Sidewalk
☠️ Alert:
? Questions:
⮟ What should pedestrians do if there is no sidewalk available? ⮟ How can pedestrians stay safe when walking near busy roads? ⮟ What are the rules for drivers regarding sidewalks and pedestrian safety? ⮟ What measures can be taken to improve pedestrian safety near traffic? ⮟ How can technology be used to improve pedestrian safety on sidewalks?
☠️ Dangers related to sidewalks
Proximity to Traffic
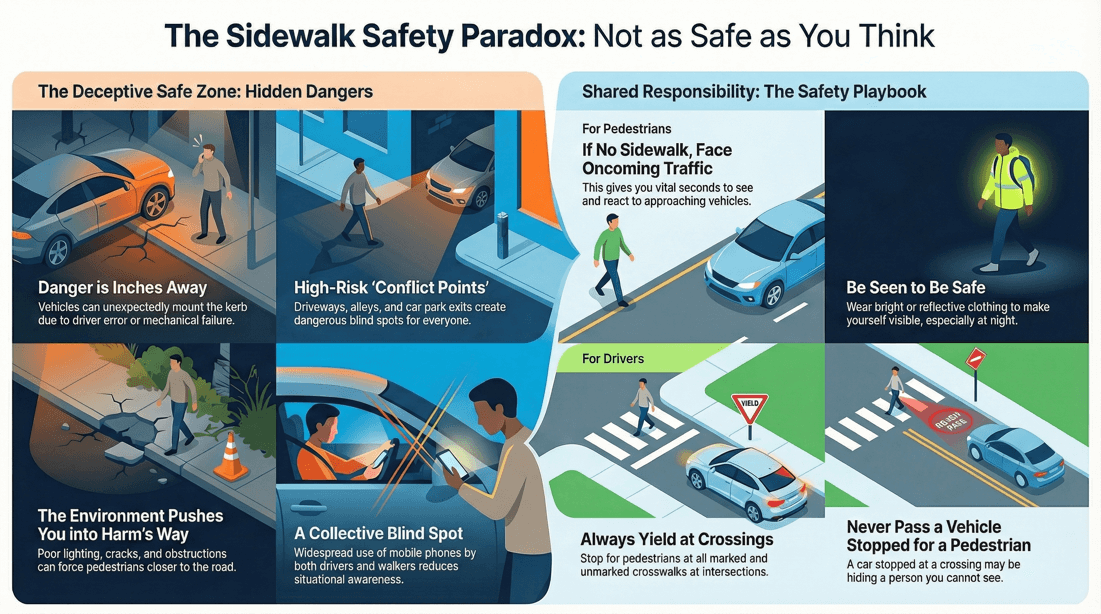
Vehicles Jumping the Curb: Cars can occasionally veer off the road and onto the sidewalk due to driver error, mechanical failure, or accidents. High-Speed Traffic: Sidewalks adjacent to high-speed roads can be particularly dangerous, as the impact of any vehicle encroachment is more severe.
Poor Sidewalk Conditions
Cracks and Uneven Surfaces: Uneven pavement, cracks, and holes can cause pedestrians to trip and fall. Obstructions: Objects like parked cars, construction materials, or overgrown vegetation can block sidewalks, forcing pedestrians onto the road.
Lack of Adequate Lighting
Nighttime Visibility: Poorly lit sidewalks are dangerous as pedestrians are less visible to drivers and more prone to tripping over unseen obstacles. Crime Risk: Dark areas can also increase the risk of crime, making pedestrians feel unsafe.
Absence of Sidewalks
Walking on the Road: In areas without sidewalks, pedestrians are forced to walk on the road, increasing the risk of being hit by a vehicle.
Poorly Designed Crosswalks
Lack of Markings: Unmarked crosswalks can lead to confusion and accidents, as drivers may not expect pedestrians to cross. Inadequate Signals: Crosswalks without signals or with poorly timed signals can be dangerous, as pedestrians may misjudge when it's safe to cross.
Distracted Pedestrians and Drivers
Mobile Device Use: Pedestrians using mobile devices are less aware of their surroundings, increasing the risk of accidents. Distracted Drivers: Drivers not paying attention to the road may not notice pedestrians, leading to potential collisions.
Bicycle and Scooter Traffic
Shared Space Conflicts: Sidewalks shared with cyclists and scooter riders can lead to collisions and injuries, especially if there are no clear lanes or rules.
Weather Conditions
Slippery Surfaces: Ice, snow, and rain can make sidewalks slippery and hazardous. Flooding: Flooded sidewalks can force pedestrians onto the road or hide obstacles that can cause trips and falls.
Driveway Crossings
Limited Visibility: Driveways intersecting sidewalks can create blind spots for both drivers exiting and pedestrians crossing.
Insufficient Width
Crowded Conditions: Narrow sidewalks can become crowded, making it difficult for pedestrians to pass each other safely and maintain a safe distance from traffic.
Aggressive Drivers
Close Passing: Drivers passing too close to the curb can create a dangerous situation for pedestrians, especially in areas without a buffer zone.
Lack of Maintenance
Debris and Litter: Unmaintained sidewalks can accumulate debris, trash, and other hazards that can cause trips and falls. Tree Roots: Roots can lift and crack the sidewalk surface, creating uneven walking conditions.
Preventive Measures
Regular Maintenance: Ensure sidewalks are regularly inspected and maintained to address cracks, uneven surfaces, and obstructions. Adequate Lighting: Install sufficient lighting to improve visibility and safety at night. Clear Signage and Markings: Use clear signage and markings for crosswalks and pedestrian zones. Traffic Calming Measures: Implement measures such as speed bumps, pedestrian islands, and curb extensions to slow down traffic and improve pedestrian safety. Education and Awareness: Promote awareness among drivers and pedestrians about the importance of paying attention and following safety rules.
? Which side of the road is safest to walk on?
Why Facing Traffic is Safer
Better Visibility: Walking on the side facing traffic allows you to see oncoming vehicles, giving you a better chance to react if a vehicle is veering toward you. Increased Awareness: When you face traffic, you can make eye contact with drivers, ensuring they see you. This mutual awareness can reduce the risk of accidents. Reacting to Danger: Facing traffic gives you the opportunity to move quickly out of the way if a vehicle is approaching too closely. Avoiding Blind Spots: Walking with your back to traffic can place you in a driver’s blind spot, especially if vehicles are turning or changing lanes.
Additional Safety Tips
Stay as Far from the Roadway as Possible: Walk on the farthest edge of the road, away from the traffic lanes. If there is a shoulder or grassy area, use it. Wear Visible Clothing: Especially at night or in low-light conditions, wearing bright, reflective clothing increases your visibility to drivers. Stay Alert: Avoid distractions such as using your phone or wearing headphones. Stay focused on the traffic and your surroundings. Use Sidewalks When Available: If there are sidewalks, always use them. They are designed to provide a safe space for pedestrians. Cross at Safe Locations: Use crosswalks and pedestrian signals when crossing the road. Avoid crossing between parked cars or in areas with poor visibility. Be Cautious at Driveways and Intersections: Watch for vehicles entering or exiting driveways and intersections. Make sure drivers see you before you cross.
Exceptions and Special Considerations
Rural Roads and Highways: On roads with high-speed traffic or limited shoulder space, extra caution is necessary. Walking facing traffic is even more critical in these environments. Groups: When walking in a group, walk in a single file to stay as far from the traffic as possible.
? What should pedestrians do if there is no sidewalk available?
Safety Tips for Pedestrians Without Sidewalks
Walk Facing Traffic: Always walk on the side of the road where you can see oncoming vehicles. This allows you to react more quickly to potential dangers. Stay as Far from the Roadway as Possible: Walk on the shoulder or grassy area if available, staying as far away from the traffic lanes as you can. Be Visible: Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially in low-light conditions such as dawn, dusk, or night. Carry a flashlight or wear reflective accessories to increase your visibility to drivers. Stay Alert: Avoid distractions like using your phone or wearing headphones. Stay focused on the traffic and your surroundings at all times. Walk in Single File: If you are walking with others, walk in a single file line rather than side-by-side to minimize your exposure to traffic. Choose Safe Walking Routes: Select routes with less traffic, lower speed limits, and wider shoulders whenever possible. Avoid walking on roads with heavy or fast-moving traffic. Be Cautious at Curves and Hills: Exercise extra caution when walking near curves or hills where drivers may have limited visibility of you. Stay as far off the road as possible in these areas. Cross Safely: When you need to cross the road, do so at safe locations such as intersections or marked crosswalks. Make sure to look both ways and wait for a gap in traffic before crossing. Make Eye Contact with Drivers: When crossing the road or when vehicles are approaching, try to make eye contact with drivers to ensure they see you. Avoid Walking at Night: If possible, avoid walking on roads without sidewalks at night. If you must walk at night, take extra precautions to make yourself visible and stay safe.
In Case of Emergency
Have a Plan: Know your route and have a plan for reaching safety if traffic becomes too heavy or if you encounter any hazards. Carry a Phone: Keep a phone with you to call for help if needed. Make sure it is fully charged before you head out.
Summary
? How can pedestrians stay safe when walking near busy roads?
Visibility
Wear Bright or Reflective Clothing: Choose brightly colored clothing during the day and reflective gear or accessories at night to make yourself more visible to drivers. Use a Flashlight: Carry a flashlight or wear LED lights if walking at night or in low-light conditions.
Awareness
Stay Alert: Avoid distractions such as using your phone, listening to music with headphones, or engaging in conversations that take your attention away from the road. Make Eye Contact: Make eye contact with drivers at intersections and crosswalks to ensure they see you before you cross.
Crossing Safely
Use Crosswalks and Intersections: Always cross at designated crosswalks and intersections where drivers expect pedestrians. Obey Traffic Signals: Follow pedestrian signals and wait for the walk sign before crossing. Do not cross on a red light or when the “Do Not Walk” signal is flashing. Look Both Ways: Look left, right, and left again before crossing the r oad. In countries where the traffic drives on the left side of the road, look right, left, and right again. C ontinue to look as you cross to stay aware of any approaching vehicles.
Positioning and Pathway Choices
Walk Facing Traffic: If there is no sidewalk, walk on the side of the road facing oncoming traffic so you can see approaching vehicles and react if necessary. Stay on Sidewalks When Available: Use sidewalks or designated pedestrian paths whenever possible. If there is no sidewalk, walk as far from the traffic lanes as you can.
Safety in Motion
Walk Single File: If you are walking with others and there is no sidewalk, walk in a single file line to minimize exposure to traffic. Avoid Blind Spots: Be cautious around driveways, alleyways, and parking lot exits where drivers might not see you.
Interaction with Traffic
Watch for Turning Vehicles: Be aware of vehicles making turns, especially at intersections. Even if you have the right of way, make sure drivers see you. Be Predictable: Follow the rules of the road and avoid sudden moves or changes in direction that could confuse drivers.
Extra Precautions
Avoid Walking at Night or in Poor Weather: If possible, avoid walking near busy roads at night, in fog, heavy rain, or snow, as visibility is reduced for both pedestrians and drivers. Plan Your Route: Choose routes with less traffic, lower speed limits, and better lighting. If you’re unfamiliar with the area, plan your walk in advance.
Emergency Situations
Carry a Mobile Phone: Have a phone with you to call for help in case of an emergency. Know Safe Spots: Identify safe places along your route where you can quickly move if you feel threatened or in danger, such as stores or well-lit public areas.
Educate Yourself and Others
Stay Informed: Be aware of local traffic laws and pedestrian regulations in your area. Spread Awareness: Encourage friends and family to follow these safety tips and raise awareness about pedestrian safety.
Summary
? What are the rules for drivers regarding sidewalks and pedestrian safety?
Yield to Pedestrians:
Crosswalks: Drivers must yield to pedestrians crossing at crosswalks, whether marked or unmarked. In many places, drivers are required to stop and allow pedestrians to cross when they are in the crosswalk or approaching it closely. Intersections: Even if there is no marked crosswalk, drivers should yield to pedestrians crossing at intersections.
Sidewalks:
Driving and Parking: Driving or parking on sidewalks is generally prohibited. Sidewalks are designated for pedestrian use, and vehicles should not obstruct them. Visibility: When approaching a sidewalk, especially when exiting a driveway or alley, drivers should stop and check for pedestrians before crossing the sidewalk.
School Zones and Pedestrian Crossings:
In areas with schools, playgrounds, or pedestrian crossings, drivers must obey reduced speed limits and be extra cautious, especially during school hours.
Turning Vehicles:
When making a turn at an intersection, drivers must yield to pedestrians crossing the street they are turning into.
Stopping for School Buses:
When a school bus is stopped with flashing lights and a stop sign extended, drivers from both directions must stop and wait until the bus resumes motion or the lights stop flashing.
No Passing Stopped Vehicles:
Drivers should not pass vehicles stopped at crosswalks, as the stopped vehicle may be allowing a pedestrian to cross.
Use of Mobile Devices:
Many jurisdictions prohibit or restrict the use of mobile devices while driving, to reduce distractions and increase pedestrian safety.
Speed Limits:
Adhering to speed limits, especially in residential areas, near schools, and in pedestrian-heavy areas, is crucial for pedestrian safety.
Alcohol and Drug Impairment:
Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs is illegal and greatly increases the risk of accidents involving pedestrians.
Special Considerations:
Be cautious of pedestrians with disabilities, children, and elderly pedestrians, who may need more time to cross the street.
? How do sidewalk designs contribute to pedestrian safety?
Physical Separation from Traffic:
Buffers: Sidewalks often include a buffer zone, such as a strip of grass, trees, or parked cars, between the pedestrian pathway and the roadway. This separation reduces the risk of pedestrians accidentally stepping into traffic and provides protection from splashes and road debris. Raised Sidewalks: Elevating sidewalks above the level of the roadway provides a physical barrier, further reducing the likelihood of vehicle-pedestrian collisions.
Visibility and Lighting:
Street Lighting: Well-lit sidewalks enhance pedestrian visibility at night, making it easier for drivers to see pedestrians and for pedestrians to see potential hazards. Clear Sight Lines: Designing sidewalks without obstructions like large signs or vegetation ensures that pedestrians can see and be seen by drivers, especially at intersections and driveways.
Crosswalks and Curb Extensions:
Marked Crosswalks: Clearly marked crosswalks signal to drivers where pedestrians are likely to cross, encouraging drivers to slow down and yield. Curb Extensions (Bulb-Outs): Extending the sidewalk at intersections reduces the crossing distance for pedestrians, making it safer and quicker to cross the street. It also improves visibility between pedestrians and drivers.
Accessible Design:
ADA Compliance: Sidewalks should be designed to be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This includes features like curb ramps, tactile paving for visually impaired individuals, and adequate width for wheelchairs and mobility devices. Smooth Surfaces: Sidewalks should have smooth, even surfaces without cracks or obstructions to prevent trips and falls.
Traffic Calming Measures:
Narrower Lanes: Sidewalks can be part of broader street design efforts that include narrower vehicle lanes, which can naturally slow down traffic. Speed Bumps and Raised Crosswalks: These features can be integrated with sidewalks to slow down vehicles near pedestrian-heavy areas.
Pedestrian Amenities:
Benches and Shelters: Providing seating and shelters along sidewalks encourages pedestrian use and offers rest points, particularly for the elderly or those with disabilities. Wayfinding Signage: Clear signage helps pedestrians navigate and can guide them to safe crossing points or pedestrian-friendly routes.
Green Infrastructure:
Street Trees and Planters: Landscaping can enhance the aesthetic appeal of sidewalks and provide shade, making walking more pleasant. Trees also act as a buffer between pedestrians and traffic. Stormwater Management: Proper drainage and design prevent water accumulation, which can make sidewalks slippery and hazardous.
Connected Network:
Continuity: A well-designed network of sidewalks ensures continuous, uninterrupted pedestrian pathways, reducing the need for pedestrians to walk on the road.
? What measures can be taken to improve pedestrian safety near traffic?
Infrastructure Improvements:
Continuous Sidewalks: Ensure there are continuous sidewalks on both sides of the street to provide safe walking paths. Marked Crosswalks: Install clearly marked crosswalks at all intersections and mid-block crossings where pedestrian traffic is high. Raised Crosswalks: These act as speed bumps, slowing down vehicles at pedestrian crossings. Pedestrian Refuge Islands: These provide a safe space for pedestrians to wait if they cannot cross the entire street in one traffic signal cycle.
Speed Bumps and Humps: Reduce vehicle speeds in areas with high pedestrian traffic. Narrower Lanes: Narrowing traffic lanes can reduce vehicle speeds and create more space for pedestrians. Chicanes and Road Diets: These measures change road layouts to slow down traffic and make streets more pedestrian-friendly.
Pedestrian Signals: Install pedestrian traffic signals at intersections, with countdown timers to inform pedestrians of remaining crossing time. Leading Pedestrian Intervals (LPI): Give pedestrians a head start at crosswalks before vehicles are given a green light, increasing their visibility. No Turn on Red: Restrict right turns on red lights in areas with heavy pedestrian traffic to reduce conflicts.
Improved Street Lighting: Enhance lighting at crosswalks, intersections, and sidewalks to increase visibility at night. High-Visibility Markings: Use high-contrast and reflective materials for crosswalks and signage to make them more visible.
Traffic Management and Control:
Lower Speed Limits: Implement lower speed limits in pedestrian-heavy areas such as school zones, residential neighborhoods, and downtown areas. Enforcement: Increase enforcement of speed limits and other traffic laws to deter dangerous driving behaviors.
Pedestrian-Only Streets: Designate certain streets or areas as pedestrian-only, especially during specific times or events. Shared Streets: Implement designs where vehicles and pedestrians share the same space but with reduced vehicle speeds and greater pedestrian priority.
Public Education and Awareness:
Safety Campaigns: Conduct public awareness campaigns to educate drivers and pedestrians about safe behaviors, such as yielding to pedestrians and avoiding distractions. School Programs: Educate children on pedestrian safety through school programs and activities.
Technology and Innovation:
Advanced Pedestrian Detection Systems: Use technology such as sensors and cameras to detect pedestrians and alert drivers. Smart Crosswalks: Implement crosswalks with embedded lights or signals that activate when pedestrians are present.
Urban Planning and Policy:
Mixed-Use Development: Encourage mixed-use developments that reduce the need for long-distance travel and encourage walking. Transit-Oriented Development: Design neighborhoods around public transit hubs to promote walking and reduce vehicle traffic.
Data Collection and Analysis:
Collision Data Analysis: Analyze data on pedestrian collisions to identify high-risk areas and develop targeted interventions. Feedback from the Community: Engage with local communities to gather insights and concerns about pedestrian safety and address specific needs.
? How can technology be used to improve pedestrian safety on sidewalks?
Smart Crosswalks
Sensors and Cameras: Smart crosswalks use sensors and cameras to detect pedestrians and automatically activate crossing signals, ensuring drivers are alerted to their presence. Illuminated Pathways: LED lights embedded in crosswalks can illuminate when pedestrians are present, making them more visible to drivers, especially at night.
Pedestrian Detection Systems
Vehicle-based Systems: Many modern vehicles come equipped with pedestrian detection systems that use cameras and radar to identify pedestrians and automatically apply brakes if a collision is imminent. Intersection Systems: These systems can be installed at intersections to monitor pedestrian movement and control traffic signals to give pedestrians more time to cross safely.
Mobile Apps and Wearables
Alert Systems: Apps can alert pedestrians of nearby traffic hazards and alert drivers of pedestrian-heavy areas. Wearables: Wearable technology, such as smartwatches or fitness bands, can vibrate or send notifications to pedestrians when they are near potentially dangerous intersections or roads.
Traffic Signal Innovations
Countdown Timers: Pedestrian countdown timers inform walkers of the remaining time to cross, reducing the likelihood of crossing during a signal change. Adaptive Signals: These traffic signals adjust the timing based on real-time pedestrian and vehicle flow, providing longer crossing times when necessary.
Autonomous Vehicles
Safety Features: Autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors and AI to detect pedestrians and take proactive measures to avoid collisions. Communication Systems: These vehicles can communicate with traffic infrastructure to optimize pedestrian safety.
Public Information Systems
Digital Signage: Interactive digital signs provide real-time information about pedestrian and vehicle traffic, weather conditions, and safety tips. Audio Alerts: Systems that provide audible alerts to pedestrians at crossings, particularly beneficial for those with visual impairments.
Geofencing and Geo-Tagging
Safety Zones: Creating virtual safety zones using geofencing technology can alert drivers when they enter areas with high pedestrian traffic. Geo-Tagged Alerts: Pedestrians can receive location-based alerts on their mobile devices about nearby traffic conditions and hazards.
Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Predictive Analysis: Using data from traffic patterns and pedestrian movements to predict high-risk areas and times, allowing for targeted safety measures. Behavioral Analysis: Machine learning algorithms can analyze pedestrian behavior to identify risky behaviors and suggest safety improvements.
Drone Surveillance
Traffic Monitoring: Drones can monitor traffic and pedestrian flow from above, providing real-time data to improve traffic management and pedestrian safety measures. Emergency Response: In case of accidents, drones can quickly provide situational awareness to emergency responders.
Connected Infrastructure
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): V2X technology enables vehicles to communicate with traffic signals, pedestrians’ mobile devices, and other infrastructure to enhance safety. Smart Lighting: Streetlights that adjust brightness based on pedestrian presence, improving visibility.
Summary
? C an a sidewalk be
private property ?
Private Sidewalks
Property Boundaries : In some residential areas, particularly in gated communities, private estates, or certain commercial properties, the sidewalk may be part of the private property. These sidewalks are typically owned and maintained by the property owner or a homeowners' association (HOA). Maintenance Responsibilities : When sidewalks are part of private property, the property owner is usually responsible for their upkeep and repair. This includes tasks such as clearing snow, fixing cracks, and ensuring the sidewalk is safe for use. Usage Restrictions : Private sidewalks may have restrictions on who can use them. For example, in gated communities, sidewalks may be accessible only to residents and their guests. Trespassing laws can be enforced if unauthorized individuals use these sidewalks.
Public Sidewalks
Public Right of Way : Most sidewalks in urban and suburban areas are part of the public right of way, even though they may run adjacent to private property. These sidewalks are typically maintained by the local government (city, town, or county). Easements : In some cases, a sidewalk may be on private land but be subject to a public easement, which means the public has the right to use the sidewalk even though it is privately owned. The property owner may still be responsible for maintenance, but they cannot restrict public access. Government Responsibility : Public sidewalks are usually maintained by the local government, which is responsible for repairs, cleaning, and ensuring accessibility.
Identifying Private vs. Public Sidewalks
Signage : Private sidewalks may have signs indicating they are private property or restricted to residents and guests. Gated Communities : Sidewalks within gated communities are often private, as the entire community is private property. Property Deeds and Maps : Property deeds and municipal maps can provide information on property boundaries and easements, indicating whether a sidewalk is private or public. Local Ordinances : Local government ordinances and regulations can also provide information on sidewalk ownership and maintenance responsibilities.
