
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS > PRECARIOUS
Precarious
💡 Tips:
? Questions:
⮟ What are the most common reasons pedestrians end up in precarious positions in traffic? ⮟ Why is it dangerous for pedestrians to stand or walk in the road instead of on the sidewalk? ⮟ What should drivers do if they encounter a pedestrian in a precarious position? ⮟ How should pedestri ans navigate around construction zones or other sidewalk obstructions? ⮟ What should pedestrians do if they are stranded in the middle of a busy road? ⮟ What are some effective public awareness campaigns for pedestrian safety?

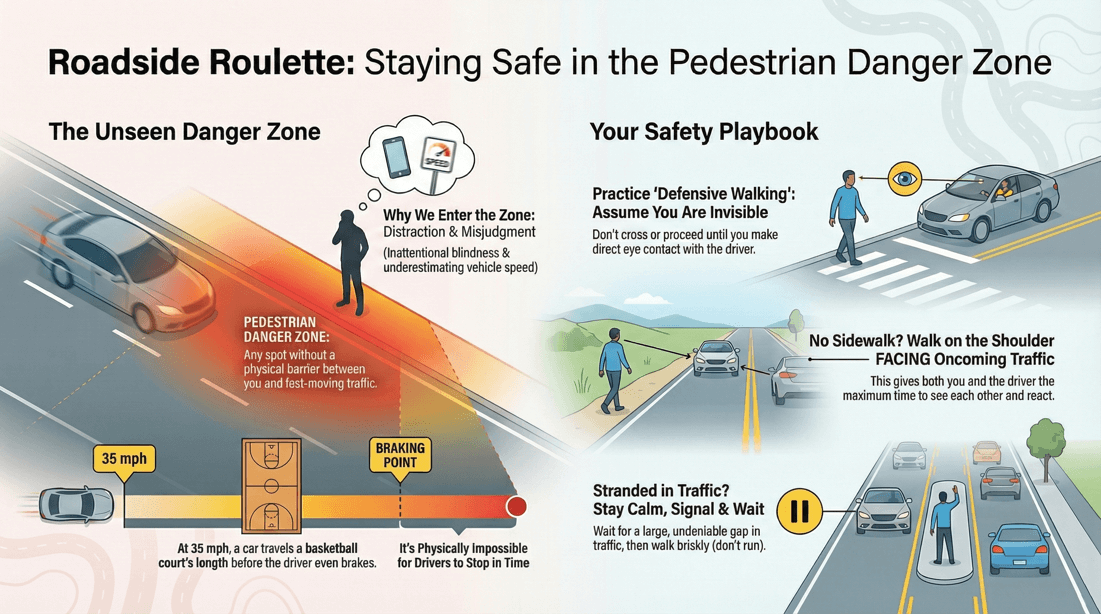
💡 Safety tips for pedestrians
General Safety Tips
Avoid Distractions: Refrain from using mobile phones or other electronic devices while walking. Listen to Your Surroundings: Avoid wearing headphones or keep the volume low to hear traffic noises.
Obey Signals: Follow pedestrian signals and cross at designated crosswalks. Use Sidewalks: Walk on sidewalks whenever available. If there are no sidewalks, walk facing traffic and stay as far off the roadway as possible.
Wear Bright Clothing: Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially at night or in low-light conditions. Use Lights: Carry a flashlight or use your phone’s flashlight when walking at night.
Crossing Streets
Designated Areas: Cross at marked crosswalks or intersections where drivers expect pedestrians. Avoid Jaywalking: Do not cross mid-block or from between parked cars.
Check for Traffic: Look left, right, and then left again before crossing. Ensure the road is clear and watch for turning vehicles.
Ensure Visibility: Make eye contact with drivers to confirm they see you before crossing in front of them.
Do Not Hesitate: Cross the street promptly but do not run. Hesitating or changing direction suddenly can confuse drivers.
Interacting with Vehicles
Watch for Reversing Cars: Pay attention to vehicles backing out of driveways or parking spaces. Stay on Designated Paths: Use pedestrian paths and avoid walking in traffic lanes.
Watch for Turning Vehicles: Even when you have the right of way, be cautious of vehicles turning into the intersection. Wait for a Safe Gap: Ensure there is enough time to cross safely before stepping onto the road.
Nighttime and Low-Light Conditions
Reflective Gear: Wear reflective vests, bands, or accessories. Light Sources: Use a flashlight or wear blinking LED lights.
Stay in Lighted Areas: Walk in well-lit areas to enhance your visibility to drivers.
Avoiding Dangerous Situations
Avoid Impairments: Do not walk near roadways if you are under the influence of alcohol or drugs, as they impair judgment and reaction times.
Adjust for Weather: Be extra cautious in adverse weather conditions like rain, snow, or fog, which can reduce visibility and make surfaces slippery.
Safety in Rural or Less-Traveled Areas
Walk Against Traffic: When walking on roads without sidewalks, walk facing the oncoming traffic to see and react to approaching vehicles. Stay on the Shoulder: Avoid the Roadway: Stay as far off the roadway as possible.
Teaching Children
Teach Crossing Techniques: Instruct children on the importance of using crosswalks, looking both ways, and making eye contact with drivers. Supervise Young Children: Always accompany young children when crossing streets and walking near traffic.
Model Safe Behavior: Demonstrate safe pedestrian practices for children to follow.
Using Public Transportation
Stay Off the Road: Wait on the sidewalk or a safe area away from the road. Watch for Traffic: Be aware of vehicles when boarding or alighting from buses.
Use Crosswalks: Do not cross the street immediately in front of or behind the bus. Walk to the nearest crosswalk or corner.
Summary
💡 How to improve pedestrian situational awareness
Stay Alert and Minimize Distractions
Avoid Using Phones: Refrain from texting, browsing, or talking on the phone while walking. If you must use your phone, stop in a safe place. Remove Headphones: If you need to listen to music, keep the volume low and use only one earbud to stay aware of your surroundings.
Pay Attention to Your Environment
Observe Traffic: Regularly scan the road for approaching vehicles, even when using crosswalks. Notice Signals and Signs: Be aware of pedestrian signals, traffic lights, and road signs.
Make Yourself Visible
Wear Bright or Reflective Clothing: Increase visibility, especially in low-light conditions. Use Lights: Carry a flashlight or use reflective gear at night.
Follow Safe Walking Practices
Use Sidewalks: Walk on sidewalks where available. If there are no sidewalks, walk facing traffic. Cross at Designated Areas: Use crosswalks and obey pedestrian signals. Avoid jaywalking.
Enhance Situational Awareness Through Techniques
Scan the Environment: Continuously look around, not just at the immediate path. Check for vehicles, cyclists, and other pedestrians. Listen to Surroundings: Stay alert to sounds that can indicate approaching vehicles or other potential hazards.
Practice Defensive Walking
Anticipate Driver Actions: Don't assume drivers will see you or stop for you. Be prepared to react if a driver doesn’t yield. Make Eye Contact: Ensure drivers see you before crossing in front of them.
Educate Yourself and Others
Learn Traffic Rules: Understand local traffic laws and pedestrian rights-of-way. Teach Children: Educate children about pedestrian safety and the importance of being aware of their surroundings.
Use Technology Wisely
Pedestrian Safety Apps: Utilize apps that alert you to traffic conditions and provide safety tips. GPS and Navigation: Use GPS to plan safe walking routes, especially in unfamiliar areas.
Be Cautious in Parking Lots and Driveways
Watch for Reversing Vehicles: Pay attention to vehicles backing out of parking spaces. Stay on Paths: Use designated walkways and be extra cautious in areas with limited visibility.
Adapt to Weather Conditions
Adjust for Visibility: Wear appropriate clothing and gear for rain, fog, or snow, which can reduce visibility. Walk Carefully: Be cautious of slippery or uneven surfaces in adverse weather.
Plan Your Route
Choose Safe Paths: Opt for well-lit, busy streets with good pedestrian infrastructure. Avoid High-Risk Areas: Steer clear of areas with high traffic speeds and poor visibility.
Stay Sober
Avoid Impairment: Alcohol and drugs can impair your judgment and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents.
Summary
? What are the most common reasons pedestrians end up in precarious positions in traffic?
Distractions
Texting or Talking: Pedestrians using their phones for texting, calling, or browsing may not be aware of their surroundings. Listening to Music: Wearing headphones can reduce awareness of traffic sounds, such as honking or approaching vehicles.
Conversations: Engaging in deep conversations with fellow pedestrians can divert attention from traffic. Daydreaming: Simply not paying attention or being lost in thought.
Poor Visibility
Nighttime: Pedestrians are harder to see after dark, especially if they are not wearing reflective clothing. Bad Weather: Rain, fog, or snow can significantly reduce visibility for both pedestrians and drivers.
Dimly Lit Areas: Walking in poorly lit areas makes pedestrians less visible to drivers.
Impatience or Inconvenience
Crossing Mid-Block: Instead of walking to a designated crosswalk, pedestrians may cross in the middle of a street to save time. Ignoring Signals: Crossing against the pedestrian signal because they don't want to wait.
Construction Zones: Walking in the street to avoid construction on sidewalks. Blocked Sidewalks: Navigating around parked cars, debris, or other obstructions.
Misjudgment
Misjudging Gaps: Misjudging the speed or distance of oncoming vehicles. False Sense of Safety: Assuming drivers will see them and stop.
Dark Clothing: Wearing dark clothes, especially at night, making it difficult for drivers to see them.
Alcohol or Substance Use
Alcohol Consumption: Being under the influence of alcohol can impair judgment and reaction time. Drug Use: Similar effects to alcohol, reducing awareness and decision-making ability.
Lack of Infrastructure
Walking on Roadways: In areas without sidewalks, pedestrians may have no choice but to walk on the road. Insufficient Crosswalks: Limited Crossing Points: Fewer crosswalks or long distances between them can lead to jaywalking.
Unexpected Situations
Sudden Situations: Being pushed into the street by a crowd or needing to quickly avoid an obstacle.
Pets or Wildlife: Moving into traffic to avoid an animal or chase a pet.
Unfamiliarity with the Area
Unfamiliar Surroundings: Tourists may not be familiar with local traffic patterns and rules. Navigating by Map: Paying more attention to maps or directions than to traffic.
Risk-Taking Behavior
Taking Risks: Believing they can safely cross or navigate through traffic despite obvious risks. Thrill-Seeking: Engaging in dangerous behavior intentionally for excitement.
Health-Related Issues
Elderly or Disabled Pedestrians: May have slower reaction times or difficulty judging traffic situations. Mental Health Issues: Individuals with certain mental health conditions may not fully appreciate the dangers.
? Why is it dangerous for pedestrians to stand or walk in the road instead of on the sidewalk?
Increased Risk of Collision
High Traffic Density: Roads are primarily designed for vehicles, which travel at higher speeds and have less reaction time to avoid pedestrians. Limited Reaction Time: Drivers may not expect pedestrians in the road and may not have sufficient time to react, increasing the likelihood of collisions.
Vehicle Blind Spots: Drivers may have blind spots where they cannot see pedestrians, particularly in larger vehicles like trucks or buses.
Reduced Visibility
Nighttime: Pedestrians are harder to see in low-light conditions, especially if not wearing reflective clothing. Weather Conditions: Rain, fog, or snow can further reduce visibility for drivers and pedestrians alike.
Road Focus: Drivers are typically focused on the road ahead and other vehicles, not on pedestrians who are unexpectedly in the road.
Limited Safe Space
Insufficient Space: Roads are designed with specific lanes for vehicles, leaving little to no safe space for pedestrians. Road Shoulders: Walking on road shoulders can still be dangerous, especially on narrow or busy roads.
Lack of Protection: Unlike sidewalks, roads lack physical barriers (like curbs) that provide a degree of separation and protection from vehicles.
Higher Vehicle Speeds
Higher Speeds: Vehicles on the road typically travel at higher speeds than those on sidewalks or pedestrian areas, increasing the severity of potential accidents. Reaction Times: Higher speeds reduce the time drivers have to react to unexpected obstacles, including pedestrians.
Force of Impact: Collisions at higher speeds result in greater force upon impact, leading to more severe injuries or fatalities for pedestrians.
Driver Distraction and Behavior
Surprise Factor: Drivers do not usually expect pedestrians to be in the road, and sudden appearances can lead to panic and erratic driving behavior. Distraction: Distracted driving (e.g., using a phone) means drivers are less likely to notice pedestrians until it's too late.
Impatient Drivers: Drivers may become frustrated with pedestrians in the road, leading to aggressive driving behaviors that can further endanger pedestrians.
Legal Implications
Jaywalking: In many places, walking in the road when sidewalks are available is illegal, and pedestrians can be fined or cited for jaywalking. Liability: Pedestrians in the road can be found at fault in the event of an accident, affecting legal and insurance outcomes.
Summary
? What should drivers do if they encounter a pedestrian in a precarious position?
Slow Down
Reduce Speed: Immediately reduce your speed as you approach the pedestrian. This gives you more time to react and reduces the severity of potential accidents. Be Prepared to Stop: Be ready to stop if necessary, especially if the pedestrian is crossing or positioned close to the road.
Increase Awareness
Watch for Movement: Pay close attention to the pedestrian’s movements and position. Look for any signs of the pedestrian attempting to cross or move. Scan the Environment: Continuously scan the area around the pedestrian for other potential hazards or changes in their behavior.
Use Your Horn if Needed
Alert the Pedestrian: If the pedestrian is in a dangerous or unexpected position and appears unaware of your presence, use your horn briefly to alert them. Avoid Excessive Use: Avoid using the horn excessively or aggressively, as it may startle the pedestrian and potentially cause confusion.
Maintain a Safe Distance
Avoid Close Encounters: Keep a safe distance from the pedestrian, especially if they are close to the road or standing on the road’s edge. Pass with Caution: If you need to pass a pedestrian who is walking along the road, do so with as much space as possible.
Be Prepared for Sudden Movements
Expect the Unexpected: Be prepared for sudden or unexpected movements from the pedestrian, such as stepping into the road or changing direction. React Calmly: Maintain control of your vehicle and react calmly to any sudden changes in the pedestrian’s position.
Yield When Required
Obey Traffic Laws: Yield to pedestrians at crosswalks and intersections as required by local traffic laws. Respect Right-of-Way: Always give pedestrians the right-of-way if they are in or approaching a crosswalk.
Avoid Aggressive Behavior
Remain Patient: Avoid aggressive driving behaviors such as honking excessively or making sudden lane changes. Drive Defensively: Use defensive driving techniques to ensure the safety of all road users.
Stop for Pedestrians at Crosswalks
Complete Stops: Make a complete stop for pedestrians at marked crosswalks and ensure they have crossed safely before proceeding. Check Both Directions: Ensure that the crosswalk is clear of pedestrians in both directions before moving forward.
Be Extra Cautious in Poor Visibility Conditions
Adapt to Conditions: Increase your caution and reduce speed in low visibility conditions such as fog, rain, or nighttime. Use Headlights Properly: Use your vehicle’s headlights effectively to improve visibility, but avoid using high beams that can glare and further reduce visibility.
Avoid Distractions
Stay Focused: Keep your attention on the road and avoid distractions such as using your phone or adjusting controls while approaching a pedestrian. Prepare for Interaction: Anticipate the need to interact with pedestrians or other road users and stay alert.
Summary
? How should pedestrians navigate around construction zones or other sidewalk obstructions?
Follow Posted Signs and Instructions
Observe Signs: Pay attention to any signage or barriers indicating changes to pedestrian routes or instructions for safely navigating the area. Follow Detours: Use any marked detours or alternative routes provided to avoid construction zones.
Stay Alert and Stay Visible
Be Aware of Surroundings: Continuously scan your environment for construction equipment, vehicles, and other potential hazards. Increase Visibility: Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially if navigating through areas with poor lighting or during low visibility conditions.
Use Designated Walkways
Stick to Paths: Follow designated pedestrian walkways or temporary paths set up around construction zones. Avoid Unauthorized Areas: Do not walk through areas that are clearly marked as off-limits or unsafe.
Look for and Use Safe Crossing Points
Find Safe Crossings: Look for safe places to cross the road or navigate around construction zones, ideally at intersections or crosswalks. Use Temporary Crossings: If available, use temporary crossings or pedestrian bridges provided to safely navigate around obstructions.
Be Cautious Around Equipment and Vehicles
Watch for Moving Equipment: Be aware of construction vehicles and equipment moving in and out of the area. Avoid walking in areas where equipment is operating. Keep a Safe Distance: Maintain a safe distance from construction vehicles and machinery, and avoid standing near or on construction barriers.
Follow Traffic Signals and Control Measures
Obey Signals: Follow any traffic signals or control measures in place to guide pedestrians safely through or around construction zones. Be Patient: Wait for clear and safe opportunities to cross streets or navigate around obstacles.
Avoid Walking in the Street
Stay on Sidewalks: If sidewalks are obstructed, use alternate routes or cross the street at designated crosswalks rather than walking in the street. Use Sidewalks When Available: Avoid walking in traffic lanes or on the road, as this increases the risk of accidents.
Use Protective Gear
Wear Safety Gear: If walking near construction sites, consider wearing safety gear such as helmets or reflective vests, especially in high-traffic areas or if advised to do so.
Communicate with Others
Inform Others: If walking with children or those who may have difficulty navigating obstacles, communicate with them about the safest route and be cautious. Ask for Help: If you’re unsure about the safest way to navigate an area, don’t hesitate to ask construction workers or other officials for guidance.
Report Unsafe Conditions
Notify Authorities: If you encounter unsafe conditions or hazards, report them to local authorities or construction site managers to address the issue.
Summary
? What should pedestrians do if they are stranded in the middle of a busy road?
Stay Calm
Avoid Panic: Try to stay calm and focused. Panic can lead to hasty decisions and increase the risk of accidents.
Assess the Situation
Look for Safe Options: Determine if there is a nearby safe place to move, such as a median, sidewalk, or pedestrian island. Check Traffic: Observe the flow of traffic to understand when it might be safest to move.
Signal to Drivers
Get Attention: Use your arms to signal to drivers that you need assistance or that you are in distress. Stand in a visible position and make yourself as noticeable as possible. Use Lights or Reflective Gear: If you have any reflective gear or a flashlight, use it to increase visibility, especially in low-light conditions.
Wait for a Safe Moment
Wait for Traffic Gaps: Wait for a significant gap in traffic before attempting to move to a safer location. Use Traffic Lights or Signals: If you are near a traffic signal or crosswalk, wait for the signal to change to indicate a safe time to cross.
Move Quickly but Carefully
Cross to Safety: Once you have a clear and safe opportunity, move quickly to the nearest sidewalk or safety area. Avoid Running: Running can increase the risk of tripping or falling. Walk briskly but carefully.
Seek Help if Needed
Contact Emergency Services: If you are unable to safely move or if you feel you are in immediate danger, call emergency services for assistance. Ask for Help: If there are other people nearby, ask them to help you navigate to safety or to call for help on your behalf.
Be Aware of Surroundings
Watch for Other Hazards: Stay alert to other potential hazards, such as oncoming traffic or construction equipment. Avoid Distractions: Do not use your phone or other distractions while trying to move to safety.
Stay Visible
Use Bright Clothing: If possible, wear bright or reflective clothing to make yourself more visible to drivers. Stand in a Safe Spot: If you cannot immediately move, try to stand in a place where you are less likely to be hit, such as on a median or a safe area in the road.
Follow Road Safety Rules
Use Crosswalks: If there is a crosswalk or pedestrian signal nearby, use it to cross the road safely. Obey Traffic Signals: Wait for traffic signals to indicate a safe time to cross if you are near an intersection.
Summary
? What are some effective public awareness campaigns for pedestrian safety?
Educational Campaigns
Brochures and Flyers: Distribute brochures and flyers with safety tips for pedestrians and drivers. Posters and Billboards: Use eye-catching visuals and concise messages on posters and billboards to highlight pedestrian safety issues.
Social Media: Utilize social media platforms to share safety tips, statistics, and real-life stories. Videos: Create engaging videos demonstrating safe pedestrian behaviors and the consequences of unsafe practices.
Community Engagement
Educational Workshops: Implement pedestrian safety workshops in schools to teach children safe walking behaviors and awareness. Safety Assemblies: Organize assemblies that involve interactive demonstrations and discussions about pedestrian safety.
Safety Fairs: Host pedestrian safety fairs with interactive booths, demonstrations, and giveaways to engage the community. Walkathons and Runs: Organize events that promote walking while emphasizing safety and raising awareness.
Collaborations
Community Groups: Partner with local community groups, businesses, and non-profits to amplify messages and reach a broader audience. Law Enforcement: Collaborate with police departments for enforcement and educational initiatives.
Local News: Work with local news outlets to feature stories, interviews, and reports on pedestrian safety issues. Radio and TV Ads: Run targeted radio and TV advertisements that highlight pedestrian safety messages.
Infrastructure and Environment
Crosswalks and Signals: Advocate for and install improved crosswalks, pedestrian signals, and road markings. Visibility Enhancements: Ensure that pedestrian crossings are well-lit and clearly marked.
Traffic Calming Measures: Support traffic calming measures such as speed bumps, roundabouts, and reduced speed limits in pedestrian-heavy areas. Safe Routes: Develop and promote safe walking routes, especially near schools and high pedestrian traffic areas.
Behavioral Interventions
Driver Training: Incorporate pedestrian safety education into driver training programs and licensing processes. Public Service Announcements: Create and distribute PSAs focusing on the importance of yielding to pedestrians and safe driving practices.
Safe Walking Practices: Educate pedestrians on safe walking practices, such as using crosswalks, being visible, and staying alert. Interactive Workshops: Offer workshops that teach practical skills for navigating busy streets safely.
Data and Research
Highlight Statistics: Use pedestrian accident statistics to underscore the importance of safety measures and drive home the message. Case Studies: Share case studies and real-life incidents to illustrate the impact of unsafe behaviors.
Surveys and Feedback: Collect feedback from the community to assess the effectiveness of safety campaigns and identify areas for improvement. Impact Analysis: Evaluate the impact of campaigns through data analysis and adjust strategies as needed.
Emotional Appeals
Testimonies: Share personal stories and testimonials from accident survivors or families affected by pedestrian accidents to create an emotional connection. Public Appeals: Use emotional appeals to motivate behavior change and emphasize the human impact of pedestrian safety issues.
Summary
? Can a
pedestrian hold a parking spot?
Legal and Traffic Regulations
Traffic Laws: Most jurisdictions have traffic laws and regulations that specifically govern the use of parking spaces by vehicles. Pedestrians do not have legal authority to control or reserve parking spots. Parking Enforcement: Parking enforcement is usually managed by local authorities or property managers, not by individuals, including pedestrians.
Safety Considerations
Safety Hazards: Allowing pedestrians to hold parking spots could create safety hazards. Drivers might not expect pedestrians to be involved in parking spot management, which could lead to confusion and accidents. Disruption: Pedestrians standing in parking spots could disrupt the flow of traffic and parking, leading to frustration among drivers and potential conflicts.
Practicality
Parking Spot Management: Managing and reserving parking spots is typically done through signage, permits, or electronic systems, not by individuals. These methods are designed to ensure fairness and order. Space Availability: Parking spots are intended for vehicles, and their availability is managed based on parking regulations, not by personal claims or reservations.
Potential Consequences
Legal Issues: A pedestrian attempting to hold or reserve a parking spot might face legal consequences if their actions lead to disputes or traffic violations. Conflict with Drivers: Such actions could lead to conflicts with drivers who are trying to park, resulting in arguments or confrontations.