
Surface
Accident: ⮟ 📹 Debris ⮟ 📹 Obstacles ⮟ 📹 Gravel ⮟ 📹 Holes ⮟ 📹 Markings ⮟ 📹 Uneven ⮟ 📹 Ice ⮟ 📹 Snow Water: ⮟ 📹 Paint ⮟ 📹 Pool ⮟ 📹 River ⮟ 📹 Slippery ⮟ 📹 Visibility
? Questions:
💡 Tips:
🛈 Info:

Accident
📹 Debris
📹 Obstacles
📹 Gravel
📹 Holes
📹 Markings
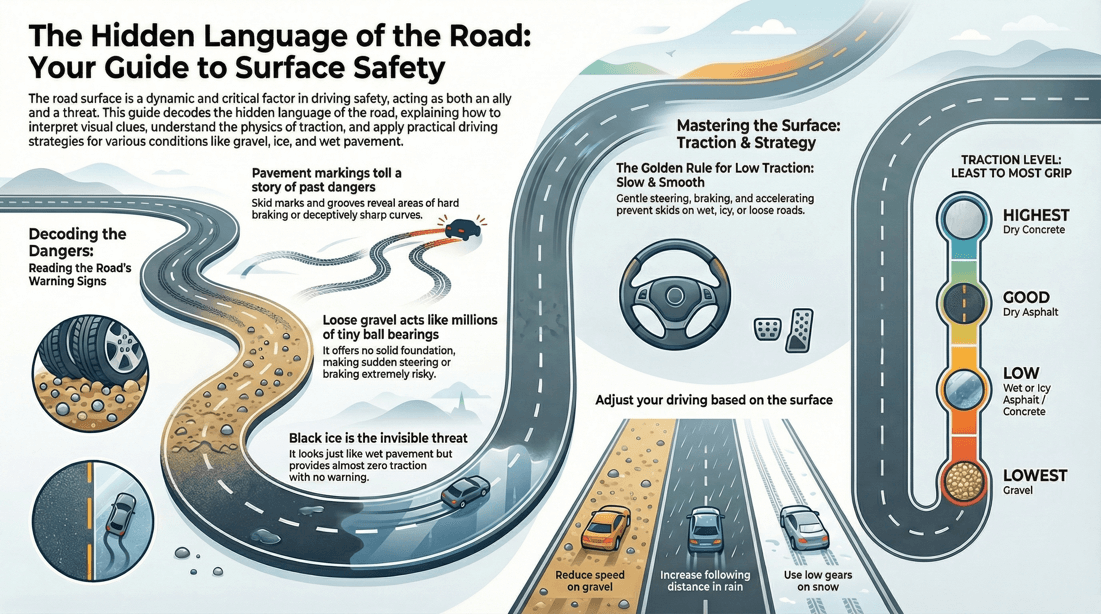
Grooving - This signals a sharp incline in the road angle such that vehicles suspension 'bottoms out' and the sump digs a groove into the road surface. Multiple skid marks: Curved - Indicates a deceptively sharp corner or curve in the road. Longitudinal - Indicates an area where harsh braking is needed for whatever reason. Sand patches - Possibility that strong winds cross that section of road. Flowing grit - Indicates that water washes across the road.
📹 Uneven
📹 Ice
📹 Snow
Water
📹 Paint
📹 Pool
📹 River
📹 Slippery
📹 Visibility
? What is the purpose of road surfacing?
Key Purposes of Road Surfacing
Comfort : A well-surfaced road provides a smooth driving experience, reducing discomfort and wear on vehicles. Traction : Proper surfacing ensures adequate traction, reducing the risk of skidding and improving vehicle control.
Durability : Surfacing protects the underlying layers of the road from traffic loads and environmental conditions, extending the road's lifespan. Load Distribution : It helps distribute the weight of vehicles more evenly, preventing damage to the base and sub-base layers.
Prevent Water Accumulation : A well-designed road surface facilitates proper drainage, preventing water from pooling on the road and reducing the risk of hydroplaning. Protect Against Erosion : Effective drainage also protects the road's foundation from erosion and water damage.
Markings and Signage : Road surfaces provide a platform for applying lane markings, crosswalks, and other traffic control indicators that enhance safety and guide drivers. Reflective Materials : Surfacing materials can include reflective elements to improve visibility at night and in adverse weather conditions.
Noise Reduction : Certain surfacing materials and techniques can help reduce the noise generated by vehicles, creating a quieter environment for nearby residents.
Longevity : High-quality surfacing reduces the frequency and extent of maintenance required, leading to lower overall maintenance costs. Preventative Maintenance : Timely resurfacing can prevent more significant repairs, preserving the road's condition.
Visual Appeal : A well-maintained road surface enhances the visual appeal of the roadway and the surrounding area, contributing to overall infrastructure quality.
Types of Road Surfacing Materials
Flexibility and Smoothness : Asphalt is widely used for its smooth finish and flexibility, which helps it withstand various traffic loads and temperature changes. Quick Application : Asphalt roads can be constructed and repaired relatively quickly.
Durability : Concrete is known for its durability and long lifespan, making it suitable for high-traffic areas. Low Maintenance : Concrete requires less frequent maintenance compared to asphalt.
Cost-Effective : Gravel is often used for rural and low-traffic roads due to its cost-effectiveness. Easy Repair : Gravel roads are relatively easy to repair and maintain.
Seals and Protects : These treatments seal the road surface, protecting it from moisture and improving traction.
Conclusion
? What is used to surface roads?
Primary Materials for Road Surfacing
Composition : A mixture of aggregates (such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone) and bitumen (a sticky, black, and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum). Usage : Widely used for highways, city streets, and airport runways. Advantages : Provides a smooth and flexible surface, quick to apply, and relatively easy to repair.
Composition : A mixture of cement, water, sand, and gravel. Usage : Commonly used for highways, bridges, and airport runways. Advantages : Highly durable and long-lasting, requires less maintenance over time compared to asphalt.
Composition : Loose aggregates like crushed stone, gravel, and sand. Usage : Typically used for rural roads, driveways, and low-traffic areas. Advantages : Cost-effective and easy to apply, with good drainage properties.
Composition : A thin layer of bitumen sprayed on the road surface, followed by a layer of aggregates. Usage : Used for rural roads, low-traffic areas, and as a maintenance technique for existing asphalt surfaces. Advantages : Seals the road surface, provides improved traction, and extends the life of existing pavements.
Composition : Individual bricks or stones laid in specific patterns. Usage : Historical areas, pedestrian zones, and decorative applications. Advantages : Aesthetic appeal, durable, and provides good traction.
Composition : Materials such as recycled asphalt pavement (RAP), recycled concrete aggregate (RCA), and other recycled construction materials. Usage : Increasingly used in road construction to reduce environmental impact. Advantages : Cost-effective, sustainable, and reduces landfill waste.
Specialized Surfacing Materials
Composition : Porous materials that allow water to pass through, such as permeable asphalt, permeable concrete, or interlocking pavers. Usage : Parking lots, walkways, and areas requiring good drainage. Advantages : Reduces runoff, helps with stormwater management, and can recharge groundwater.
Composition : Asphalt mixed with crumb rubber from recycled tires. Usage : Highways, city streets, and areas requiring noise reduction. Advantages : Reduces road noise, enhances durability, and recycles old tires.
Composition : Asphalt emulsion mixed with aggregates, applied without heating. Usage : Temporary road repairs, patching potholes, and low-traffic areas. Advantages : Easy to apply in cold weather, cost-effective for small repairs.
Conclusion
? What causes the corrugations on a dirt road ?
Causes of Corrugations on Dirt Roads
High Speeds : When vehicles travel at high speeds, the suspension system causes the tires to bounce, creating repeated impacts on the road surface. This bouncing motion can initiate the formation of ridges. Resonance : If vehicles consistently travel at a certain speed, the frequency of the bouncing can match the natural resonance of the road material, exacerbating the formation of corrugations.
Acceleration and Braking : Rapid acceleration or braking can cause tires to dig into the loose surface, creating small mounds of displaced material that grow into corrugations over time. Skidding : Tires that skid, either from braking or cornering, can push loose material into ridges.
Granular Surface : Dirt roads with a granular surface of sand, gravel, or loose soil are more prone to washboarding because the particles can easily be displaced. Moisture Content : Roads that are too dry or too wet can both be susceptible to corrugations. Dry conditions reduce cohesion between particles, while overly wet conditions can make the surface unstable.
Consistent Traffic : Roads with consistent traffic volume see more repeated tire impacts, which contribute to the formation and propagation of corrugations. Vehicle Type and Weight : Heavier vehicles and those with stiff suspensions can cause more significant road deformation, leading to washboarding.
Inadequate Maintenance : Lack of regular maintenance, such as grading and compacting, allows corrugations to develop and worsen. Improper Grading : Incorrect grading techniques can inadvertently create conditions that favor the formation of corrugations.
Mitigation and Prevention
Regular Grading : Periodically grading the road to smooth out corrugations and redistribute material can help maintain a flat surface. Compaction : Ensuring proper compaction during road construction and maintenance can reduce the likelihood of material displacement.
Speed Limits : Implementing and enforcing speed limits can reduce the bouncing effect of vehicles, minimizing the formation of corrugations. Speed Bumps : Installing speed bumps can encourage drivers to slow down, reducing the impact forces on the road surface.
Stabilizing Agents : Adding stabilizing agents like clay, lime, or cement can improve the cohesion of road materials, making them less prone to displacement. Watering : In dry conditions, periodically watering the road can help bind the surface particles together.
Proper Drainage : Ensuring good drainage to prevent water from pooling on the road surface can help maintain the integrity of the road material. Crowning and Sloping : Designing the road with a slight crown or slope can aid in water runoff, reducing erosion and material displacement.
Conclusion
💡 Tips for safe driving on various road surfaces
Pavement Roads:
Maintain a safe following distance to allow for proper braking and reaction time. Watch out for potholes, cracks, or uneven surfaces that may affect vehicle stability. Avoid sudden maneuvers or abrupt braking, especially on wet or slippery pavement. Be mindful of painted road markings and reflectors, which may become slick when wet.
Gravel Roads:
Reduce your speed to maintain control and prevent skidding or sliding on loose gravel. Keep a firm grip on the steering wheel and avoid sudden steering inputs, as gravel can cause the vehicle to drift. Use caution when braking, as gravel roads may have reduced traction compared to paved surfaces. Watch out for washboard or rutted sections, which can affect vehicle stability and ride comfort.
Dirt Roads:
Drive at a safe speed that allows you to maintain control and react to obstacles or hazards on the road. Be prepared for changes in road conditions, such as mud, sand, or loose soil, which can affect traction. Use caution when cornering or braking, as dirt roads may lack the grip of paved surfaces. Keep your headlights on, especially during low-light conditions, to improve visibility and alert other drivers to your presence.
Wet or Rainy Roads:
Slow down and increase your following distance to account for reduced traction and longer braking distances. Avoid sudden maneuvers, such as sharp turns or rapid acceleration, which can lead to hydroplaning. Turn on your headlights and use windshield wipers as needed to maintain visibility. Watch out for standing water, which can conceal potholes or other hazards.
Snowy or Icy Roads:
Drive at a reduced speed and brake gently to avoid skidding on icy patches. Use winter tires or tire chains for added traction in snowy or icy conditions. Keep a safe distance from other vehicles and be prepared for longer stopping distances. Use low gears and avoid sudden acceleration or braking to maintain control on slippery surfaces.
Windy Roads:
Keep both hands on the steering wheel and maintain a firm grip to counteract gusts of wind. Reduce your speed and use caution when passing or being passed by large vehicles, which can create wind turbulence. Watch out for debris or obstacles that may have been blown onto the road by the wind. Be prepared for sudden changes in wind direction or intensity, especially in open or exposed areas.
🛈 List of road surfaces from the least to the best traction
Gravel : Gravel surfaces, particularly those with loose or large particles, generally offer the least traction. The loose nature of gravel can make it challenging for vehicles to maintain good grip, especially during wet or icy conditions. Wet or Icy Asphalt : While asphalt is generally considered to provide good traction, it can become slippery when wet or icy. Water or ice on the surface reduces tire grip, making it more challenging for vehicles to maintain traction and control. Wet or Icy Concrete : Similar to asphalt, concrete surfaces can become slippery when wet or icy, reducing traction. However, compared to asphalt, concrete surfaces tend to have a slightly better grip in wet conditions due to their more textured surface. Dry Asphalt : Dry asphalt surfaces offer relatively good traction. The texture and composition of asphalt provide sufficient grip for tires to maintain traction, allowing for safe and controlled driving in normal conditions. Dry Concrete : Dry concrete surfaces generally offer the highest traction among common road surfaces. Concrete provides good grip due to its textured surface, allowing for confident and controlled driving.