
MAINTENANCE > ECONOMY > PURCHASING
Purchasing
🛈 Info:
💡 Tips:
? Questions:
Buying: Selling:
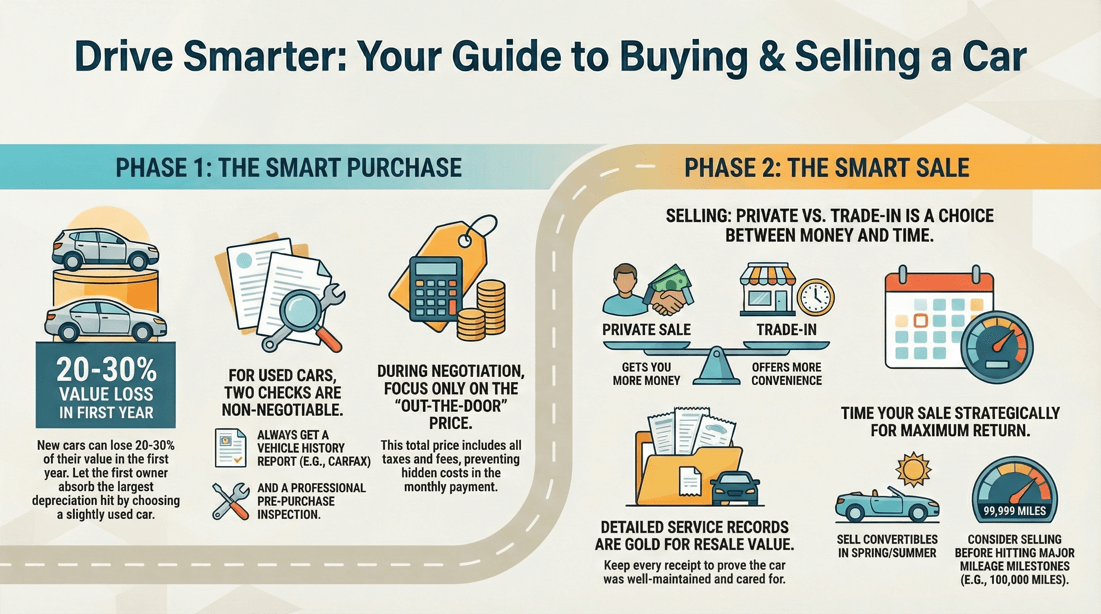
🛈 Factors to consider before purchasing a vehicle
Budget
Purchase Price : Determine how much you can afford upfront, whether you're paying in full or financing. Financing Options : If you're financing, consider the down payment, loan term, and interest rates. Total Cost of Ownership : Factor in taxes, registration fees, insurance premiums, fuel costs, and maintenance expenses.
New vs. Used
Depreciation : New cars lose value quickly, whereas used cars offer better value but may come with more wear and tear. Warranty : New cars typically come with a warranty, while used cars may not. However, some certified pre-owned vehicles come with warranties. Condition and History : If buying used, check the vehicle's history (accidents, maintenance, mileage) and have a trusted mechanic inspect it.
Vehicle Type and Purpose
Intended Use : Consider how you will use the vehicle (e.g., daily commuting, long road trips, off-roading, family transport). Size and Space : Think about the number of passengers and cargo space you'll need, and whether you require a sedan, SUV, truck, or van. Fuel Efficiency : Evaluate the fuel economy for long-term savings, especially if you have a long commute or frequent trips.
Safety Features
Essential Features : Look for airbags, anti-lock brakes, traction control, and stability control. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) : Consider newer safety technologies like lane departure warnings, blind-spot monitoring, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. Crash Test Ratings : Check the vehicle’s safety ratings from organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
Reliability and Maintenance
Reliability Ratings : Research the vehicle’s reliability ratings from sources like Consumer Reports or J.D. Power. Maintenance Costs : Consider the frequency and cost of repairs and routine maintenance for the make and model. Availability of Parts : Some vehicles have more expensive or harder-to-find parts, which could increase maintenance costs.
Resale Value
Depreciation Rate : Research which models retain their value better over time. Vehicles from brands known for reliability and quality often hold their value longer. Demand for Model : Popular models tend to have a better resale value when you decide to trade in or sell the car.
Insurance Costs
Vehicle Type : Insurance premiums vary by vehicle type. High-performance cars or luxury vehicles tend to have higher premiums. Safety and Security Features : Vehicles equipped with advanced safety and anti-theft features often qualify for lower insurance rates.
Fuel Type
Gasoline, Diesel, Hybrid, or Electric : Consider the type of fuel that suits your driving habits, cost, and environmental concerns. Charging Infrastructure : If considering an electric vehicle, check the availability of charging stations near your home and routes you frequently drive.
Test Drive
Comfort and Handling : Ensure the vehicle is comfortable, drives well, and meets your personal preferences in terms of handling, visibility, and ergonomics. Technology and Features : Test the usability of the vehicle’s infotainment system, navigation, and any other tech features that are important to you.
Dealer and Manufacturer Reputation
Reputation for Service : Research the dealer's reputation for customer service, including after-sales support and repair services. Manufacturer's Track Record : Look into the manufacturer's history regarding recalls, customer satisfaction, and long-term reliability.
💡 Tips before buying a car
Determine Your Budget
Set a Budget : Decide how much you can afford to spend, including the purchase price, insurance, taxes, registration, maintenance, and fuel. Consider Financing Options : If you plan to finance your car, research loan options, interest rates, and get pre-approved for a loan to understand your purchasing power.
Assess Your Needs
Evaluate Your Requirements : Consider factors like the size of the car, fuel efficiency, safety features, cargo space, and any specific needs (e.g., towing capacity, off-road capability). Future Considerations : Think about your future needs, such as growing family size or changes in your commute.
Research
Car Models and Reviews : Research different models, read reviews, and check reliability ratings. Websites like Consumer Reports, Edmunds, and Kelley Blue Book are valuable resources. Cost of Ownership : Consider long-term costs like fuel, maintenance, repairs, and depreciation.
New vs. Used
Pros and Cons : Decide whether you want a new or used car. New cars come with warranties and the latest features but depreciate quickly. Used cars are cheaper but may require more maintenance. Certified Pre-Owned (CPO) : If considering a used car, look into CPO programs that offer inspected, refurbished vehicles with warranties.
Test Drive
Test Multiple Vehicles : Test drive several models to compare comfort, performance, and features. Check for Comfort and Fit : Ensure the car fits your body comfortably, and you have good visibility. Check the ease of entry and exit, as well as the comfort of the seats.
Inspection
Professional Inspection : For used cars, get a pre-purchase inspection by a trusted mechanic to uncover any hidden issues. Vehicle History Report : Obtain a vehicle history report (e.g., Carfax) to check for accidents, title issues, or odometer fraud.
Negotiate the Price
Research Market Value : Use resources like Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds to determine the fair market value of the car. Be Prepared to Negotiate : Don’t accept the first offer. Be ready to negotiate the price, including any additional fees.
Review the Paperwork
Read the Fine Print : Carefully review the sales contract, including all terms and conditions, fees, and financing terms. Warranties and Return Policies : Understand the warranty coverage and any return or exchange policies.
Consider Additional Costs
Insurance : Get insurance quotes to understand how the new vehicle will affect your premiums. Taxes and Fees : Account for sales tax, registration fees, and any other costs associated with the purchase.
Plan for Future Maintenance
Maintenance Schedule : Know the recommended maintenance schedule for the vehicle and plan for regular servicing. Dealership vs. Independent Mechanic : Decide where you will have your car serviced and check for warranty requirements.
Check for Recalls
Recall Information : Check if the vehicle has any open recalls and ensure they are addressed before purchase.
Environmental Impact
Fuel Efficiency : Consider the fuel efficiency of the vehicle and its impact on the environment. Alternative Options : Look into hybrid or electric vehicles if you are concerned about environmental impact.
Conclusion
💡 Tips before buying a used car
Determine Your Budget
Set a Budget : Decide how much you can afford, considering the purchase price, insurance, taxes, registration, maintenance, and repairs. Consider Financing Options : If financing, research loan options, interest rates, and get pre-approved to understand your purchasing power.
Research
Car Models and Reviews : Research different models, read reviews, and check reliability ratings. Use resources like Consumer Reports, Edmunds, and Kelley Blue Book. Cost of Ownership : Consider long-term costs like fuel, maintenance, repairs, and depreciation.
Find the Right Car
Evaluate Your Needs : Determine what you need in a car (size, fuel efficiency, features, etc.) and make a list of potential models. Search Listings : Look for used cars from dealerships, private sellers, and online platforms like Autotrader, Cars.com, and Craigslist.
Vehicle History Report
Check History : Obtain a vehicle history report (e.g., Carfax or AutoCheck) to check for accidents, title issues, service history, and odometer readings.
Inspect the Car
Exterior : Check for rust, dents, and mismatched paint. Inspect the tires for wear and the lights for functionality. Interior : Look for signs of wear, stains, and unpleasant odors. Test all controls, including the air conditioning, heating, windows, and locks. Under the Hood : Check for leaks, corrosion, and worn belts or hoses. Look at the oil, transmission fluid, and coolant for signs of proper maintenance.
Test Drive
Test Multiple Vehicles : Test drive several cars to compare performance and comfort. Drive in Different Conditions : Test the car on highways, city streets, and different road conditions. Pay attention to how it handles, brakes, and accelerates. Listen and Feel : Listen for unusual noises and feel for any vibrations or handling issues.
Get a Professional Inspection
Mechanic Inspection : Have a trusted mechanic perform a pre-purchase inspection to identify any hidden issues. This can save you from costly repairs later.
Check for Recalls
Recall Information : Use the NHTSA's recall database to check if the car has any open recalls and ensure they have been addressed.
Negotiate the Price
Research Market Value : Use Kelley Blue Book, Edmunds, or NADA to determine the fair market value of the car. Be Prepared to Negotiate : Don’t accept the first offer. Be ready to negotiate the price and consider any repairs needed when making your offer.
Review the Paperwork
Read the Fine Print : Carefully review the sales contract, including all terms and conditions, fees, and warranties. Confirm Title and Ownership : Ensure the seller has clear ownership of the car and there are no liens on it.
Consider Additional Costs
Insurance : Get insurance quotes to understand how the used vehicle will affect your premiums. Taxes and Fees : Account for sales tax, registration fees, and any other costs associated with the purchase.
Verify the VIN
VIN Verification : Make sure the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on the car matches the VIN on the title and the history report.
Check for Warranty
Manufacturer’s Warranty : Determine if any of the manufacturer’s warranty is still in effect or if the car comes with a dealership warranty. Extended Warranty : Consider purchasing an extended warranty if you want additional coverage.
Plan for Future Maintenance
Maintenance Schedule : Know the recommended maintenance schedule for the vehicle and plan for regular servicing. Reliable Mechanic : Find a reliable mechanic familiar with the vehicle make and model.
Be Cautious of Scams
Avoid Unusual Payment Methods : Be wary of sellers asking for unusual payment methods or pressuring you to make a quick decision. Trust Your Instincts : If something feels off, walk away. It's better to be safe than sorry.
💡 What to look for when inspecting a second hand car
Exterior Condition :
Check for any signs of rust, dents, scratches, or paint damage. Inconsistent Paintwork: Look for mismatched paint, uneven surfaces, or variations in color. These signs may suggest previous repairs or bodywork, potentially indicating prior accidents or damage. Poor Alignment: Check if the car appears to be aligned properly. Uneven gaps between body panels, misaligned doors or trunk, or asymmetrical components can suggest previous damage or poor repairs. Ensure that all doors, windows, and the trunk open and close smoothly. Inspect the condition of the tires, including tread depth and even wear. Fluid Leaks: Check under the car for any visible signs of fluid leaks. Oil, coolant, or other fluid leaks can indicate mechanical problems or insufficient maintenance. Strange Odors: Pay attention to any unusual smells inside or around the car. Foul odors could indicate issues with the engine, exhaust system, or other mechanical components.
Interior Condition :
Check the overall cleanliness of the interior and look for any signs of excessive wear, stains, or damage. Test all seats, including adjustments and reclining mechanisms. Inspect the condition of the dashboard, controls, and instrumentation. Verify that all interior lights, windows, and other electronic features are functioning properly.
Mechanical Components :
Check the engine compartment for any signs of leaks, loose wires, or worn-out belts. Examine the battery for any corrosion or signs of aging. Electrical System Issues: Test all electrical components such as lights, windows, air conditioning, audio system, and navigation (if applicable). Malfunctioning or non-functional features may indicate electrical system problems. Engine Noises: Listen for any strange noises when starting the engine, during idling, acceleration, and deceleration. Unusual sounds like knocking, grinding, or rattling may indicate engine or mechanical problems. Smoke from the Exhaust: Excessive smoke from the exhaust can be a sign of engine problems or oil burning. Blue smoke indicates oil consumption, white smoke can indicate coolant leakage, and black smoke may suggest a fuel system issue.
Test Drive :
Take the car for a test drive to evaluate its performance and handling. Dashboard Warning Lights: Check if all the dashboard warning lights illuminate when turning the key to the "on" position. Make sure they turn off after the engine starts. Persistent warning lights may indicate underlying problems. Pay attention to the brakes, steering, and suspension for any issues. Observe how the transmission shifts gears, and listen for any strange noises. Test the acceleration and braking responsiveness. Check for any abnormal vibrations or pulling to one side.
Vehicle History and Documentation :
Request the vehicle's history report, which can provide information about accidents, previous owners, maintenance records, and mileage. Verify that the vehicle identification number (VIN) matches the documents and matches the one on the report. Check the service history and ensure that the car has been regularly maintained.
Additional Considerations :
Inspect the condition of the brakes and tires, including the depth of tire tread. Check the functionality of features such as air conditioning, heating, audio system, and other electronic components. Look for signs of any fluid leaks underneath the car. If possible, have a trusted mechanic conduct a thorough inspection to identify any hidden issues.
? What
should I look for during a test drive?
1. Comfort and Ergonomics
2. Performance and Handling
3. Noise Levels
4. Transmission and Gear Shifts
5. Functionality of Features
6. Safety Features
? How
do I negotiate the best price for a car?
1. Do Your Homework
2. Set Your Budget and Stick to It
3. Be Ready to Walk Away
4. Start with a Lower Offer
5. Focus on the Total Price, Not Monthly Payments
6. Look for Additional Discounts and Incentives
7. Don’t Reveal Your Trade-in Too Early
8. Be Polite and Professional
Car Negotiation Script for Getting the Best Price
Additional Tips for Success:
Take notes on all offers and conditions. Stay calm and don’t rush. Remember, you’re the customer — the dealer wants to sell, so use that to your advantage. If possible, bring a friend for support or a second opinion.
? What
financing options are available for car purchases?
1. Bank or Credit Union Loan
Often lower interest rates than dealers. You know your budget before shopping. Greater transparency and control.
May require stronger credit. Slower approval compared to dealer financing.
2. Dealership Financing
One-stop shop — everything handled in one place. Sometimes offers promotional rates (e.g., 0% APR). Easier for buyers with credit challenges.
Can come with marked-up interest rates. May push extended warranties or add-ons.
3. Manufacturer Financing
Very low or zero interest (if you qualify). Often bundled with other perks (e.g., maintenance plans).
Usually reserved for buyers with excellent credit. Only applies to certain makes or models.
4. Personal Loan
No need for a vehicle inspection or lien. Works well for private sales or older cars.
Higher interest rates than secured loans. Often limited to borrowers with solid credit.
5. Hire Purchase (HP) or Lease Purchase (if available in your country)
Easier approval, even with average credit. Fixed monthly payments.
Higher total cost compared to upfront purchase. You don’t own the car until the last payment is made.
Pro Tips:
Always check your credit score before applying. Use online auto loan calculators to understand what you can afford. Get pre-approval to strengthen your negotiating power. Don’t focus only on the monthly payment — look at the total cost over the loan term.
? How can I improve the resale value of my car?
Regular Maintenance
Follow the Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule : Adhere to the recommended service intervals for oil changes, brake checks, tire rotations, and other essential maintenance. Keeping detailed service records can also prove the car has been well-maintained. Fix Issues Promptly: Address any mechanical issues as soon as they arise. This prevents small problems from becoming larger, more expensive ones and shows potential buyers that the car was cared for. Maintain Proper Fluid Levels : Regularly check and top off fluids such as oil, coolant, transmission fluid, brake fluid, and power steering fluid. Clean fluid systems suggest a well-maintained vehicle.
Keep the Car Clean
Exterior : Wash your car regularly to remove dirt, grime, and road salt that can damage the paint and undercarriage. Wax the car every few months to protect the paint and keep it looking shiny. Interior : Vacuum the interior, clean the upholstery, and wipe down the dashboard and other surfaces regularly. Avoid smoking or eating in the car to prevent stains and odors. Protect Against Sun Damage: Use sunshades and park in the shade or a garage whenever possible to protect the interior from UV damage, which can cause the dashboard and seats to fade or crack.
Avoid Excessive Wear and Tear
Drive Smoothly: Avoid aggressive driving, such as hard braking, rapid acceleration, and high-speed driving, which can cause premature wear on the engine, brakes, and tires. Protect the Tires : Maintain proper tire pressure and alignment. Rotate the tires regularly to ensure even wear. Keep Mileage Low: The more miles on the odometer, the lower the car’s value. While this isn’t always controllable, consider using other transportation options for short trips.
Make Smart Upgrades
Consider Popular Features: If you’re upgrading your car, consider features that add value, such as a modern infotainment system, navigation, backup cameras , or advanced safety features. Use Quality Parts: If you need to replace parts, choose high-quality OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts, as they’re typically more reliable and preferred by buyers. Avoid Excessive Customization: While some customization may appeal to certain buyers, excessive or highly personalized modifications can reduce the car's appeal to a broader audience.
Protect the Paint and Bodywork
Use Paint Protection: Consider applying a paint protection film or ceramic coating to guard against chips, scratches, and UV damage. Fix Dents and Scratches: Address any minor dents or scratches promptly to prevent rust and keep the car looking well-maintained.
Store the Car Properly
Use a Garage or Car Cover: If possible, park your car in a garage to protect it from the elements. If a garage isn’t available, use a high-quality car cover to shield it from rain, snow, and sunlight. Avoid Long Periods of Inactivity: If you won’t be driving the car for a while, take steps to store it properly, including disconnecting the battery , inflating the tires, and using a fuel stabilizer.
Keep Comprehensive Records
Document Maintenance and Repairs: Keep all receipts and records of maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. A well-documented history can reassure buyers that the car has been well cared for. Keep an Accident-Free Record: Avoid accidents if possible. Even minor accidents can significantly decrease a car’s value.
Research the Market
Timing the Sale : Certain times of the year may be better for selling your car, depending on its type. For example, convertibles may sell better in the spring and summer, while SUVs might be more in demand during the fall and winter. Know Your Car’s Value: Regularly check the market value of your car. Websites like Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds can help you gauge your car’s worth based on its make, model, year, condition, and mileage.
Consider Professional Detailing Before Selling
Detailing Services: Investing in professional detailing before selling can make your car more appealing to buyers. This includes deep cleaning the interior, polishing the exterior, and possibly even minor paint correction.
? When is the best time to sell your car?
Vehicle Condition : Selling your car when it's in good condition, both mechanically and aesthetically, can help you fetch a higher price. Consider selling your car before it requires major repairs or when it has relatively low mileage. Seasonal Demand : Seasonal factors can impact the demand and value of certain types of vehicles. For example, convertible cars tend to be more desirable during the summer months. If your car is influenced by seasonal demand, consider selling it when demand is high to potentially get a better price. Market Demand : Keep an eye on the local and national market demand for the type of vehicle you're selling. Research current market trends, including popular makes and models, to determine if there is a higher demand for your specific vehicle. Selling when demand is strong can increase your chances of finding a buyer quickly and receiving a favorable price. New Model Releases : If you own a popular model that is about to be replaced or updated, selling before the new model hits the market can be advantageous. Buyers may be more interested in the latest version, causing the value of the older model to decrease. Capitalize on the anticipation for the new model by selling your car beforehand. Mileage Considerations : Mileage plays a role in the value of a used car. Selling your car before it reaches significant mileage milestones, such as 100,000 miles, can help you attract potential buyers who may be wary of higher mileage vehicles. However, keep in mind that exceptionally low mileage may also be appealing to some buyers. Financial Considerations : Personal financial circumstances may influence the decision to sell your car. If you're facing financial difficulties or have a pressing need for funds, selling your car sooner rather than later may be a practical choice. Vehicle Age : Generally, newer cars tend to have a higher resale value. However, this can vary depending on the make and model. Consider the age of your vehicle and how it compares to similar models on the market. Selling while your car is still relatively new can help you fetch a higher price.
? Should I sell my car privately or trade it in?
Selling Your Car Privately
Pros
Higher Sale Price : You can typically get more money by selling your car privately compared to trading it in. Control Over the Sale : You have the flexibility to negotiate the price and terms directly with the buyer. Wider Market : You can reach a larger audience through online listings and word of mouth.
Cons
Time-Consuming : Finding a buyer can take time, and you’ll need to handle all inquiries, test drives, and negotiations. Effort Required : Preparing your car for sale, advertising, and meeting with potential buyers requires effort and coordination. Safety Concerns : Meeting strangers for test drives and negotiations can pose safety risks. Paperwork : You’ll need to manage all the necessary paperwork, including the bill of sale, title transfer, and possibly smog certification.
Trading In Your Car
Pros
Convenience : Trading in your car is quick and easy. The dealer handles the paperwork and you can apply the trade-in value directly to your new purchase. Immediate Transaction : You can complete the transaction on the same day you buy your new car, making it a one-stop process. Tax Benefits : In some regions, you may only have to pay sales tax on the difference between the new car price and the trade-in value, potentially saving money.
Cons
Lower Value : Dealerships typically offer less for your car compared to what you could get in a private sale because they need to resell it for a profit. Limited Negotiation : You may have less room to negotiate the trade-in value compared to a private sale price. Condition Dependent : Dealers may offer significantly less if your car has high mileage or is in poor condition.
Factors to Consider
Car Condition :If your car is in excellent condition, you might get significantly more from a private sale. For older cars with high mileage or issues, trading in might be more practical. Time and Effort : Consider how much time and effort you’re willing to invest. If you need a quick sale and value convenience, trading in is the better option. Financial Needs : If you need to maximize your sale price to pay off a loan or get the best deal, a private sale is likely more beneficial. Market Demand : Research the demand for your car model. High-demand cars sell faster and for more money privately.
Tips for Selling Privately
Prepare Your Car : Clean it thoroughly, fix minor issues, and gather maintenance records. Advertise Effectively : Use multiple platforms like Craigslist, Autotrader, and local classifieds. Set a Fair Price : Research similar listings and set a competitive price. Safety First : Meet potential buyers in safe, public places and consider bringing someone with you. Be Ready with Paperwork : Have all necessary documents ready, including the title and bill of sale.
Tips for Trading In
Research Your Car’s Value : Use tools like Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds to understand your car’s trade-in value. Negotiate Separately : Negotiate the trade-in value separately from the new car purchase price to avoid confusion. Get Multiple Offers : Visit several dealerships to get competing offers and ensure you get the best deal.
