lenses: Don’t wear sunglasses or glasses with tinted lenses at night, as they reduce the amount of light that reaches your eyes.
Increase Following Distance:
Safe Distance: Increase your following distance at night to give yourself more time to react to any potential hazards. This also helps reduce the glare from the headlights of vehicles behind you.
Use Road Markings and Reflectors:
Follow Lane Markings: Use lane markings and road reflectors to help guide your vehicle, especially on winding or unfamiliar roads. These are often more visible than the road itself in low-light conditions. Focus on the Right Edge: If you’re blinded by the headlights of oncoming traffic, focus on the right edge of the road to guide your vehicle safely without being distracted by the glare.
Regularly Check and Maintain Your Vehicle:
Headlight Maintenance: Replace any burned-out bulbs immediately and consider upgrading to higher-intensity bulbs if your current ones are dim. Wiper Blades: Ensure your windshield wipers are in good condition and replace them if they leave streaks. Good wipers are essential for keeping your windshield clear in case of rain or snow at night.
Reduce Your Speed:
Drive Slower: Since visibility is reduced at night, it’s important to reduce your speed to give yourself more time to identify and react to potential hazards.
Be Mindful of Fatigue:
Avoid Drowsy Driving: Driving while tired can impair your vision and reaction time. Take breaks if you’re feeling drowsy, and avoid driving late at night if possible.
Avoid Looking Directly at Oncoming Lights:
Look to the Right: When faced with the headlights of oncoming vehicles, avoid looking directly at the lights. Instead, shift your gaze slightly to the right to reduce the impact of the glare.
Use Polarized or Yellow-Tinted Glasses:
Polarized Lenses: If you experience significant glare from oncoming headlights, consider wearing polarized glasses designed to reduce glare. Yellow-Tinted Glasses: Some drivers find that yellow-tinted glasses can enhance contrast and reduce glare, although their effectiveness can vary between individuals.
Stay Alert for Animals:
Watch for Reflections: At night, animals are often visible only by the reflection of your headlights in their eyes. Watch for these reflections, especially in rural areas.
Know Your Route:
Plan Ahead: Familiarize yourself with the route, especially if driving on unfamiliar roads. Knowing where turns and intersections are located can help you navigate more safely in low-light conditions.
Use Your Rearview Mirror’s Night Setting:
Night Mode: Most rearview mirrors have a night or anti-glare setting, which tilts the mirror to reduce glare from headlights behind you. Use this feature to minimize glare and improve your rear visibility.
Adjust Your Side Mirrors:
Mirror Angles: Adjust your side mirrors slightly downward to reduce glare from the headlights of vehicles behind you while still maintaining a clear view of the road.
Conclusion:
? How do I know if I'm visible to other drivers in poor weather conditions?
Check Your Vehicle's Lighting:
Headlights: Make sure your headlights are on and functioning correctly. In poor weather conditions like rain, fog, or snow, use your low beams rather than high beams, as high beams can reflect off the precipitation and reduce visibility. Fog Lights: If your vehicle has fog lights, use them in foggy or misty conditions to increase visibility close to the ground. Taillights: Ensure your taillights are on when your headlights are on. This helps other drivers see you from behind. Brake Lights: Regularly check that your brake lights are functioning properly. They are crucial for alerting drivers behind you when you slow down or stop. Turn Signals: Use your turn signals well in advance to communicate your intentions clearly to other drivers.
Use Hazard Lights When Necessary:
Hazard Lights: If visibility is extremely poor, such as during a heavy downpour or dense fog, consider using your hazard lights to increase your visibility to other drivers. However, avoid using them while driving at normal speeds, as this can confuse other drivers.
Drive with the Appropriate Speed:
Adjust Your Speed: Reduce your speed to give yourself and others more time to react. Slower speeds also help maintain better control over your vehicle in slippery or low-visibility conditions. Maintain a Safe Distance: Keep a greater following distance from the vehicle ahead to ensure you can stop safely if needed.
Keep Your Vehicle Clean:
Windshield and Windows: Ensure your windshield, windows, and mirrors are clean and free of fog or dirt, both inside and out. Use your windshield wipers and defrosters to keep them clear during adverse weather. Headlights and Taillights: Clean your headlights and taillights regularly, as dirt and grime can significantly reduce their effectiveness.
Positioning on the Road:
Stay in Your Lane: Maintain a consistent lane position to avoid drifting into other lanes, which can happen more easily in poor visibility. Use the Right Lane: If possible, drive in the right lane, as it is typically safer and allows faster-moving vehicles to pass you on the left.
Wear High-Visibility Clothing (For Pedestrians and Cyclists):
Reflective Gear: If you are a pedestrian or cyclist in poor weather conditions, wear reflective clothing or accessories to increase your visibility to drivers.
Be Aware of Your Surroundings:
Check Mirrors Frequently: Regularly check your mirrors to be aware of vehicles around you. If you can see other vehicles clearly, it's a good sign that you are likely visible to them as well. Watch for Reactions: Observe the behavior of other drivers. If they seem to react to your presence, such as slowing down or changing lanes, it indicates that they see you.
Consider Adding Extra Reflective Elements:
Reflective Tape: Adding reflective tape to your vehicle, particularly on the sides and rear, can increase visibility in low-light and poor weather conditions.
Be Cautious with Daytime Running Lights (DRLs):
Understand DRLs: Some vehicles have daytime running lights (DRLs), which are typically not as bright as regular headlights and may not activate the rear lights. In poor weather, manually turn on your full headlights to ensure both your front and rear lights are on.
Use Technology:
Adaptive Lighting: Some modern vehicles are equipped with adaptive lighting systems that adjust the intensity and direction of your headlights based on driving conditions. Familiarize yourself with these features if your vehicle has them. Automatic Lights: If your car has automatic lights, make sure they are set to activate in poor visibility. However, be aware that these systems may not always respond quickly enough in rapidly changing conditions.
Know When to Pull Over:
Safety First: If visibility is so poor that you are unsure whether you are visible to other drivers, or if you cannot see the road clearly, it may be safer to pull over and wait for conditions to improve. Choose a safe spot, such as a parking lot or rest area, and turn on your hazard lights while you wait.
Conclusion:
? How does weather (e.g., fog, rain, snow) affect visibility between drivers?
Fog
Light Scattering: Fog diffuses light, causing headlights to reflect off the water droplets and create a wall of glare. This limits the effective range of visibility, sometimes to just a few meters. Reduced Depth Perception: Fog can make it difficult to judge distances, which may cause drivers to misestimate the proximity of other vehicles, road signs, or obstacles. Hidden Hazards: Objects and vehicles can appear suddenly out of the fog, giving drivers little time to react.
Rain
Windshield Obscuration: Rainwater on the windshield can distort vision, especially if the wipers are not functioning effectively. Even with wipers, heavy rain can create a constant blur. Reflections and Glare: Wet roads reflect streetlights, headlights, and other sources of light, which can cause glare and make it difficult to see lane markings or distinguish objects. Reduced Contrast: Rain reduces the contrast between objects, making it harder to see other vehicles, pedestrians, or road signs, particularly at night. Water Spray: Vehicles, especially large trucks, create a spray that further reduces visibility for drivers behind them.
Snow
Blowing Snow: Wind-blown snow can create whiteout conditions where visibility is reduced to near zero. This makes it extremely difficult to see other vehicles or the road itself. Accumulation on Windshield: Snow can quickly accumulate on the windshield, reducing visibility. If wipers or defrosters are not functioning properly, this can lead to dangerously obscured vision. Glare: Snow on the ground reflects light, which can cause glare during the day or at night from headlights. This glare can be blinding, especially if you're driving in bright sunlight or under streetlights. Obscured Road Markings: Snow can cover lane markings, making it difficult to stay in your lane or judge the position of other vehicles.
Ice
Glare and Reflections: Ice on the road can create reflective surfaces that cause glare from headlights and streetlights, making it difficult to see clearly. Windshield Frost: Ice can form on the windshield, either during a drive or after stopping for a while, obstructing visibility. If the defroster isn't working well, this can quickly become a serious issue.
Hail
Sudden Obscuration: Hail can rapidly reduce visibility as it pelts down, making it difficult to see other vehicles, especially if it’s accompanied by heavy rain. Windshield Damage: Large hailstones can crack or shatter windshields, severely impairing visibility.
Mist
Mild Obscuration: Mist can cause a slight blur that reduces the clarity of your view, particularly at a distance. It may not be as severe as fog but still requires cautious driving.
General Effects of Poor Weather on Visibility:
Reduced Reaction Time: Poor visibility means you have less time to react to other vehicles, pedestrians, or obstacles. This increases the risk of collisions. Impaired Communication: Turn signals, brake lights, and other visual cues can be harder to see in bad weather, making it difficult for drivers to communicate their intentions. Increased Fatigue: Driving in poor visibility conditions requires more concentration, leading to faster driver fatigue and increased risk of errors. Disorientation: In extreme conditions, such as heavy fog or snow, drivers may become disoriented, losing their sense of direction or even driving off the road.
Safety Tips for Driving in Poor Weather:
Use Appropriate Lighting: Always use your headlights in poor weather conditions, but avoid using high beams in fog or heavy snow, as they can reduce visibility. Slow Down: Reduce your speed to allow more time to react to sudden obstacles or changes in road conditions. Increase Following Distance: Give yourself more space between your vehicle and the one ahead to account for reduced visibility and longer stopping distances. Stay in Your Lane: Use road markings, if visible, or follow the edge of the road to stay in your lane. Avoid Sudden Movements: Sudden braking, accelerating, or turning can cause skidding, especially on wet or icy roads. Pull Over If Necessary: If visibility is too poor, pull over to a safe location and wait for conditions to improve.