
Rage
⮟ 📹 Brake Checking ⮟ 📹 Crashing ⮟ 📹 Cut Off ⮟ 📹 Pedestrian ⮟ 📹 Stopping ⮟ 📹 Tailgating
🛈 Info:
? Questions:

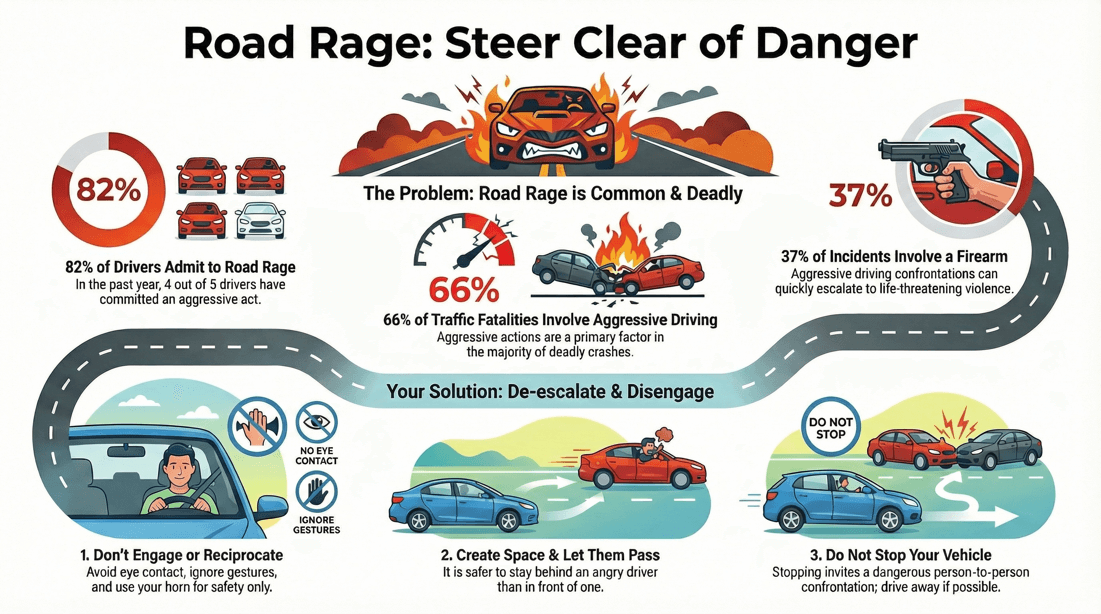
Control your anger :
Give yourself enough time to get to your destination. Don’t reciprocate. Ignore the temptation to react to the other driver. Do not make obscene gestures. Do not tailgate. Use your horn sparingly – even a polite honk can be misinterpreted.
Avoidance measures :
Avoid making eye contact with an aggressive driver. If someone wants to pass, slow down and let them. Stay behind the person who is angry at all costs. They can do less damage if you are behind them. Don’t stop. Stopping could lead to a person-to-person confrontation, which could be dangerous. If they have forced you to a stop, make sure you have either enough space in front to go around them, or behind you to reverse out the way. If necessary, pull off the road or take an exit and let them go on by.
📹 Crashing
📹 Cut Off
📹 Pedestrian
📹 Stopping
📹 Tailgating
🛈 Why road rage is so common
Stress and Frustration:
Daily Stress: Commuting can be stressful, especially in heavy traffic , leading to frustration and anger. Life Stress : Personal problems or stress from work can spill over into driving behavior.
Time Pressure:
Running Late: Many drivers are in a hurry to reach their destinations, leading to impatience and aggressive driving. Tight Schedules: The pressure to adhere to strict schedules can make drivers more prone to frustration when faced with delays.
Impatience:
Instant Gratification Culture: Society's increasing expectation for instant results and lack of patience can manifest as road rage. Slow Drivers: Encountering slow drivers or traffic jams can easily trigger aggressive responses.
Anonymity:
Lack of Personal Connection: The anonymity of being inside a vehicle can reduce empathy and increase aggressive behavior. Dehumanization: Drivers may view other vehicles as obstacles rather than as people, leading to a lack of consideration.
Environmental Factors:
Traffic Congestion: Heavy traffic can create a stressful driving environment, increasing the likelihood of road rage. Weather Conditions: Bad weather can exacerbate stress and lead to more aggressive driving behaviors.
Behavioral Factors:
Aggressive Personality : Some individuals have a naturally aggressive personality, making them more prone to road rage. Learned Behavior: Drivers may imitate aggressive behaviors they have seen or experienced .
Cultural Factors:
Cultural Norms: In some cultures, aggressive driving may be more socially acceptable or common. Driving Culture: Areas with a competitive driving culture can have higher instances of road rage.
Perceived Disrespect:
Rudeness: Perceived rudeness or inconsiderate driving by others can trigger aggressive responses. Territoriality: Drivers may feel a sense of ownership over their lane or space on the road, leading to aggressive behavior when they feel it's threatened.
Impairment:
Substance Use: Alcohol and drugs can impair judgment and increase the likelihood of aggressive driving. Fatigue : Tired drivers are more prone to irritability and aggressive behavior.
Lack of Consequences:
Low Enforcement: Perceived lack of consequences for aggressive driving can embolden drivers to engage in road rage. Hit and Run Mentality: Some drivers may believe they can get away with aggressive behavior without facing repercussions.
Technological Distractions:
Mobile Devices : Distracted driving due to smartphones and other devices can lead to frustration and road rage incidents.
🛈 Road rage triggers
Common Triggers of Road Rage
Description : Heavy traffic and long delays can cause frustration and impatience. Impact : Drivers may become irritated by the slow pace and start taking aggressive actions to move faster.
Description : Being followed too closely by another vehicle can create a sense of pressure and danger. Impact : The driver being tailgated may react aggressively, such as brake-checking or gesturing at the tailgater.
Description : When another driver abruptly moves in front of someone without proper signaling or space. Impact : The driver who is cut off may feel disrespected or endangered, leading to aggressive responses.
Description : Drivers who hog the left lane or fail to yield when others are trying to merge can frustrate others. Impact : This behavior can cause anger and prompt aggressive maneuvers like tailgating or unsafe lane changes.
Description : Excessive honking or making rude gestures can escalate tensions between drivers. Impact : These actions are often seen as personal attacks, provoking retaliatory behavior.
Description : Driving significantly below the speed limit or being indecisive can irritate other drivers. Impact : Slow drivers can cause others to become impatient and engage in risky overtaking maneuvers.
Description : Drivers who are visibly distracted by their phones, eating, or other activities. Impact : Distracted driving can lead to erratic driving patterns, causing frustration and anger in other drivers.
Description : Not using turn signals when changing lanes or turning can surprise and annoy other drivers. Impact : This can lead to misunderstandings and aggressive driving responses.
Description : Conflicts over parking spaces , such as someone taking a spot that another driver was waiting for. Impact : Such incidents can escalate quickly into confrontational or aggressive behavior .
Description : Unexpected roadwork or detours causing delays and confusion. Impact : Drivers may become frustrated by the inconvenience and take out their anger on other road users.
Description : Drivers playing loud music or making excessive noise can irritate others. Impact : Noise can be distracting and annoying, potentially triggering aggressive responses.
Psychological Triggers
Description : Drivers who are already stressed or tired are more prone to irritation. Impact : They may have a shorter fuse and be more likely to react aggressively to minor annoyances.
Description : Problems at home or work can contribute to a driver’s irritability and short temper. Impact : These drivers are more likely to take out their frustrations on the road.
Description : Feeling that another driver has disrespected or challenged them. Impact : This can lead to a desire to "teach the other driver a lesson" through aggressive behavior.
Description : The feeling of being anonymous in a vehicle can embolden drivers to act out. Impact : Drivers might behave more aggressively because they feel they are less likely to be held accountable.
Strategies to Manage and Avoid Road Rage
Practice deep breathing and relaxation techniques to stay calm in frustrating situations.
Allow extra time for your trips to reduce stress from rushing and delays.
Stay clear of drivers who exhibit aggressive behaviors and do not engage with them.
Maintain a safe following distance, be courteous, and anticipate potential issues on the road.
Play soothing music or use audiobooks/podcasts to keep your mood positive.
Use GPS to find the least congested routes and stay informed about traffic conditions.
On long drives , take regular breaks to rest and refresh.
Accept that delays and traffic are part of driving and manage your expectations accordingly.
Conclusion
🛈 Road rage statistics ( The Zebra )
In 2019, 82% of people admitted to committing an act of road rage in the past year. A total of 12,610 injuries and 218 murders have been attributed to road rage over a seven-year period in the United States. 66% of traffic fatalities are caused by aggressive driving. Road rage has been responsible for about 300 deaths since 2013. Over a seven-year time period, more than 200 murders and 12,000 injuries were attributed to road rage. 30 murders annually are linked to road rage. 50% of drivers respond to the careless acts of other drivers with aggressive behavior themselves. 94% of traffic accidents are caused by driver error. 37% of aggressive driving incidents involve a firearm. Aggressive driving played a role in 56% of fatal crashes from 2003 through 2007 500% increase in reported cases of road rage over the last 10 years.
? What are the types of road rage?
Verbal Road Rage:
Yelling and Shouting: Drivers may yell or shout at other road users out of frustration. Honking Excessively: Using the horn aggressively to express anger or impatience. Insulting Gestures: Making rude or offensive hand gestures toward other drivers.
Confrontational Road Rage:
Tailgating : Driving very close to the vehicle in front to intimidate the driver. Cutting Off : Deliberately cutting in front of another vehicle, often without signaling. Blocking : Intentionally blocking another vehicle from changing lanes or merging.
Physical Road Rage:
Speeding : Driving at excessive speeds to overtake or intimidate other drivers. Brake Checking : Suddenly braking to scare or force the driver behind to slow down. Swerving : Making sudden, aggressive lane changes or swerving to intimidate other drivers.
Aggressive Driving:
Weaving Through Traffic : Changing lanes frequently and abruptly to get ahead. Running Red Lights and Stop Signs : Ignoring traffic signals out of impatience or frustration. High-Speed Chases: Engaging in dangerous high-speed pursuits to confront or evade another driver.
Intentional Damage:
Ramming : Deliberately hitting another vehicle with the intention of causing damage. Throwing Objects: Throwing items at other vehicles or occupants.
Psychological Road Rage:
Passive-Aggressive Driving: Deliberately driving slowly in front of another vehicle to irritate the driver. Road Blocking: Driving side-by-side with another vehicle at the same speed to prevent others from passing.
Extreme Road Rage:
Physical Confrontation: Exiting the vehicle to engage in physical fights or altercations. Weapon Use: Using weapons or objects to threaten or harm other drivers or passengers.
Factors Contributing to Road Rage:
Stress and Frustration: High levels of stress and frustration can lead to aggressive driving behaviors. Traffic Congestion : Heavy traffic and delays can increase the likelihood of road rage incidents. Anonymity: The perceived anonymity of being in a vehicle can make drivers feel less accountable for their actions. Cultural and Regional Norms: In some regions, aggressive driving may be more socially accepted or common.
Prevention and Mitigation:
Stay Calm : Practice techniques to remain calm and composed while driving. Avoid Confrontation: Do not engage with aggressive drivers; maintain a safe distance. Report Aggressive Drivers : If you encounter extreme road rage, report the incident to the authorities. Plan Ahead: Allow extra time for your journey to reduce stress and the temptation to drive aggressively. Safe Driving Practices: Follow traffic rules, signal your intentions , and be courteous to other road users.
? Is road rage a crime?
Legal Implications of Road Rage Behaviors:
Aggressive driving behaviors such as speeding , reckless driving, tailgating , and running red lights can result in traffic citations or fines. These violations are typically classified as traffic offenses rather than criminal offenses but can still carry penalties like fines, points on a driver's license, or license suspension.
In extreme cases, road rage incidents can escalate to physical altercations between drivers or confrontations outside vehicles. Physical aggression, threats, or actions that cause harm to others can lead to criminal charges such as assault, battery, or even charges related to using a vehicle as a weapon (e.g., assault with a deadly weapon).
Intentional damage to another person’s vehicle or property during a road rage incident can result in charges of vandalism or criminal mischief.
Behaviors that put others at risk of harm, such as aggressive driving maneuvers or blocking traffic, can lead to charges of reckless endangerment.
Depending on the severity and jurisdiction, individuals involved in road rage incidents may face fines, probation, community service, or even imprisonment. Repeat offenders or those involved in serious incidents could face more severe penalties, including longer license suspensions or revocations.
Handling Road Rage:
Avoid Escalation : If you encounter an aggressive driver, avoid engaging or escalating the situation. Focus on driving defensively and safely. Report Dangerous Behavior : If you feel threatened or witness dangerous driving, report it to law enforcement. Provide details such as vehicle description, license plate number, and location. Stay Calm : Manage your own emotions and avoid reacting impulsively to provocation on the road.
Conclusion:
? Will insurance cover road rage ?
Damage to Your Vehicle (Collision Coverage) :
If your vehicle is damaged due to a collision resulting from road rage (e.g., another driver intentionally ramming into your car), collision coverage under your auto insurance policy may cover the cost of repairs, minus your deductible. This coverage generally applies regardless of fault, but you must file a claim and provide evidence of the incident.
Damage to Others’ Property (Liability Coverage) :
If you are involved in a road rage incident where you cause damage to another person’s vehicle or property, your liability coverage should cover the cost of repairs or replacement up to your policy limits. Liability coverage is essential for situations where you are found legally responsible for causing damage to others during a road rage incident.
Injuries (Medical Payments or Personal Injury Protection) :
Medical payments (MedPay) or Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage may help pay for medical expenses for you and your passengers if you are injured in a road rage incident. These coverages typically apply regardless of who is at fault for the accident, providing compensation for medical bills, lost wages, and other related expenses.
Legal Defense Costs (Optional Coverage) :
Some insurance policies offer optional coverage for legal expenses and defense costs if you are sued as a result of a road rage incident. This coverage can help pay for legal representation and court costs if you face lawsuits related to the incident.
Exclusions and Considerations:
Intentional Acts : Insurance policies generally do not cover intentional acts or criminal behavior. If you intentionally cause harm or damage during a road rage incident, your insurance may deny coverage. Policy Limits : Coverage limits in your insurance policy dictate the maximum amount your insurer will pay for covered claims. Review your policy to understand these limits. Claims Process : To receive coverage for road rage-related incidents, you must report the incident promptly to your insurance company and provide accurate information about what occurred.