
MAINTENANCE > ROADWORTHY > MIRRORS
Mirrors (Roadworthy)
💡 Tips:
? Questions:

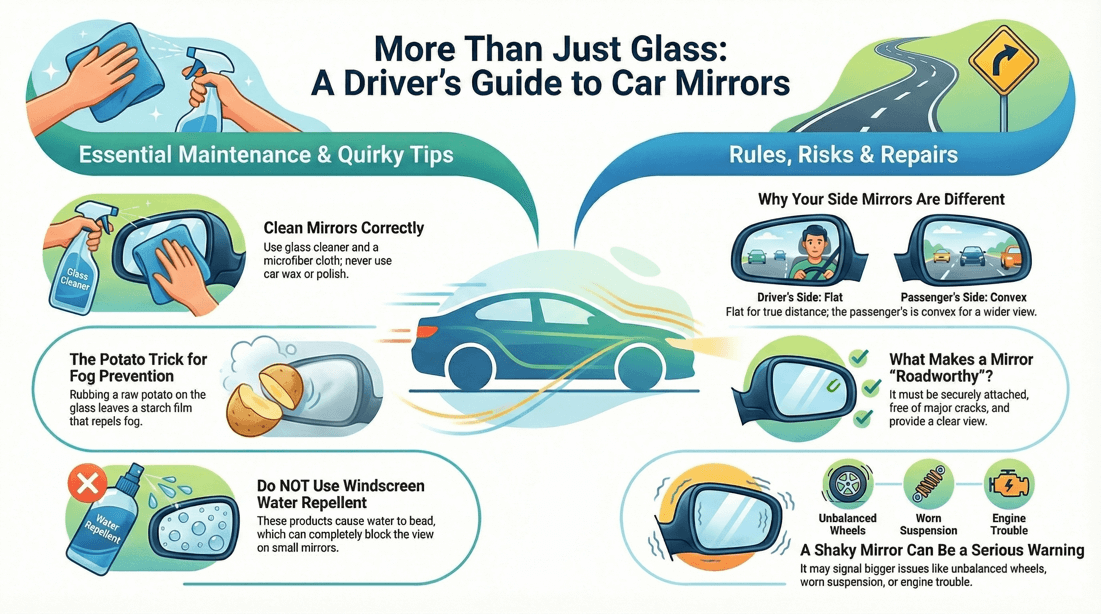
💡 Tips to prevent mirrors from fogging
Clean mirrors are less prone to fogging or misting. See windows . If your car has it, use the built in heating. It normally is switched on in conjunction with the rear window defrosting element. Use an alcohol wipe. Make sure you don't get any liquid onto the rest of the body and if you do, wipe off immediately. Alternatively, cut a potato in half, wipe over the surface of the mirror and then clean off with tissue paper. Yes, it does work! Do NOT use any water repellent products designed for the windshield. This will cause the water to bead up and the drops will limit your view in the mirror. See Motorhills for more info.
? Questions about vehicle mirror maintenance
It is recommended to inspect your vehicle mirrors every time you wash your car or at least once a week. Look for cracks, chips, or other signs of damage that may obstruct your view.
No, it is not recommended to use wax or polish on your vehicle mirrors, as they can leave behind a residue that can obstruct your view. Use a cleaning solution specifically designed for glass surfaces.
To protect your vehicle mirrors from scratches, avoid parking too close to other cars or objects and be careful when cleaning them. If you have to wipe away dirt or debris, use a microfiber cloth and avoid using abrasive materials.
If you live in an area with extreme weather conditions, such as heavy snow or hail, it may be a good idea to cover your vehicle mirrors to prevent damage. Use a cover specifically designed for vehicle mirrors and make sure it is secured tightly.
If your power mirrors stop working, first check the fuse and replace it if necessary. If the fuse is not the issue, it may be a problem with the mirror motor or switch. It is recommended to have a professional diagnose and repair the issue.
? What are the legal requirements for vehicle mirrors?
Number of Mirrors
Requirement: Most countries require at least one interior rearview mirror that provides a clear view of the road behind the vehicle.
Requirement: Vehicles are typically required to have at least one side mirror on the driver’s side. In many regions, passenger-side mirrors are also required, especially for newer vehicles. Exception: In some regions, if the rear window is obstructed (e.g., in trucks, vans, or vehicles with trailers), both side mirrors are required.
Mirror Coverage and Visibility
Requirement: Mirrors must provide a clear and unobstructed view of specific areas around the vehicle. The rearview mirror should cover the entire rear window, and side mirrors should give a view of the sides and rear of the vehicle, reducing blind spots.
Requirement: Mirrors must be adjustable so that the driver can set them to provide an optimal field of view.
Mirror Condition
Requirement: All mirrors must be in good condition, free from cracks, and securely attached to the vehicle. Damaged or loose mirrors are not legal and must be repaired or replaced.
Requirement: Mirrors must be kept clean and free of obstructions (such as stickers or other items) that could impair visibility.
Types of Mirrors
Requirement: The rearview mirror and the driver’s side mirror are usually required to be flat mirrors, offering a true reflection without distortion.
Requirement: Passenger-side mirrors are often convex to provide a wider field of view, though they come with the warning that objects may appear closer than they are.
Height and Position
Requirement: Mirrors must be mounted at a height and position that provides the driver with the required visibility. They should be positioned so that they don’t obstruct the driver’s view through the windshield or windows.
Regulation: If aftermarket mirrors are installed, they must meet the same legal requirements as the original equipment mirrors, including size, position, and coverage.
Electronic Mirrors
Acceptance: In some regions, digital or camera-based rearview systems are becoming accepted as an alternative to traditional mirrors, but they must meet specific regulatory standards for visibility and reliability.
Requirement: Backup cameras are increasingly required by law in many regions, particularly in new vehicles. However, they are considered supplemental to mirrors and do not replace the legal requirement for physical mirrors.
Special Vehicle Requirements
Requirement: Larger vehicles often have additional mirror requirements, such as wide-angle or extended mirrors, to ensure that the driver has sufficient visibility of blind spots and the area around the vehicle.
Regulatory Compliance
Requirement: During vehicle inspections or roadworthiness tests, mirrors are often checked for compliance with legal standards, and vehicles can fail inspection if mirrors are missing, damaged, or improperly positioned.
Summary:
Minimum Mirrors: Most vehicles require at least one interior rearview mirror and one exterior side mirror on the driver’s side; passenger-side mirrors are often required as well. Condition and Functionality: Mirrors must be in good condition, provide a clear and unobstructed view, and be adjustable. Type and Position: Mirrors should be flat on the driver’s side and rearview, and convex on the passenger side, mounted at a suitable height and position. Electronic Mirrors: Camera-based systems may be acceptable in some regions, but traditional mirrors are still required in most cases. Compliance: Mirrors must meet legal standards, and vehicles may fail inspections if mirrors are not compliant.
? Are there regulations for vehicle mirror size and placement?
Key Points of Regulation:
Size: The rearview mirror should be large enough to provide a clear view of the road behind the vehicle. Specific size requirements can vary by region, but the mirror must allow the driver to see a minimum field of view. Placement: The rearview mirror is typically placed on the upper center of the windshield, directly in the driver’s line of sight to provide the best possible view of the area behind the vehicle.
Size: Side mirrors must be of adequate size to cover the driver’s blind spots and provide a clear view of the road on both sides of the vehicle. Regulations may specify minimum and maximum mirror sizes. Placement: Side mirrors are usually placed on the exterior of the vehicle, on the driver’s and passenger’s doors. In many countries, at least the driver's side mirror is mandatory, while both mirrors are required in others, especially if the rear window view is obstructed.
Coverage: Regulations often specify the minimum field of view that mirrors must cover. This ensures that drivers can see critical areas around their vehicle, reducing the likelihood of collisions when changing lanes or reversing. Adjustability: Mirrors should be adjustable to accommodate drivers of different heights and seating positions. This adjustability is often a requirement in many jurisdictions.
Convex Mirrors: Some regulations permit or require the use of convex mirrors, especially on the passenger side, to provide a wider field of view. Heated Mirrors: In colder climates, regulations may allow or require heated mirrors to prevent fogging or icing, which can obstruct visibility.
Commercial Vehicles: Larger vehicles like trucks and buses often have additional requirements for mirrors, including the use of extended or supplementary mirrors to cover larger blind spots. Motorcycles: Motorcycles are also subject to mirror regulations, typically requiring mirrors on both sides to ensure the rider has sufficient rear visibility.
Manufacturing Standards: Vehicle manufacturers must ensure that mirrors meet these regulatory standards before vehicles can be sold. Vehicle Inspections: Regular vehicle inspections may include checks to ensure that mirrors are properly installed, functional, and compliant with size and placement regulations.
Regional Variations:
United States: The Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) outline specific requirements for mirror size and placement in the U.S. European Union: The European Union has its own set of regulations under the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) guidelines, particularly Regulation No. 46, which specifies the requirements for the installation and field of vision for mirrors. Other Regions: Countries like Canada, Australia, and Japan have similar regulations that align closely with either U.S. or European standards but may have unique requirements tailored to local driving conditions.
Summary:
? What should I do if my vehicle mirrors are broken or damaged?
Assess the Damage
Extent of Damage: Determine whether the mirror is cracked, shattered, loose, or completely missing. Assess whether the damage affects your ability to see clearly around your vehicle. Mirror Type: Check if the damaged mirror is the rearview mirror, driver’s side mirror, or passenger-side mirror, as different mirrors have different levels of importance and legal requirements.
Temporary Solutions
Secure Loose Mirrors: If the mirror is loose but not completely broken, try to secure it temporarily with tape or another adhesive until you can get it properly repaired or replaced. Use a Portable Mirror: In an emergency, you can use a portable mirror (like a bicycle mirror) as a temporary fix for side mirrors, although this is not ideal and should only be a short-term solution. Avoid Driving: If the damage severely limits your visibility, it’s safest to avoid driving until the mirror is fixed. Consider arranging for a tow or repair service to come to you.
Replace or Repair the Mirror
DIY Replacement: If you’re comfortable with car repairs, you can buy a replacement mirror from an auto parts store or online and install it yourself. Ensure you follow the instructions carefully to secure it properly. Professional Repair: For a more reliable fix, take your vehicle to a mechanic or auto body shop. They can replace the mirror and ensure it’s installed correctly and securely. Insurance Claim: If the damage was caused by an accident, check with your insurance provider to see if the repair or replacement is covered under your policy.
Legal Considerations
Driving Laws: Driving without functioning mirrors is illegal in many regions and can result in fines or penalties. Ensure that your vehicle meets the minimum legal requirements for mirrors before driving. Inspection Requirements: If your vehicle is due for an inspection, damaged or missing mirrors will likely cause it to fail. Address the issue before your next inspection.
Safety Concerns
Reduced Visibility: Driving without properly functioning mirrors greatly increases the risk of accidents, as you’ll have significant blind spots. Prioritize getting your mirrors fixed to ensure you can see vehicles, cyclists, pedestrians, and other obstacles around you. Backup Options: If only one mirror is damaged and you need to drive before it’s repaired, be extra cautious. Use the remaining mirrors and physically turn your head to check blind spots more frequently.
Summary
Assess Damage: Determine the extent of the damage and its impact on visibility. Temporary Fixes: Secure loose mirrors or use a portable mirror as a short-term solution, but avoid driving if visibility is severely impaired. Repair or Replace: Get the mirror repaired or replaced, either by doing it yourself or through a professional service. Legal and Safety: Ensure your vehicle meets legal requirements and prioritize safety by fixing mirrors promptly.
? How do I fix a broken or loose vehicle side mirror?
Assess the Damage
Broken Glass: If only the mirror glass is broken, you may only need to replace the glass. Loose Mirror: If the entire mirror housing is loose, it could be due to loose screws, a broken mounting bracket, or damaged internal components. Damaged Housing: If the mirror housing is cracked or broken, you may need to replace the entire side mirror assembly.
Fixing a Loose Side Mirror
Screwdriver (Phillips or flathead, depending on the screws), possibly a socket wrench.
Inspect the Mounting Screws: Open the vehicle door and look for the screws that hold the mirror assembly in place. They are usually accessible from inside the door panel or under a plastic cover on the outside. Tighten the Screws: If the mirror is loose, tighten the screws with the appropriate tool. Ensure all screws are secure, but avoid over-tightening, which could damage the mounting. Check for Damage: If the screws are tight but the mirror is still loose, the mounting bracket inside the door or the mirror assembly itself might be damaged, requiring further inspection or replacement.
Replacing Broken Mirror Glass
Replacement mirror glass, adhesive or double-sided tape, gloves (to protect your hands from broken glass).
Purchase the Replacement Glass: Ensure you get the correct size and shape for your vehicle’s model. You can find these at auto parts stores or online. Remove the Broken Glass: Carefully pry out the remaining glass pieces from the mirror housing. Use gloves to avoid cuts. Clean the Housing: Remove any adhesive residue and clean the surface where the new glass will be mounted. Attach the New Glass: Apply adhesive or double-sided tape to the back of the new mirror glass. Press it firmly into place within the mirror housing. Allow to Set: If using adhesive, allow the mirror to set for the recommended time before driving the vehicle.
Replacing the Entire Side Mirror Assembly
Screwdriver, socket wrench, replacement mirror assembly.
Remove the Interior Door Panel: To access the mirror mounting bolts, you may need to remove the interior door panel. This usually involves removing screws and carefully prying the panel off. Disconnect the Wiring: If your side mirror has electronic features (like power adjustment or heating), disconnect the electrical connector. Remove the Old Mirror: Unscrew the bolts holding the mirror assembly in place and carefully remove it from the vehicle. Install the New Mirror: Position the new mirror assembly, thread the mounting bolts, and tighten them securely. Reconnect Wiring: If applicable, reconnect the electrical wiring. Reattach the Door Panel: Once everything is secure, reattach the door panel, ensuring all clips and screws are in place.
Professional Help
If the damage is severe, or if you’re unsure about any step in the process, it’s best to take your vehicle to a professional mechanic or auto body shop. They can properly diagnose and fix the problem, ensuring the mirror is securely installed and functional.
Temporary Fixes
Duct Tape: If you're in a pinch, you can temporarily secure a loose mirror with duct tape, but this is not a permanent solution. Mirror Repair Kits: Available at auto parts stores, these kits can provide temporary fixes for cracked or loose mirrors but may not offer a long-term solution.
Summary:
? What causes my vehicle mirrors to vibrate or shake?
Loose Mounting Hardware
Loose Screws or Bolts: If the screws or bolts that hold the mirror in place are loose, the mirror may vibrate or shake, especially when the vehicle is in motion. Over time, these fasteners can loosen due to vibrations from the road, causing the mirror to become unstable. Worn or Damaged Brackets: The brackets or clips that secure the mirror to the vehicle can wear out or break, leading to a loose fit and mirror vibration.
Poor Quality or Damaged Mirror Housing
Cheap or Aftermarket Mirrors: Lower-quality or poorly made mirrors may not fit as securely as original equipment manufacturer (OEM) mirrors, making them more prone to vibrations. Cracked or Damaged Housing: If the mirror housing is cracked or damaged, it may not hold the mirror glass securely, leading to shaking or vibrating, especially at higher speeds.
Engine or Vehicle Vibrations
Engine Vibrations: Vibrations from the engine, especially in vehicles with rough idling or engine issues, can transfer to the mirrors. This is more noticeable in older vehicles or those with poorly maintained engines. Wheel Imbalance or Suspension Issues: Imbalanced wheels, worn tires, or suspension problems can cause vibrations throughout the vehicle, which may cause the mirrors to shake, particularly at certain speeds.
Aerodynamic Forces
High Speeds: At high speeds, aerodynamic forces can cause mirrors to vibrate, especially if they are not securely mounted or have a large surface area. Wind: Strong winds or driving in windy conditions can cause external mirrors to vibrate or shake, especially if the mirror housing is not aerodynamically designed or securely attached.
Misaligned Mirrors
Incorrect Installation: If the mirror was not installed correctly or is not properly aligned with the vehicle's body, it might catch more wind or experience more vibrations, leading to shaking.
Deterioration of Mirror Components
Aging or Worn Components: Over time, the components that hold the mirror in place, such as plastic clips, rubber seals, or adhesives, can deteriorate. This wear and tear can result in a less secure mirror, leading to vibration.
Vibration from the Road Surface
Rough Roads: Driving on rough or uneven road surfaces can cause vibrations that travel through the vehicle's body and into the mirrors. Poor Shock Absorbers: If the vehicle’s shock absorbers are worn, they may not adequately dampen road vibrations, which can cause the mirrors to shake.
External Add-Ons or Modifications
Aftermarket Accessories: External add-ons like mirror extensions or additional side-view mirrors can disrupt the vehicle's aerodynamics, leading to increased vibration. Increased Mirror Weight: If you’ve added accessories to the mirror or replaced the mirror glass with a heavier option, this could lead to increased vibration.
Solutions to Reduce Mirror Vibration:
Tighten Mounting Hardware: Check and tighten any loose screws or bolts securing the mirror. Inspect and Replace Worn Components: If the mirror housing, brackets, or seals are worn or damaged, consider replacing them. Balance Wheels and Check Suspension: Ensure your wheels are balanced and your suspension is in good condition to minimize vehicle vibrations. Upgrade to OEM Mirrors: If you're using aftermarket mirrors, consider upgrading to OEM mirrors designed specifically for your vehicle. Use Mirror Stabilizers: Some vehicles may benefit from aftermarket mirror stabilizers designed to reduce vibrations.