
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS > VISIBILITY
Visibility (Pedestrians)
💡 Tips:
? Questions:
⮟ What are the common mistakes pedestrians make regarding visibility? ⮟ Are there specific safety measures for children to increase visibility? ⮟ What are the best practices for walking in poorly lit areas? ⮟ How can roadways be improved to enhance pedestrian visibility? ⮟ What should pedestrians do if they encounter a vehicle that doesn’t see them? ⮟ How can technology assist in improving pedestrian visibility?

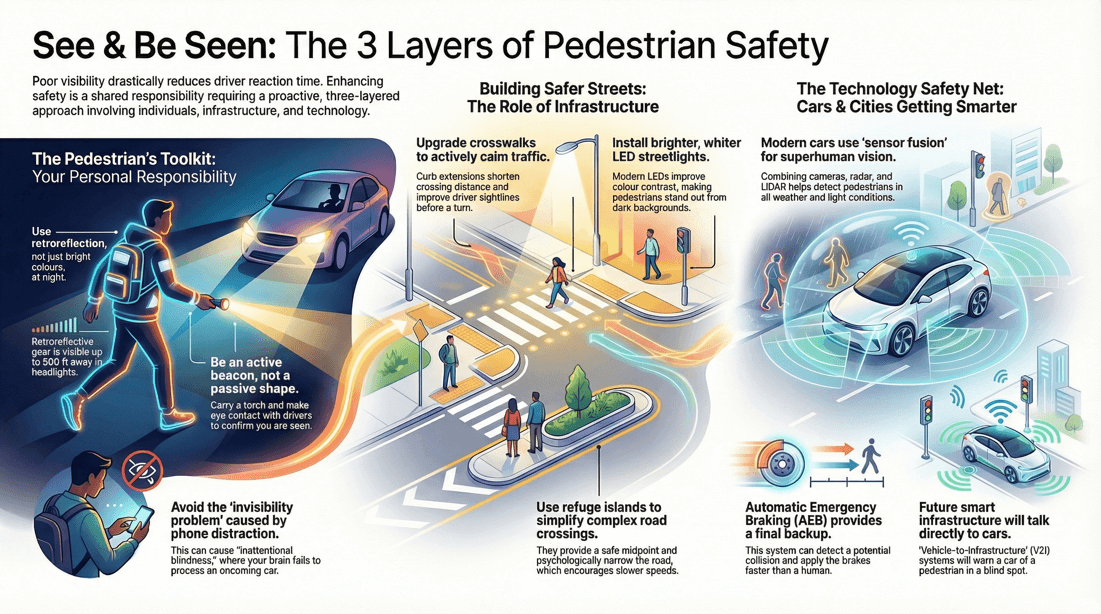
💡 Tips on i mproving pedestrian visibility
Wear Visible Clothing
Daytime: Wear bright or neon-colored clothing during the day, such as fluorescent yellow or orange. Reflective Materials: Opt for clothing with reflective strips or patches to increase visibility.
Vests and Armbands: Use reflective vests or armbands, especially if walking in low-light conditions or at night. Headwear and Bags: Consider reflective accessories for hats, backpacks, and other gear.
Use Lighting and Reflective Gear
Carry a Light: Use a flashlight or headlamp when walking in the dark or in poorly lit areas. Wearable Lights: Opt for wearable lights that attach to clothing or backpacks for added visibility.
Reflective Tape: Apply reflective tape to clothing, bags, or gear for increased visibility. LED Lights: Use small LED lights or blinkers that can be attached to clothing or bags.
Choose Safe Walking Routes
Stay on Sidewalks: Walk on designated sidewalks whenever available to avoid walking in the street. Avoid Roads Without Sidewalks: If sidewalks are not available, choose routes with the least traffic.
Street Lighting: Walk in areas with adequate street lighting to enhance visibility. Avoid Dark Areas: Avoid walking in areas that are poorly lit or without street lighting.
Improve Roadside Visibility
Avoid Obstacles: Ensure there are no obstructions, like large signs or bushes, that might block the view of pedestrians from vehicles. Trim Vegetation: Work with local authorities to keep vegetation trimmed around crosswalks and pedestrian areas.
Bright Crosswalks: Use bright, reflective paint for crosswalks to make them more visible. Signage: Install clear pedestrian crossing signs and signals to alert drivers.
Increase Awareness Among Drivers
Public Education: Support campaigns that educate drivers about the importance of looking out for pedestrians and respecting crosswalks. School Programs: Implement pedestrian safety programs in schools to raise awareness among students and parents.
Driver Training: Promote defensive driving techniques that include scanning for pedestrians, especially in areas where they are likely to cross.
Implement Community Measures
Install Additional Lighting: Advocate for the installation of additional street lighting and pedestrian lighting in high-traffic areas. Lighting Upgrades: Upgrade existing street lighting to brighter, more energy-efficient options.
Pedestrian Islands: Install pedestrian islands or refuges in the middle of wide roads to provide a safe place for pedestrians to wait. Advance Warning Systems: Implement pedestrian-activated crossing signals that alert drivers when a pedestrian is about to cross.
Use Technology
Safety Alerts: Utilize mobile apps that provide safety alerts for pedestrians and drivers, such as those that signal when pedestrians are crossing.
Smart Wearables: Consider wearable technology that enhances visibility, such as smart vests with integrated lights or reflective materials.
Advocate for Policy Changes
Safety Regulations: Advocate for local policies that mandate better pedestrian infrastructure, such as more crosswalks and improved street lighting. Community Involvement: Participate in community meetings to discuss and promote pedestrian safety improvements.
Conclusion
? What are the common mistakes pedestrians make regarding visibility?
Wearing Dark Clothing
Issue: Dark or non-reflective clothing is difficult for drivers to see, especially in low-light conditions. Solution: Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially at night or in poor weather conditions.
Not Using Reflective Gear
Issue: Failing to use reflective accessories such as vests, armbands, or backpacks reduces visibility. Solution: Utilize reflective gear or accessories that enhance visibility to drivers.
Walking in Poorly Lit Areas
Issue: Walking in areas without adequate street lighting can make pedestrians less visible. Solution: Stick to well-lit paths and sidewalks, and use a flashlight or headlamp if walking in dark areas.
Being Distracted by Mobile Devices
Issue: Using mobile phones or other devices can distract pedestrians from their surroundings and reduce awareness of oncoming traffic. Solution: Stay alert and avoid using devices while walking, especially when crossing streets.
Crossing Streets Outside of Crosswalks
Issue: Crossing outside designated crosswalks or intersections can make it harder for drivers to see and anticipate pedestrians. Solution: Use crosswalks and pedestrian signals whenever possible, and cross streets at designated points.
Not Making Eye Contact with Drivers
Issue: Failing to make eye contact with drivers can lead to misunderstandings about who has the right-of-way. Solution: Make eye contact with drivers when crossing streets to ensure they see you and acknowledge your presence.
Ignoring Weather Conditions
Issue: Bad weather conditions, such as rain, fog, or snow, can reduce visibility for both pedestrians and drivers. Solution: Adjust your visibility strategies based on weather conditions, such as using additional lighting or reflective gear.
Walking in Blind Spots
Issue: Walking in areas where drivers have limited visibility, such as behind parked cars or near large vehicles, increases risk. Solution: Avoid walking in blind spots and stay visible by positioning yourself where drivers can see you clearly.
Crossing Without Checking Traffic
Issue: Not looking for oncoming traffic before crossing can result in dangerous situations. Solution: Always look both ways before crossing and ensure it is safe to proceed.
Misunderstanding Pedestrian Signals
Issue: Misinterpreting pedestrian signals or crossing when signals are not active can lead to accidents. Solution: Follow pedestrian signals and wait for the “Walk” signal before crossing the street.
Wearing Inappropriate Footwear
Issue: Wearing footwear that is not suitable for walking, such as high heels or slippery shoes, can increase the risk of tripping or falling. Solution: Wear appropriate, comfortable footwear that provides good traction and support.
Overlooking Pedestrian Safety Rules
Issue: Not adhering to pedestrian safety rules, such as walking against traffic or jaywalking, can increase risks. Solution: Follow all pedestrian safety rules and regulations to ensure safe crossing and walking practices.
? How can pedestrians increase their visibility to drivers?
Wear Bright and Reflective Clothing
Bright Colors: Opt for clothing in bright, neon colors such as fluorescent yellow, orange, or green, especially in low-light conditions. Reflective Materials: Choose clothing with reflective strips or patches that catch and reflect light from vehicles.
Use Reflective and LED Accessories
Reflective Vests and Armbands: Wear reflective vests, armbands, or bands on your arms and legs to increase visibility. LED Lights: Attach small LED lights or blinkers to your clothing, backpack, or shoes to make yourself more noticeable.
Carry a Flashlight or Headlamp
Flashlights: Use a flashlight when walking in the dark to illuminate your path and make yourself visible to drivers. Headlamps: Wear a headlamp for hands-free lighting and visibility.
Stick to Well-Lit Areas
Street Lighting: Walk in areas with adequate street lighting to ensure you are visible to drivers. Avoid Dark Areas: Stay away from poorly lit or unlit areas where visibility is compromised.
Use Designated Crosswalks and Pedestrian Signals
Crosswalks: Always use crosswalks when available. They are often marked with reflective paint and are designed to make pedestrians more visible. Pedestrian Signals: Wait for pedestrian signals to cross streets, and ensure drivers see you before stepping onto the roadway.
Make Eye Contact with Drivers
Visibility Check: Make eye contact with drivers when crossing streets to ensure they see you and are aware of your presence. Non-Verbal Communication: Use hand signals or gestures if necessary to communicate with drivers.
Avoid Distractions
Stay Alert: Avoid using mobile phones or other distractions while walking. Focus on your surroundings and traffic conditions. Awareness: Be mindful of your environment and the traffic around you.
Walk on the Sidewalk
Sidewalks: Use sidewalks whenever possible to stay off the road and avoid potential conflicts with vehicles. Pedestrian Paths: Choose pedestrian paths or designated walking areas rather than walking directly on the roadway.
Be Cautious Around Parked Vehicles
Blind Spots: Avoid walking between parked cars where drivers may not see you. Use crosswalks and wait until you are clearly visible. Visibility Check: Ensure you are visible to drivers before crossing in front of parked vehicles.
Adapt to Weather Conditions
Rain and Fog: In adverse weather conditions, use additional lighting and reflective gear to enhance visibility. Avoid walking in heavy rain or fog if possible. Snow and Ice: Be cautious of slippery conditions and wear appropriate footwear to prevent accidents.
Educate Others
Awareness Campaigns: Support or participate in local safety campaigns that promote pedestrian visibility and road safety. Community Involvement: Advocate for better pedestrian infrastructure and safety measures in your community.
Consider Safety Technology
Wearable Technology: Explore wearable safety technology such as smart vests or jackets equipped with LED lights and reflective materials. Safety Apps: Use mobile apps that provide safety alerts and help keep pedestrians informed about traffic conditions.
? What should pedestrians wear to be visible at night?
Bright and Reflective Clothing
Bright Colors: Wear clothing in bright, fluorescent colors like neon yellow, orange, or pink, which stand out in low-light conditions. Reflective Materials: Opt for clothing with reflective strips or panels that catch and reflect headlights from vehicles.
Reflective Accessories
Reflective Vests: Use a reflective vest designed specifically to increase visibility. These vests often have bright colors and reflective bands. Reflective Armbands and Leg Bands: Wear reflective armbands or leg bands that can be easily seen from different angles.
LED Lights
Clip-On Lights: Attach small LED clip-on lights to your clothing, backpack, or hat. These lights can blink or glow to attract attention. Headlamps: Wear a headlamp for hands-free lighting. It illuminates your path and makes you more visible to drivers.
Light-Up Gear
Light-Up Shoes: Consider wearing shoes with built-in LED lights or reflective strips to enhance visibility. Light-Up Accessories: Use light-up accessories like necklaces or wristbands designed for visibility.
Reflective Tape
Personal Gear: Apply reflective tape to personal items like backpacks, jackets, or hats to improve visibility. Bicycles and Other Equipment: If carrying a bicycle or other equipment, use reflective tape to ensure they are also visible.
Bright Outerwear
Jackets and Coats: Choose outerwear that is brightly colored and has reflective features. High-visibility jackets are specifically designed for this purpose.
Flashlights and Headlamps
Handheld Flashlights: Carry a flashlight to light your path and make yourself more visible to drivers. Headlamps: Wear a headlamp for a hands-free solution that provides both illumination and visibility.
Avoid Dark Clothing
Avoid Dark Colors: Refrain from wearing dark or muted colors at night as they blend into the environment and reduce visibility. Layering: If wearing dark clothing, layer it with reflective accessories to improve visibility.
Safety Gear for Children
Bright and Reflective Clothing: Ensure children wear bright, reflective clothing and accessories. This is particularly important for their safety while walking to and from school or other activities.
Footwear
Reflective Shoes: Opt for shoes with reflective elements or add reflective stickers to your footwear. Non-Slip Soles: Wear footwear with good traction to avoid slips and falls in low-light conditions.
Use of Technology
Wearable Tech: Explore wearable safety technology such as smart vests or jackets equipped with LED lights and reflective materials. Safety Apps: Use mobile apps designed to enhance pedestrian safety and provide visibility alerts.
? Are there specific safety measures for children to increase visibility?
Bright and Reflective Clothing
Bright Colors: Dress children in bright, neon colors such as fluorescent yellow, orange, or pink to make them more noticeable, especially in low-light conditions. Reflective Clothing: Use clothing with reflective strips, patches, or designs that catch and reflect headlights from vehicles.
Reflective Accessories
Reflective Vests: Equip children with reflective vests, which are designed to enhance visibility with bright colors and reflective materials. Reflective Armbands and Leg Bands: Have children wear reflective armbands or leg bands that can be seen from different angles.
Light-Up Gear
LED Lights: Attach small LED lights to children’s backpacks, clothing, or hats. These lights can blink or glow to attract attention. Light-Up Shoes: Consider shoes with built-in LED lights or reflective elements for added visibility.
Safety Gear for Walking
Backpacks: Choose backpacks with reflective strips or LED lights for increased visibility. Headlamps: For older children, a headlamp can provide hands-free lighting and improve visibility.
Use of Technology
Wearable Technology: Explore wearable tech like smart vests or jackets equipped with LED lights and reflective materials. Safety Apps: Utilize mobile apps that offer visibility alerts and safety features for children walking to and from school.
Walking in Groups
Buddy System: Encourage children to walk with friends or in groups, as multiple people are more likely to be seen by drivers. Supervision: Where possible, supervise children walking to ensure they are following safety practices and staying visible.
Safe Routes
Designated Walkways: Ensure children use designated pedestrian paths and crosswalks. Avoid Dangerous Areas: Guide children to avoid walking near busy roads or areas with high traffic where visibility might be compromised.
Educate Children
Road Safety Education: Teach children about road safety rules, including the importance of staying visible, looking both ways before crossing, and using crosswalks. Visibility Importance: Explain why being seen is important and how reflective clothing and accessories help.
Avoid Distractions
No Mobile Devices: Ensure children are not distracted by mobile phones or other devices while walking. They should stay focused on their surroundings.
Traffic Awareness
Look for Cars: Teach children to make eye contact with drivers before crossing the street and to be aware of their surroundings. Obey Signals: Instruct children to follow pedestrian signals and wait for the “Walk” signal before crossing.
Regular Checks
Clothing and Gear: Regularly check that reflective gear and accessories are in good condition and properly worn. Proper Fit: Ensure that reflective clothing and accessories fit well and are comfortable for children.
? What are the best practices for walking in poorly lit areas?
Use Personal Lighting
Flashlight: Carry a handheld flashlight to illuminate your path and make yourself more visible to others. Headlamp: Wear a headlamp for hands-free lighting, which provides visibility and allows you to see obstacles more easily.
Wear Reflective and Bright Clothing
Reflective Gear: Wear clothing with reflective strips or patches that can catch and reflect light from vehicles and streetlights. Bright Colors: Choose bright, neon-colored clothing that stands out in low-light conditions.
Use Reflective Accessories
Reflective Armbands and Leg Bands: Wear reflective armbands or leg bands to enhance visibility from different angles. Reflective Tape: Apply reflective tape to your clothing, backpack, or other personal items.
Stick to Well-Trodden Paths
Established Routes: Use well-established paths, sidewalks, or pedestrian walkways that are likely to be safer and more visible. Avoid Overgrown Areas: Stay away from areas with dense foliage or obstacles that could obstruct your path.
Be Aware of Your Surroundings
Stay Alert: Pay close attention to your surroundings, including traffic, road conditions, and potential hazards. Avoid Distractions: Avoid using mobile devices or other distractions that could impair your awareness of the environment.
Walk in Groups
Buddy System: Whenever possible, walk with others. Groups are more visible and can offer additional safety. Stay Together: Ensure that everyone in the group stays close together and maintains visibility.
Choose Safe Crossing Points
Use Crosswalks: Cross streets at designated crosswalks or intersections where drivers are more likely to see you. Wait for Traffic: Wait for a safe gap in traffic and make eye contact with drivers before crossing.
Be Predictable
Follow Traffic Rules: Adhere to traffic signals and pedestrian signals to make your movements predictable to drivers. Signal Your Intentions: Use hand signals or gestures if necessary to indicate your intentions to drivers or other pedestrians.
Ensure Good Footwear
Proper Shoes: Wear shoes with good traction to prevent slips and falls, especially on uneven or slippery surfaces. Comfort: Choose comfortable, supportive footwear to make walking safer and more manageable.
Carry Emergency Contact Information
Identification: Carry identification and emergency contact information in case of an accident or emergency. Inform Someone: Let someone know your route and expected arrival time if walking alone.
Avoid Walking Alone When Possible
Walk with Company: Whenever possible, walk with friends, family, or trusted individuals to enhance safety. Avoid Risky Areas: Be cautious when walking in unfamiliar or high-risk areas, especially if alone.
Improve Pathway Lighting
Advocate for Lighting: Support community efforts to improve lighting in poorly lit areas to enhance safety for all pedestrians. Install Personal Lighting: If possible, install personal lighting solutions, such as solar-powered garden lights, in your walking areas.
? How can roadways be improved to enhance pedestrian visibility?
Improve Street Lighting
Increase Illumination: Install brighter streetlights or additional lighting along pedestrian routes and crosswalks to improve visibility at night. LED Lights: Use LED lights for better illumination and energy efficiency. Ensure lights are well-maintained and functioning.
Enhance Crosswalk Visibility
High-Visibility Markings: Use bold, bright, and reflective paint for crosswalks to make them more visible to drivers. Enhanced Markings: Consider using raised crosswalks or textured surfaces to draw attention to pedestrian crossings. Pedestrian Crossing Signs: Install highly visible pedestrian crossing signs with reflective materials.
Add Reflective Elements
Street Furniture: Incorporate reflective materials into street furniture, such as benches, bus stops, and signs. Traffic Control Devices: Equip traffic signals, signs, and posts with reflective elements to improve visibility.
Install Pedestrian Signals
Dedicated Signals: Use pedestrian signals with clear, illuminated walk/don’t walk indicators at intersections. Countdown Timers: Provide countdown timers to inform pedestrians of the time remaining to cross safely.
Use Traffic Calming Measures
Speed Bumps: Install speed bumps or rumble strips near crosswalks to slow down vehicles and enhance pedestrian safety. Curb Extensions: Extend curbs at intersections to shorten crossing distances and increase visibility.
Improve Road Design
Raised Crosswalks: Design raised crosswalks that elevate the pedestrian crossing area, making it more visible and slowing down traffic. Pedestrian Refuge Islands: Use refuge islands in the middle of wide roads to provide a safe waiting area for pedestrians.
Implement Advanced Warning Systems
Pedestrian Alerts: Install flashing pedestrian crossing signs or warning lights to alert drivers to the presence of pedestrians. In-Road Lights: Use in-road lighting or embedded lights at crosswalks to make pedestrian crossings more prominent.
Enhance Roadway Markings
High-Contrast Markings: Use high-contrast road markings, such as white or yellow paint, for crosswalks and pedestrian zones. Zebra Stripes: Implement zebra-striped crosswalks for better visibility and to indicate pedestrian priority.
Improve Sidewalk Design
Well-Maintained Sidewalks: Ensure sidewalks are well-maintained, with clear pathways and no obstructions. Wide Sidewalks: Provide wide sidewalks to accommodate pedestrians and improve visibility.
Provide Pedestrian Islands and Refuge Areas
Safe Crossings: Create pedestrian islands and refuge areas at busy intersections and mid-block crossings to offer a safe place for pedestrians.
Educate Drivers and Pedestrians
Awareness Campaigns: Conduct public awareness campaigns about pedestrian safety and the importance of visibility. Driver Education: Promote driver education programs that emphasize the need to watch for pedestrians, especially at crosswalks.
Use Technology
Smart Traffic Signals: Implement smart traffic signals that detect pedestrian presence and adjust signal timings accordingly. Pedestrian Detection Systems: Use pedestrian detection systems that alert drivers to pedestrians in their path.
Encourage Community Involvement
Local Input: Involve local communities in the planning and design of pedestrian safety improvements to address specific needs and concerns. Volunteer Programs: Encourage volunteer programs that help with maintaining and improving pedestrian infrastructure.
? What role do streetlights play in pedestrian visibility?
Increased Illumination
Improved Visibility: Streetlights provide essential lighting that helps pedestrians see their surroundings and be seen by drivers, reducing the risk of accidents. Safe Navigation: Well-lit streets and crosswalks allow pedestrians to navigate more safely by clearly revealing potential hazards such as potholes, obstacles, or uneven surfaces.
Enhanced Awareness
Driver Visibility: Streetlights make pedestrians more visible to drivers, allowing them to spot pedestrians from a greater distance, especially during low-light conditions or at night. Reduced Blind Spots: Effective street lighting can reduce the impact of drivers' blind spots, making it easier for them to detect pedestrians at intersections and crosswalks.
Defined Pathways
Clear Boundaries: Streetlights help define pedestrian pathways and crosswalks, making it clear where pedestrians should walk and where drivers should expect to see them. Guidance: Illuminated pathways provide guidance for pedestrians, ensuring they can follow safe routes even in dark conditions.
Deterrent to Crime
Increased Security: Well-lit areas are less attractive to criminals and can increase the perceived safety of walking in those areas, encouraging more people to walk rather than use potentially unsafe routes. Public Safety: Streetlights can deter criminal activities such as theft or assault, making pedestrians feel more secure.
Traffic Control
Crosswalk Visibility: Streetlights enhance the visibility of crosswalks, making it easier for drivers to see and stop for pedestrians. Signal Visibility: Illuminated traffic signals and pedestrian crossing signals become more noticeable, reducing the likelihood of traffic signal-related accidents.
Consistency and Uniformity
Even Lighting: Consistent and uniform street lighting reduces dark spots and shadows that could hide pedestrians or create unsafe conditions. Avoidance of Glare: Properly designed streetlights minimize glare and ensure that light distribution is even, which improves overall visibility.
Environmental Design
Lighting Design: Well-designed street lighting can improve overall urban aesthetics and make public spaces more inviting for pedestrians. Lighting Placement: Strategic placement of streetlights can ensure that key areas such as bus stops, crosswalks, and parking lots are adequately illuminated.
Improved Navigation
Landmark Visibility: Streetlights help pedestrians recognize landmarks and navigate through neighborhoods or unfamiliar areas more easily. Safe Crossings: Adequate lighting at intersections and pedestrian crossings helps pedestrians make safe and informed decisions when crossing streets.
Technological Advancements
Smart Lighting: Advances in streetlight technology, such as smart lighting systems, can adjust brightness based on real-time conditions and improve energy efficiency while enhancing visibility. Adaptive Lighting: Some modern streetlights can adapt to the presence of pedestrians or vehicles, providing increased illumination when needed.
? What should pedestrians do if they encounter a vehicle that doesn’t see them?
Immediate Actions
Wave or Signal: Use hand gestures or wave to catch the driver's attention. Use a Light Source: If it’s dark, use a flashlight, phone light, or any reflective accessory to increase visibility.
Retreat to Safety: Move back to the sidewalk or a safe area away from the vehicle's path. Avoid the Blind Spot: Ensure you are not standing in a vehicle’s blind spot where the driver cannot see you.
Confirm Awareness: Try to make eye contact with the driver to ensure they are aware of your presence.
Preventive Measures
Bright and Reflective Gear: Wear bright, reflective clothing or accessories, especially in low-light conditions.
Stay in Lighted Areas: Opt for routes with good lighting to increase visibility.
Use Crosswalks: Cross at designated crosswalks where drivers expect pedestrians. Obey Signals: Only cross when the pedestrian signal indicates it is safe to do so.
At Crosswalks and Intersections
Cross with the Signal: Ensure the pedestrian signal is in your favor before crossing. Look Both Ways: Even with a walk signal, check for vehicles that may be turning or not stopping.
Be Decisive: Cross the street promptly and avoid lingering in the roadway.
In Parking Lots and Driveways
Watch for Reversing Vehicles: Pay attention to vehicles backing out of parking spots. Stay on Designated Paths: Use sidewalks and pedestrian paths provided in parking areas.
Avoid Stopping in the Path of Vehicles: Continue walking briskly to minimize the time spent in the vehicle’s path.
Communicate with Drivers
Indicate Intentions: Use clear body language to show your intention to cross the street. Point in the Direction: Point in the direction you are going to cross to make your intentions obvious.
If a Collision Seems Imminent
Dodge Out of the Way: If you notice a vehicle approaching and it hasn’t seen you, quickly move out of its path. Avoid Running: Running can make your movements unpredictable to the driver.
Yell to Alert the Driver: Use your voice to alert the driver to your presence if other methods fail.
Reporting Unsafe Situations
Report Dangerous Areas: If you notice areas where drivers frequently fail to see pedestrians, report these to local traffic authorities. Suggest Improvements: Advocate for better lighting, signage, or pedestrian signals in dangerous areas.
Summary
? How can technology assist in improving pedestrian visibility?
Wearable and Personal Technologies
Reflective Gear: Jackets, vests, armbands, and shoes with reflective materials that bounce light back to drivers, making pedestrians more visible. LED Accessories: Clip-on LED lights, armbands, or shoe lights that actively illuminate the pedestrian.
Integrated LEDs: Clothing with built-in LED lights that can be turned on during low visibility conditions. Light-Up Backpacks: Backpacks with integrated lights and reflective materials.
Visibility Alerts: Apps that use GPS and real-time data to notify pedestrians of low visibility conditions and suggest using visibility gear. Personal Safety Apps: Apps that allow pedestrians to activate lights or send alerts when walking in dark areas.
Vehicle Technologies
Pedestrian Detection: Cameras, radar, and LIDAR systems that detect pedestrians and alert the driver or automatically apply brakes if necessary. Night Vision Systems: Infrared cameras that enhance the driver’s ability to see pedestrians in the dark.
Smart Headlights: Headlights that adjust their intensity and direction based on driving conditions, improving visibility of pedestrians without blinding oncoming traffic. Pedestrian Spotlights: Systems that specifically highlight pedestrians detected near the roadway.
Infrastructure and Smart City Technologies
In-Road Lighting: LED lights embedded in crosswalks that activate when a pedestrian is present, increasing visibility. Illuminated Signage: Signs with built-in lights that activate when a pedestrian is crossing, alerting drivers.
Pedestrian Detection: Sensors at intersections that detect pedestrians and adjust signal timings to ensure safe crossing periods. Audible and Visual Alerts: Traffic signals that provide both visual and audible alerts to make pedestrians aware of crossing times and to alert drivers of pedestrian presence.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Communication: Systems that allow traffic signals and other infrastructure to communicate with vehicles, warning drivers of pedestrians at crossings. Smart Street Lighting: Street lights that adjust brightness based on pedestrian activity and environmental conditions.
Community and Public Safety Technologies
Digital Signage: Interactive and dynamic digital signs that provide real-time safety messages and visibility tips for pedestrians. Educational Apps: Mobile applications that educate users about the importance of visibility and provide tips on staying safe.
Wearable Visibility Programs: Distribution of reflective gear and LED accessories to communities, especially in high-risk areas. Safe Routes Programs: Development of well-lit, safe walking routes for schools and neighborhoods, supported by community apps and maps.
Emerging Technologies
AR Glasses: Glasses that enhance a pedestrian’s view by highlighting safe routes and alerting to hazards. AR Mobile Apps: Apps that provide real-time overlays on smartphone screens, showing the safest and most visible paths to take.
Aerial Monitoring: Drones equipped with cameras and lights that can monitor pedestrian traffic and enhance visibility in certain areas, such as large events or poorly lit streets.
Integration and Data Analytics
Traffic and Safety Data: Using data analytics to identify high-risk areas for pedestrians and implementing targeted visibility improvements. Predictive Analytics: Using machine learning to predict pedestrian traffic patterns and dynamically adjust lighting and signal timings.
? What is pedestrian detection?
Components of Pedestrian Detection Systems
Cameras: Optical cameras capture images and video, which are analyzed to detect pedestrians. Infrared Sensors: Detect heat signatures from pedestrians, useful in low-light conditions. Radar: Uses radio waves to detect the presence and movement of pedestrians. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Uses laser beams to create detailed 3D maps of the environment, identifying pedestrians accurately.
Machine Learning: Algorithms are trained to recognize pedestrian shapes and movements from sensor data. Image Processing: Software analyzes visual data to distinguish pedestrians from other objects. Tracking: Continuously monitors detected pedestrians to predict their movement and potential interactions with vehicles.
Applications of Pedestrian Detection
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Detects pedestrians and automatically applies brakes if a collision is imminent. Collision Warning: Alerts the driver if pedestrians are detected in the vehicle’s path. Adaptive Cruise Control: Adjusts the vehicle's speed to maintain a safe distance from detected pedestrians.
Smart Traffic Signals: Detects pedestrians at crossings and adjusts signal timing to ensure safe crossing periods. Pedestrian Counting: Monitors pedestrian traffic to optimize signal timing and improve traffic flow.
Crowd Monitoring: Identifies and tracks pedestrians in public spaces for security and crowd management. Incident Detection: Recognizes unusual pedestrian behavior that might indicate security threats or accidents.
Benefits of Pedestrian Detection
Reduced Accidents: Prevents collisions between vehicles and pedestrians by alerting drivers and/or taking automatic action. Improved Traffic Flow: Optimizes signal timing to accommodate pedestrian crossings, reducing traffic congestion.
Adaptive Systems: Adapts to real-time conditions, providing efficient and responsive traffic management. Data Collection: Gathers valuable data on pedestrian movements, aiding in urban planning and infrastructure development.
Accessibility: Provides additional safety measures for visually impaired and other vulnerable pedestrians through audible signals and longer crossing times.
Challenges and Considerations
Weather Impact: Rain, fog, and snow can affect the accuracy of some detection systems. Lighting Conditions: Low light or glare can challenge camera-based systems, though infrared and LIDAR can mitigate this.
Crowded Areas: High pedestrian density can make individual detection and tracking more complex. Dynamic Scenes: Rapidly changing environments require highly adaptive and responsive systems.
False Positives/Negatives: Systems must minimize incorrect detections to avoid unnecessary braking or missed detections. Processing Power: Advanced detection and analysis require significant computational resources.
Future Developments
Advanced Perception: Enhanced pedestrian detection is critical for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles. Shared Data: Vehicles and infrastructure sharing data to improve overall traffic safety and efficiency.
Connected Systems: Integration of pedestrian detection with broader smart city systems for real-time traffic management and public safety. Predictive Analytics: Using data from pedestrian detection systems to predict and respond to traffic patterns and potential hazards proactively.