Resistance
⫸ Free YouTube Subscription
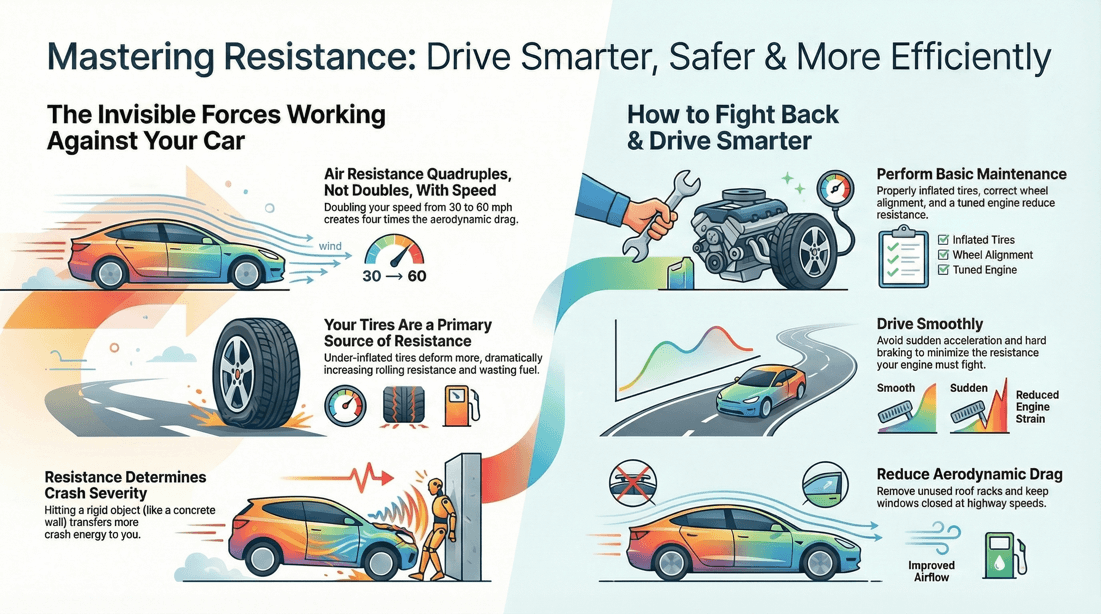
Every time your car moves forward, powerful yet invisible forces are working to slow it down. From the friction of your tires against the road to the drag of wind pushing against your vehicle at higher speeds, resistance is always at play. These forces affect everything from how quickly you can accelerate to how far it takes you to stop. Understanding driving resistance is essential to improving fuel efficiency, maintaining better control, and making safer decisions on the road.
What is driving resistance and how does it affect fuel efficiency? How does rolling resistance impact your ability to accelerate or brake? Why does wind resistance increase at higher speeds? How does tire pressure affect resistance and handling? What role does road surface play in creating resistance? How does resistance change in uphill or downhill driving?
This page explores the different types of resistance—rolling, aerodynamic, mechanical, and gravitational, and how each one influences your vehicle's motion. You'll learn how these forces impact your car’s stopping distance, fuel consumption, and overall performance. Whether you're navigating steep hills or cruising on the highway, understanding resistance helps you anticipate how your vehicle will respond and gives you a clear advantage in both everyday driving and emergency situations.
Mechanical resistance is the force that tends to opposes or retard motion.
From this broad definition, you can see that with regards to vehicles, there are a number of factors that could retard its motion, such as:
When colliding with an object, the greater the resistance that object has, the greater its effect will be on you.
⧋
🛈 Info:
⧋