MAINTENANCE > ROADWORTHY > LIGHTS
Lights (Roadworthy)
💡 Tips:
? Questions:
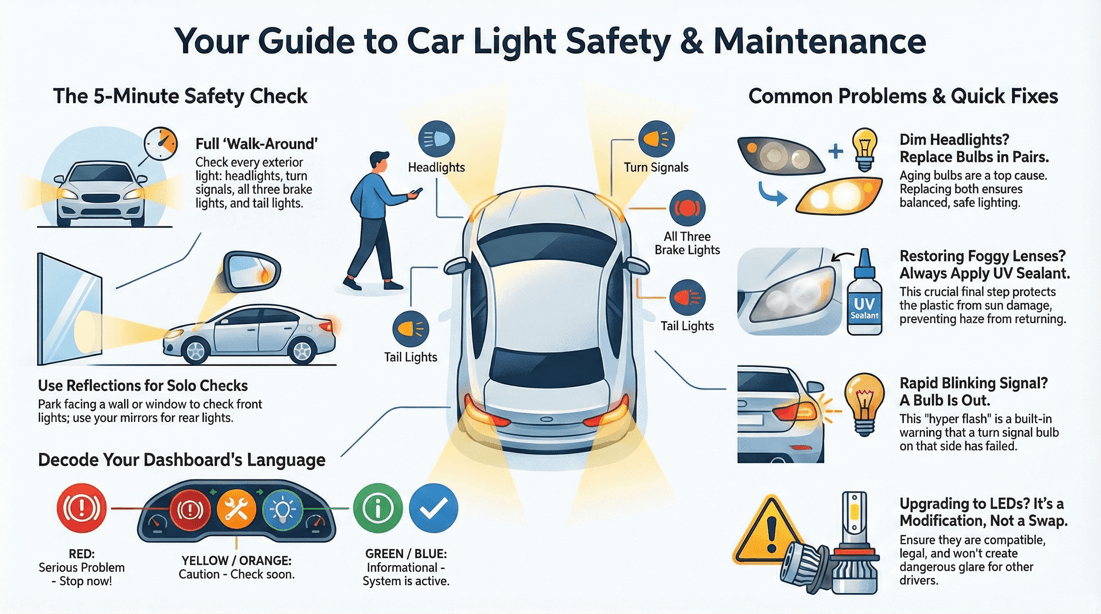
💡 Tips on checking your vehicle lights
Check All Lights Regularly
Headlights : Inspect both high and low beams. Turn Signals : Test both front and rear turn signals. Brake Lights : Ensure all brake lights (including the third brake light) are working. Reverse Lights : Verify that the reverse lights illuminate when the car is in reverse. Fog Lights : If your vehicle has fog lights, check their functionality. Tail Lights : Make sure all tail lights are working. Side Marker Lights: Check these if your vehicle is equipped with them. License Plate Lights: Ensure the lights illuminating the license plate are working.
Perform a Visual Inspection
Turn On the Lights: Turn on each set of lights (headlights, turn signals, etc.) one at a time. Walk Around the Vehicle: Walk around the vehicle to visually inspect each light. Check for Cracks or Damage: Look for any cracks, condensation, or other damage to the light covers that could affect visibility.
Use Reflective Surfaces
Garage Door: Park in front of a garage door or wall and turn on the lights. This can help you see if both sides are functioning correctly. Mirrors: Use mirrors or reflective surfaces to check rear lights if you don’t have someone to help.
Enlist Help
Have Someone Assist You: Ask a friend or family member to help you check the lights. They can observe from outside while you operate the lights from inside the vehicle.
Check the Dashboard Indicators
Warning Lights: Pay attention to any dashboard warning lights indicating a bulb issue. Turn Signal Speed: A rapid flashing turn signal indicator can signal a bulb is out.
Inspect the Bulbs and Fuses
Remove and Inspect Bulbs: If a light is out, remove the bulb and inspect it for broken filaments or discoloration. Check Fuses: Refer to your vehicle’s manual to locate the fuse box and check for any blown fuses related to the lighting system.
Use a Multimeter
Test Voltage: If you're comfortable with using a multimeter, you can check the voltage at the bulb socket to ensure there’s power.
Keep Spare Bulbs and Fuses
Carry Extras: Keep spare bulbs and fuses in your vehicle for quick replacements if a light goes out while you’re on the road.
Clean the Lights
Clean the Lenses: Regularly clean the light lenses to remove dirt and grime that can diminish light output. Polish Headlights: If your headlights are foggy, clean and polish them to restore clarity.
Professional Inspection
Regular Service: During routine maintenance, ask your mechanic to check all vehicle lights. Safety Inspections: Consider having professional safety inspections periodically to ensure all lights are functioning correctly.
? What do dashboard warning lights mean?
Red warning light: Usually signals a serious problem that requires immediate action, such as low oil pressure, brake failure, or an overheating engine. Yellow or orange light: Typically means something needs to be checked soon, like the check engine light, low tire pressure, or ABS warning. Green or blue light: Is generally just informational, such as high beams being on or cruise control being active.
Check Engine Light: Signals engine or emissions-related issues. Battery Light: Indicates a charging problem, possibly with the battery or alternator. Oil Pressure Light: Warns of dangerously low oil pressure. Brake System Light: Could point to worn brake pads, low fluid, or a system malfunction. Tire Pressure Light: Suggests that one or more tires may be underinflated.
? When is it time to replace headlights or taillights?
Dimming or Flickering: If your headlights or taillights are not as bright as they used to be or if they flicker, it could mean the bulb is nearing the end of its life. Burned-Out Bulbs: If a light has gone out completely, it should be replaced immediately to maintain visibility and ensure other drivers can see you. Cracked or Foggy Lenses: Even if the bulbs are still working, damage or cloudiness in the lens can reduce effectiveness and should be addressed. Warning Lights: Some vehicles will display a dashboard warning if a light is out or malfunctioning. Color Change: If the light output changes color, such as a white headlight turning yellow, it's a sign that the bulb is wearing out.
? What do I do if my lights aren’t working?
Check the Headlight Switch
Cause: The headlight switch might be in the wrong position or could be faulty. Solution: Ensure the switch is in the correct position for the lights you want to activate (headlights, fog lights, etc.). If the switch feels loose or doesn’t respond, it may need to be replaced.
Inspect the Fuses
Cause: A blown fuse could be preventing the lights from functioning. Solution: Locate the fuse box (usually under the dashboard or in the engine compartment) and check the fuse related to the lights. If the fuse is blown, replace it with one of the same rating. If it blows again immediately, there may be a short circuit that needs professional attention.
Test the Bulbs
Cause: Burned-out bulbs are a common reason for lights not working. Solution: Remove the light bulbs and inspect them for broken filaments or darkened glass. If a bulb is burned out, replace it with the correct type as specified in your vehicle’s manual.
Examine the Wiring and Connections
Cause: Loose, damaged, or corroded wiring and connections can prevent lights from working. Solution: Check the wiring and connectors leading to the lights. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or disconnection. Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
Inspect the Relays
Cause: A faulty relay can prevent power from reaching the lights. Solution: Locate the relay associated with your lights (often found in the fuse box). Swap it with a similar relay that you know is working to see if the lights turn on. If they do, the relay needs to be replaced.
Check the Headlight Grounds
Cause: Poor grounding can prevent the lights from functioning. Solution: Locate the ground wire for the lights and ensure it is securely attached to a clean, unpainted metal surface on the vehicle’s chassis. Clean any corrosion or rust from the grounding point.
Test the Battery and Alternator
Cause: A weak battery or failing alternator can cause electrical components, including lights, to fail. Solution: Test the battery and alternator using a multimeter. If the battery is weak, recharge or replace it. If the alternator isn’t charging properly, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
Look for a Faulty Light Control Module
Cause: In modern vehicles, a light control module controls the lights. If this module fails, it can cause the lights to stop working. Solution: If all other components are working correctly, the issue might be with the light control module. This typically requires diagnosis and replacement by a professional.
Consider Environmental Factors
Cause: Moisture, extreme temperatures, or physical damage from debris could affect the lights. Solution: Inspect the light housings and connectors for signs of moisture or damage. Ensure that the light assembly is sealed properly to prevent water ingress.
Consult a Professional Mechanic
**If you’ve gone through these steps and the lights still aren’t working, it’s time to take your vehicle to a professional mechanic. They can perform a more thorough diagnosis using specialized tools and equipment.
Summary
Headlight Switch: Ensure it’s functioning correctly. Fuses: Replace blown fuses with the correct rating. Bulbs: Replace any burned-out bulbs. Wiring and Connections: Repair any damaged or loose wiring. Relays: Replace faulty relays. Grounds: Ensure proper grounding of the lights. Battery /Alternator: Test and replace if needed. Light Control Module: Have it diagnosed and replaced by a professional if necessary. Environmental Factors: Protect the lights from moisture and damage.
? How do I know if a light bulb is burnt out?
Visual Inspection
Turn Off the Lights : Make sure the lights are off before inspecting. Remove the Bulb : Access the bulb by opening the appropriate light housing. This may require removing a cover or unscrewing the bulb. Check the Filament : Look at the filament inside the bulb (the thin wire that glows). If the filament is broken, discolored, or has blackened spots, the bulb is likely burnt out. Inspect the Bulb Base : Look for signs of corrosion, burn marks, or discoloration at the base of the bulb, which can also indicate a burnt-out bulb.
Test the Lights
Turn on the Lights : Activate the lights in question (headlights, brake lights, turn signals, etc.). Check the Bulb Operation : Walk around the vehicle or have someone help you observe whether all the lights are working. If a light is not illuminating, the bulb may be burnt out.
Use a Multimeter
Remove the Bulb : Take the bulb out of the light housing. Set the Multimeter to Continuity or Resistance Mode : For continuity: Place the multimeter probes on the bulb's contacts. If the multimeter beeps, the bulb is good. No sound indicates a break in the filament, meaning the bulb is burnt out. For resistance: Place the probes on the bulb's contacts. A very high resistance reading (or no reading at all) indicates the bulb is burnt out, while a low resistance reading means the bulb is functioning.
Swap the Bulb with a Known Good Bulb
Remove the Suspected Burnt-Out Bulb : Take the bulb out of its socket. Insert a Working Bulb : Take a bulb that you know works (from another functioning light or a new bulb) and place it in the socket. Test the Light : Turn on the lights to see if the new bulb illuminates. If it does, the original bulb was likely burnt out.
Dashboard Warning Lights
Modern Vehicles: Some modern cars have warning lights on the dashboard that indicate when a bulb is out. If a light on the dashboard indicates a bulb failure, check the lights as indicated.
Summary
Visual Inspection: Look for a broken or discolored filament and signs of damage at the bulb base. Test the Lights: Activate the lights and see if they illuminate. Use a Multimeter: Test for continuity or resistance to check the filament. Swap with a Good Bulb: Replace the suspected bulb with a working one to confirm. Dashboard Warning Lights: Check for any bulb failure warnings on your dashboard.
? Why are my headlights dim?
Old or Fading Bulbs
Cause: Headlight bulbs naturally dim over time as the filament wears out. Solution: Replace the bulbs. It’s often recommended to replace both headlights at the same time to ensure even brightness.
Dirty or Cloudy Headlight Lenses
Cause: Dirt, grime, or oxidation on the headlight lenses can reduce the amount of light that passes through. Solution: Clean the lenses with a headlight restoration kit or a mixture of toothpaste and water. If the lenses are severely cloudy, consider replacing them.
Electrical Issues
Cause: Problems with the vehicle’s electrical system, such as loose wiring, corroded connectors, or a weak ground connection, can reduce the voltage reaching the headlights. Solution: Inspect and repair any loose or corroded connections. If the problem persists, have a professional check the vehicle’s electrical system.
Weak Battery or Charging System
Cause: A weak battery or failing alternator may not supply enough power to the headlights, causing them to appear dim. Solution: Test the battery and alternator. If either is failing, it may need to be replaced.
Faulty Headlight Switch or Relay
Cause: A malfunctioning headlight switch or relay can reduce the power supplied to the headlights. Solution: Have the headlight switch or relay tested and replaced if necessary.
Incorrect Bulb Type
Cause: Installing the wrong type of bulb or using low-quality bulbs can result in dimmer light output. Solution: Ensure you’re using the correct bulb type specified in your vehicle’s manual. Consider upgrading to higher-quality or higher-output bulbs if needed.
Worn or Damaged Alternator Belt
Cause: A worn or loose alternator belt can cause the alternator to undercharge the battery, leading to dim headlights. Solution: Inspect and replace the alternator belt if it is worn or loose.
Dimming Due to Automatic Daytime Running Lights (DRLs)
Cause: Some vehicles automatically dim the headlights when the daytime running lights (DRLs) are active. Solution: Check if your vehicle is in DRL mode. Switching to regular headlight mode should restore full brightness.
Grounding Issues
Cause: Poor grounding of the headlight circuit can cause resistance, leading to dim headlights. Solution: Inspect the ground connection for corrosion or looseness and repair as needed.
Summary
Old Bulbs: Replace if dim due to age. Dirty Lenses: Clean or restore lenses to improve brightness. Electrical Issues: Check wiring, connectors, and grounds. Weak Battery/Alternator: Test and replace if necessary. Faulty Switch/Relay: Replace if defective. Incorrect Bulb Type: Ensure correct bulb type is installed. Alternator Belt: Replace if worn or loose. DRL Mode: Switch to regular headlight mode. Grounding Issues: Repair or clean the ground connection.
? Why is one of my headlights brighter than the other?
Burned-Out or Failing Bulb
Cause: One of the bulbs may be old, near the end of its life, or partially burned out, causing it to emit less light than the other. Solution: Replace both headlight bulbs to ensure even brightness.
Incorrect Bulb Installation
Cause: If a bulb is not installed correctly, it may not sit properly in the housing, causing uneven light distribution. Solution: Check the bulb installation, ensuring that it’s seated correctly in the headlight housing.
Different Bulb Types or Wattages
Cause: Using different types of bulbs or bulbs with different wattages in each headlight can result in uneven brightness. Solution: Ensure both headlights are using the same type of bulb with identical specifications.
Dirty or Cloudy Headlight Lenses
Cause: One headlight lens might be dirtier or more oxidized than the other, reducing the amount of light that can pass through. Solution: Clean or restore both lenses to ensure they are clear and allow maximum light output.
Electrical Issues
Cause: A problem in the wiring, such as a loose connection, corrosion, or a weak ground, can cause one headlight to receive less power, making it dimmer. Solution: Inspect and repair any wiring issues, ensuring that both headlights receive the same voltage.
Faulty Headlight Reflector or Housing
Cause: If the reflector inside the headlight housing is damaged or not aligned properly, it can affect the light output. Solution: Inspect the headlight housing and reflector. If damaged, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
Alternator or Battery Issues
Cause: A weak battery or alternator could cause inconsistent power distribution, leading to one headlight being dimmer than the other. Solution: Test the battery and alternator, and replace if necessary.
Grounding Issues
Cause: A poor ground connection on one side can cause a drop in voltage to that headlight, making it dimmer. Solution: Check and clean the ground connections for both headlights, ensuring they are secure and corrosion-free.
Summary
Burned-Out/Failing Bulb: Replace both bulbs to match brightness. Incorrect Installation: Ensure bulbs are properly seated. Different Bulb Types: Use identical bulbs on both sides. Dirty Lenses: Clean or restore headlight lenses. Electrical Issues: Repair any wiring or connection problems. Faulty Reflector/Housing: Inspect and repair or replace as needed. Battery /Alternator Issues: Test and replace if necessary. Grounding Issues: Check and clean ground connections.
? How do I clean foggy headlights?
Soap and Water Method
Materials Needed: Mild soap Water Sponge or cloth Bucket.
Mix soap with water in a bucket. Use a sponge or cloth to clean the headlights, removing surface dirt and grime. Rinse with clean water and dry with a soft cloth.
Toothpaste Method
Toothpaste (preferably non-gel, whitening) Soft cloth Water Clean towel.
Apply a small amount of toothpaste to a damp cloth. Rub the toothpaste onto the headlight in small circular motions, applying moderate pressure. Continue rubbing for about 5 minutes per headlight. Rinse with water and dry with a clean towel.
Baking Soda and Vinegar Method
Baking soda White vinegar Water Cloth.
Mix 3 parts baking soda with 1 part water to form a paste. Apply the paste to the headlights using a cloth. Gently rub the paste in circular motions. Rinse with water. For extra cleaning, mix equal parts white vinegar and water and wipe the headlights with this solution. Rinse and dry with a clean cloth.
Commercial Headlight Restoration Kits
Headlight restoration kit (available at auto stores), microfiber cloths, and water.
Follow the instructions provided with the kit. Typically, these kits include a cleaner, a polish, and sometimes a protective sealant. Use the provided materials to clean and polish the headlights. Apply the sealant if included to protect the headlights from future fogging.
Sandpaper Method
Wet/dry sandpaper (1000, 2000, and 3000 grit), water, masking tape, polish, and a microfiber cloth.
Tape around the headlights to protect the surrounding paint. Wet the sandpaper and headlights with water. Start with 1000 grit sandpaper, sanding the headlights in a horizontal motion. Move to 2000 grit sandpaper, sanding in a vertical motion. Finish with 3000 grit sandpaper, sanding in circular motions. Rinse the headlights with water and dry with a microfiber cloth. Apply a polish to restore clarity and shine.
UV Sealant Method
UV sealant (available at auto stores) Microfiber cloths.
Clean the headlights using one of the methods above. Apply the UV sealant according to the manufacturer's instructions. This will help protect the headlights from future UV damage and fogging.
Tips for Best Results:
Regular Maintenance: Regularly clean your headlights to prevent severe fogging. Avoid Abrasives: Be careful not to use overly abrasive materials that could scratch the headlight lens. Protective Coating: Consider applying a protective coating or wax after cleaning to maintain clarity longer. Professional Help: If the headlights are severely fogged and home remedies don’t work, consider seeking professional restoration services.
? How does moisture get into a headlamp?
Cracked or Damaged Headlamp Housing
Description: Physical damage to the headlamp housing, such as cracks or breaks, can allow moisture to enter. Solution: Inspect the headlamp for visible damage and replace or repair the housing if necessary.
Worn or Damaged Seals
Description: The rubber or silicone seals around the headlamp can degrade over time, losing their ability to keep moisture out. Solution: Check the seals around the headlamp for wear or damage and replace them if needed.
Poorly Fitted Bulb or Missing Gasket
Description: If a bulb is not properly fitted or if the gasket around the bulb is missing or damaged, moisture can seep into the headlamp. Solution: Ensure the bulb is correctly installed and that all gaskets are intact and in good condition.
Condensation Build-Up
Description: Condensation can occur when there is a significant temperature difference between the inside and outside of the headlamp. Solution: Ventilation systems in modern headlamps are designed to allow condensation to escape. Make sure the vents are not blocked. If necessary, remove the headlamp and allow it to dry out completely before reinstalling.
Incorrect Installation
Description: If the headlamp assembly was not installed correctly, gaps could allow moisture to enter. Solution: Double-check the installation process and ensure all components are securely in place.
Submersion in Water
Description: Driving through deep water or submerging the vehicle can cause water to enter the headlamp assembly. Solution: Avoid driving through deep water when possible. If submersion occurs, dry out the headlamp and inspect for any damage or breaches in the housing.
Preventative Measures:
Regular Inspections: Periodically check the headlamp housing, seals, and gaskets for signs of wear or damage. Proper Installation: Ensure that bulbs and headlamp assemblies are installed correctly and securely. Use of Silica Gel Packets: Placing silica gel packets inside the headlamp housing can help absorb moisture and prevent condensation.
Removing Moisture from Headlamps:
Removing Headlamp Assembly: If moisture is present, remove the headlamp assembly and let it dry out completely. Use a hairdryer or place it in a warm, dry area to speed up the process. Using Desiccants: Place silica gel packets inside the headlamp housing to absorb any remaining moisture. Seal Maintenance: Replace any worn or damaged seals and ensure all components are properly installed to prevent future moisture ingress.
? What should I do if my lights are flickering?
Check the Battery
Cause: A weak or dying battery might not provide consistent power, leading to flickering lights. Solution: Test the battery with a multimeter. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the car is off and 13.7-14.7 volts when the engine is running. If the battery is weak, recharge or replace it.
Inspect the Alternator
Cause: A failing alternator may not be supplying a consistent voltage to the electrical system, causing lights to flicker. Solution: Have the alternator tested to ensure it’s charging the battery properly. If it’s not functioning correctly, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
Examine the Wiring and Connections
Cause: Loose, frayed, or corroded wires and connections can cause inconsistent power delivery, leading to flickering lights. Solution: Inspect the wiring for damage or corrosion, especially around the battery , alternator, and fuse box. Tighten any loose connections and clean any corroded terminals.
Check the Ground Connections
Cause: Poor or loose ground connections can cause electrical issues, including flickering lights. Solution: Locate the ground wires and ensure they are securely connected to the chassis. Clean any corrosion and ensure a tight connection.
Inspect the Headlight Bulbs
Cause: Loose or improperly installed headlight bulbs can cause flickering. Solution: Ensure the bulbs are securely installed in their sockets. If the bulbs appear worn or damaged, replace them.
Look at the Headlight Switch
Cause: A faulty or worn headlight switch can cause flickering by intermittently cutting power to the lights. Solution: If the flickering occurs when you adjust the headlight switch, the switch may need to be replaced.
Examine the Fuse Box and Relays
Cause: A faulty fuse or relay can cause inconsistent power to the lights, leading to flickering. Solution: Check the fuses and relays associated with the lighting system. Replace any that are blown or malfunctioning.
Check for a Failing Voltage Regulator
Cause: A malfunctioning voltage regulator can cause voltage fluctuations, leading to flickering lights. Solution: The voltage regulator is often integrated into the alternator. If it’s failing, the alternator may need to be replaced.
Consider Environmental Factors
Cause: External factors like moisture or extreme temperatures can cause electrical connections to contract or expand, leading to flickering. Solution: Ensure that all connections are sealed and protected from moisture. If flickering only occurs in certain weather conditions, consider this as a potential cause.
Consult a Professional
**If you’ve checked the above items and the issue persists, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic. They can perform a more thorough diagnosis using specialized equipment.
Summary
Battery : Test and replace if weak or dying. Alternator: Ensure it’s charging correctly; replace if necessary. Wiring: Inspect for damage and repair as needed. Ground Connections: Ensure secure and clean connections. Headlight Bulbs: Check for secure installation; replace if worn. Headlight Switch: Replace if faulty. Fuse Box/Relays: Replace any blown or malfunctioning components. Voltage Regulator: Check and replace if necessary. Environmental Factors: Protect connections from moisture and temperature extremes.
? Why do my turn signals blink rapidly?
Burnt-Out Bulb
Cause: One of the most common reasons for a rapid blinking turn signal is a burnt-out bulb. The turn signal system is designed to blink faster if one of the bulbs (front or rear) is not working. Solution: Check both the front and rear turn signal bulbs on the side that is blinking rapidly. If you find a bulb that isn’t working, replace it with a new one.
Faulty Bulb or Socket
Cause: Even if the bulb isn’t burnt out, it might not be seated properly in the socket, or the socket itself could be corroded or damaged, leading to improper electrical contact. Solution: Inspect the bulb and socket for corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Clean the socket and ensure the bulb is properly installed. Replace the socket if it’s damaged.
Wiring Issues
Cause: A wiring problem, such as a short circuit, broken wire, or poor connection, can cause the turn signal to blink rapidly. Solution: Inspect the wiring connected to the turn signals for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Repair or replace any faulty wiring.
Faulty Flasher Relay
Cause: The flasher relay controls the blinking speed of your turn signals. If it’s malfunctioning, it can cause the signals to blink too quickly. Solution: If the bulbs and wiring are in good condition, the issue may be with the flasher relay itself. Replacing the flasher relay is usually straightforward and can resolve the issue.
Aftermarket LED Bulbs
Cause: If you’ve replaced your turn signal bulbs with aftermarket LED bulbs, they might draw less power than the original incandescent bulbs, causing the system to blink rapidly as it interprets the low power draw as a bulb failure. Solution: Use load resistors or LED-compatible flasher relays to correct the blinking speed when using LED bulbs.
Faulty Turn Signal Switch
Cause: In some cases, a problem with the turn signal switch itself could cause the signals to blink rapidly. Solution: If other solutions don't fix the problem, the turn signal switch may need to be inspected and possibly replaced by a professional.
Summary
Burnt-Out Bulb: Check and replace any burnt-out turn signal bulbs. Faulty Bulb/Socket: Ensure bulbs are properly seated and the socket is not corroded. Wiring Issues: Inspect and repair any damaged or loose wiring. Faulty Flasher Relay: Replace the flasher relay if it's malfunctioning. Aftermarket LED Bulbs: Use load resistors or LED-compatible relays to correct blinking speed. Turn Signal Switch: If all else fails, the switch may need to be checked.
? Why do my brake lights stay on?
Faulty or Misadjusted Brake Light Switch
Cause: The brake light switch is located near the brake pedal and is responsible for turning the brake lights on and off when you press or release the pedal. If the switch is faulty or not properly adjusted, it may stay engaged, keeping the brake lights on. Solution: Check the brake light switch for proper adjustment. It should be positioned so that it disengages when the pedal is not pressed. If the switch is damaged, it will need to be replaced.
Stuck Brake Pedal
Cause: Sometimes, the brake pedal can get stuck in a slightly depressed position due to dirt, debris, or mechanical issues, causing the brake lights to remain on. Solution: Inspect the brake pedal to ensure it returns fully to its resting position after being pressed. Clean any dirt or debris, and check for any mechanical issues that might be causing it to stick.
Short Circuit in the Wiring
Cause: A short circuit in the wiring of the brake light system can cause the lights to stay on continuously. Solution: Inspect the wiring connected to the brake lights and brake light switch for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Repair or replace any faulty wiring.
Faulty Brake Light Relay
Cause: Some vehicles use a relay to control the brake lights. If the relay is stuck in the closed position, it will keep the brake lights on. Solution: Check the brake light relay and replace it if it’s faulty.
Aftermarket Modifications
Cause: If you’ve installed aftermarket parts like a trailer wiring harness or other modifications, they might interfere with the brake light circuit, causing the lights to stay on. Solution: Check any recent modifications to ensure they are installed correctly and not interfering with the brake light system.
Moisture or Corrosion in the Tail Light Assembly
Cause: Moisture or corrosion in the tail light assembly can create a short circuit, causing the brake lights to stay on. Solution: Inspect the tail light assemblies for signs of moisture or corrosion. Dry out or clean the assemblies and repair any damage.
Damaged Brake Light Bulb Socket
Cause: A damaged or corroded bulb socket can cause an electrical malfunction, leading to the brake lights staying on. Solution: Check the bulb sockets for damage or corrosion. Clean or replace the sockets if necessary.
Summary
Brake Light Switch: Check for proper adjustment or replace if faulty. Stuck Brake Pedal: Ensure the pedal fully returns to its resting position. Wiring Issues: Inspect and repair any damaged or shorted wiring. Brake Light Relay: Replace the relay if it’s stuck or malfunctioning. Aftermarket Modifications: Ensure they aren’t interfering with the brake light circuit. Moisture or Corrosion: Inspect and clean the tail light assembly if needed. Bulb Socket: Check and replace any damaged or corroded sockets.
? Can I use LED bulbs in my vehicle?
Benefits of Using LED Bulbs:
Energy Efficiency: LED bulbs consume less power than traditional incandescent or halogen bulbs, which can reduce the load on your vehicle's electrical system and improve fuel efficiency slightly. Longer Lifespan: LEDs typically last much longer than conventional bulbs, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Brighter Light: LED bulbs often provide a brighter, more focused light, which can improve visibility and safety. Faster Response Time: LEDs light up quicker than traditional bulbs, which is particularly beneficial for brake lights, as it can give other drivers more time to react.
Considerations for Using LED Bulbs:
Electrical System: LED bulbs draw less power, so your vehicle’s electrical system might not recognize them properly, potentially causing issues like hyper-flashing in turn signals or warning lights on the dashboard. Solution: To avoid these issues, you may need to install load resistors or LED-compatible flasher relays, which mimic the power consumption of regular bulbs.
Reflectors and Projectors: LED bulbs work differently from halogen or incandescent bulbs, and the reflectors or projectors in your headlights or taillights are designed for specific types of bulbs. Improper beam patterns from incompatible LED bulbs can cause glare and reduce visibility for other drivers. Solution: Use LED bulbs specifically designed for automotive use and check that they are compatible with your vehicle’s reflectors or projectors.
Regulations: Some regions have strict regulations regarding the use of LED bulbs in vehicles, especially for headlights. Using non-compliant LED bulbs in place of halogens can lead to your vehicle failing an inspection or receiving a ticket. Solution: Ensure that any LED bulbs you purchase are road-legal and meet the standards set by your local authorities.
Error Codes: Many modern vehicles have a CanBus system that monitors the electrical load of the bulbs. If the LED bulbs draw less current than expected, the system may trigger a bulb-out warning. Solution: Choose CanBus-compatible LED bulbs or install a CanBus adapter to prevent warning lights from appearing.
Where to Use LED Bulbs:
Headlights and Fog Lights: Make sure the LEDs are designed for automotive use and comply with legal standards. Brake Lights and Turn Signals: LEDs are a popular choice for these because of their quick response time, but be aware of potential hyper-flashing. Interior Lighting: LED bulbs are commonly used for interior lights due to their low power consumption and bright light.
Summary:
Yes, you can use LED bulbs in your vehicle, but make sure they are compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system, produce the correct beam pattern, and comply with legal regulations. Consider: Installing load resistors or CanBus adapters if needed, and ensuring that the LED bulbs you select are designed for automotive use.
