
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS
Pedestrians
🛈 Info:
☠️ Alert:
? Questions:

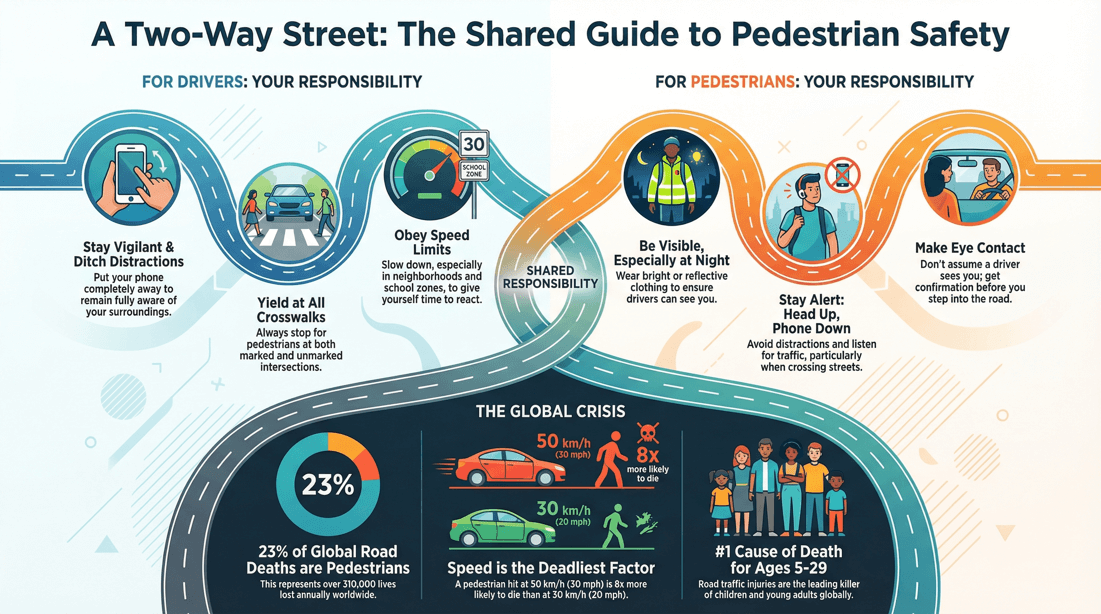
🛈 Statistics on pedestrian deaths around the world
Global Overview
Annual Deaths : Approximately 1.35 million people die each year as a result of road traffic crashes. Pedestrians account for about 23% of these fatalities, which translates to around 310,500 pedestrian deaths annually. Leading Cause : Road traffic injuries are the leading cause of death for children and young adults aged 5-29 years.
Low- and Middle-Income Countries : Over 90% of road traffic deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, even though these countries have approximately 60% of the world’s vehicles. High-Income Countries : High-income countries tend to have better road safety records, but pedestrian deaths still account for a significant portion of road fatalities.
Country-Specific Data
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Report : In 2020, 6,516 pedestrians were killed in traffic crashes, accounting for 17% of all traffic fatalities in the US. Trend : Pedestrian fatalities have been increasing in recent years, with a 46% increase from 2010 to 2019.
European Commission : In 2019, there were approximately 3,983 pedestrian fatalities in the EU, accounting for 20% of all road deaths. Safety Improvements : The EU has seen a general decrease in pedestrian fatalities over the past decade due to improved road safety measures and infrastructure.
Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) Report : In 2019, India reported 25,858 pedestrian deaths, making up 18.4% of total road traffic fatalities. Urban Areas : A significant number of pedestrian fatalities occur in urban areas with high traffic volumes and inadequate pedestrian infrastructure.
National Statistics : In 2019, China reported approximately 26,000 pedestrian deaths, accounting for a significant proportion of road traffic fatalities. Urbanization Impact : Rapid urbanization and high vehicle densities contribute to high numbers of pedestrian deaths.
Contributing Factors
Speeding : Higher vehicle speeds increase both the likelihood of a crash occurring and the severity of injury if a crash does occur. A pedestrian hit by a car traveling at 50 km/h is far more likely to be killed than if hit at 30 km/h. Alcohol and Drug Use : Impairment due to alcohol or drugs is a significant factor in pedestrian deaths, affecting both drivers and pedestrians. Inadequate Infrastructure : Lack of sidewalks, pedestrian crossings, and safe walking paths contribute to higher pedestrian fatalities. Distracted Driving : The use of mobile phones and other distractions increases the risk of crashes involving pedestrians. Visibility Issues : Poor lighting and visibility conditions, especially at night, increase the risk of pedestrian accidents.
Prevention and Safety Measures
Traffic Calming Measures : Implementing speed bumps, raised pedestrian crossings, and roundabouts to slow down traffic. Improved Infrastructure : Building and maintaining sidewalks, pedestrian overpasses/underpasses, and well-marked crosswalks. Education and Awareness : Public awareness campaigns focused on both drivers and pedestrians about the risks and safety practices. Enforcement of Traffic Laws : Strict enforcement of speed limits, DUI laws, and regulations regarding distracted driving. Technological Innovations : Use of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), pedestrian detection technologies, and automated braking systems in vehicles.
Summary
☠️Pedestrians
most at risk
Children
Lack of Experience : Children often lack the experience and understanding of road safety rules. Impulsive Behavior : They may suddenly dart into the street without looking for oncoming traffic. Shorter Height : Their smaller stature makes them less visible to drivers, especially in busy traffic areas. School Zones : Areas around schools are particularly high-risk due to the concentration of children.
Elderly
Slower Mobility : Older adults generally move slower, making it harder for them to cross streets quickly. Vision and Hearing Impairments : Age-related declines in vision and hearing can make it difficult to detect oncoming traffic. Physical Limitations : They may have reduced agility and balance, increasing their vulnerability. Complex Intersections : Elderly pedestrians may struggle with complex traffic environments.
Individuals with Disabilities
Mobility Challenges : People with physical disabilities may use mobility aids that slow them down and make crossing streets more difficult. Sensory Impairments : Those with visual or hearing impairments may have trouble detecting traffic. Cognitive Disabilities : Some individuals may have cognitive impairments that affect their ability to understand and navigate traffic safely.
Distracted Pedestrians
Mobile Device Usage : Pedestrians using smartphones or other electronic devices are often distracted and less aware of their surroundings. Headphones : Listening to music or other audio through headphones can reduce the ability to hear oncoming traffic.
Intoxicated Pedestrians
Alcohol and Drug Use : Pedestrians under the influence of alcohol or drugs are at higher risk due to impaired judgment, slower reaction times, and reduced coordination.
Pedestrians in Low-Income Areas
Lack of Infrastructure : Low-income neighborhoods may have inadequate pedestrian infrastructure, such as poorly maintained sidewalks and insufficient crosswalks. Higher Traffic Volume : These areas may also experience higher traffic volumes and fewer traffic calming measures.
Pedestrians During Low Visibility Conditions
Nighttime : Walking at night poses higher risks due to reduced visibility and higher likelihood of impaired drivers. Bad Weather : Rain, fog, and snow can decrease visibility for both pedestrians and drivers, increasing the risk of accidents. Poor Lighting : Areas with inadequate street lighting make it harder for drivers to see pedestrians.
Young Adults
Risk-Taking Behavior : Young adults may engage in riskier behaviors, such as jaywalking or crossing streets in non-designated areas. High Traffic Areas : They are more likely to be found in high-traffic urban areas, increasing their exposure to traffic hazards.
Preventive Measures
Education and Awareness Campaigns : Targeted campaigns to educate both drivers and pedestrians about road safety, focusing on vulnerable groups. Improved Infrastructure : Building and maintaining safe pedestrian pathways, well-marked crosswalks, and pedestrian-friendly traffic signals. Traffic Calming Measures : Implementing speed bumps, reduced speed zones, and pedestrian islands to slow down traffic in high-risk areas. Enhanced Lighting : Improving street lighting in areas with high pedestrian traffic to ensure better visibility at night. Technology Solutions : Utilizing advanced technologies like pedestrian detection systems in vehicles and smart traffic signals. Strict Law Enforcement : Enforcing traffic laws strictly to prevent speeding, distracted driving, and driving under the influence.
Summary
? W here do
most pedestrian accidents occur?
Urban Areas
Higher Traffic Volumes : Urban areas have higher traffic volumes, increasing the chances of pedestrian-vehicle interactions. More Pedestrians : Cities have more pedestrians due to higher population density and greater reliance on walking for transportation. Intersections and Crosswalks : Many pedestrian accidents happen at intersections and crosswalks where pedestrians and vehicles meet frequently.
Non-Intersections
Mid-Block Crossings : Pedestrians often cross streets at non-intersection locations, increasing the risk of accidents as drivers may not expect pedestrians to cross mid-block. Jaywalking : Crossing streets at non-designated points can surprise drivers and lead to accidents.
Parking Lots and Driveways
Low-Speed Zones : Despite the low speeds, the presence of both vehicles and pedestrians in confined spaces can lead to accidents. Backing Up : Drivers backing out of parking spaces may not see pedestrians, leading to collisions.
High-Speed Roads
Limited Pedestrian Infrastructure : Highways and arterial roads often lack adequate pedestrian infrastructure, such as sidewalks and crosswalks. Greater Impact Force : Higher vehicle speeds on these roads increase the severity of injuries in the event of a collision.
Residential Areas
Children Playing : Residential streets often see children playing, running, or biking, which can lead to unexpected pedestrian activity on the road. Local Traffic : Drivers may be less vigilant in familiar residential areas, increasing the risk of accidents.
School Zones
High Pedestrian Activity : School zones have high concentrations of children walking to and from school. Increased Traffic : The combination of buses, cars, and pedestrians creates a complex and risky environment.
Shopping Areas and Commercial Districts
High Foot Traffic : These areas see a lot of pedestrian movement, especially near entrances and exits of stores. Distractions : Both drivers and pedestrians may be distracted by commercial activities.
Public Transportation Stops
Bus Stops and Train Stations : Areas around public transportation stops often see high pedestrian activity as people get on and off buses and trains. Crossing Streets : Pedestrians may cross streets to reach transportation stops, sometimes in unsafe conditions.
Poorly Lit Areas
Nighttime Visibility : Poor lighting at night makes it harder for drivers to see pedestrians and for pedestrians to see vehicles. Higher Risk : Accidents are more likely in poorly lit areas, especially during early morning and late evening hours.
Construction Zones
Obstructed Pathways : Construction can obstruct normal pedestrian pathways, forcing pedestrians to walk in the street. Increased Hazards : The presence of construction equipment and vehicles increases the risk of accidents.
Contributing Factors
Distracted Driving : Drivers using mobile phones or other distractions are less likely to notice pedestrians. Alcohol and Drug Use : Impaired drivers and pedestrians are at higher risk of accidents. Speeding : Higher speeds reduce reaction times and increase the severity of accidents. Weather Conditions : Rain, fog, and snow can reduce visibility and make it harder for drivers to see pedestrians.
Prevention Measures
Improved Infrastructure : Building and maintaining sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian overpasses/underpasses. Traffic Calming Measures : Implementing speed bumps, pedestrian islands, and reducing speed limits in high-risk areas. Enhanced Lighting : Installing better street lighting in areas with high pedestrian traffic. Public Awareness Campaigns : Educating drivers and pedestrians about road safety. Strict Law Enforcement : Enforcing laws related to speeding, distracted driving, and DUI. Technological Innovations : Using advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and pedestrian detection systems in vehicles.
Summary
? W hy do pedestrians have the right of way?
Vulnerability and Safety
Physical Vulnerability : Pedestrians are more physically vulnerable than occupants of vehicles. In the event of a collision, pedestrians are far more likely to sustain serious injuries or fatalities. Protection Priority : Traffic laws are designed to protect the most vulnerable road users. Giving pedestrians the right of way helps prevent accidents and reduces the severity of injuries when accidents do occur.
Encouraging Walking and Sustainable Transportation
Promoting Walking : Granting pedestrians the right of way encourages walking, which is a healthy and environmentally friendly mode of transportation. Reducing Traffic Congestion : Encouraging walking can help reduce traffic congestion and pollution, contributing to more sustainable urban environments.
Urban Design and Pedestrian Accessibility
Designing for Safety : Urban areas are often designed with pedestrian accessibility in mind, including sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian signals. Enhancing Livability : Prioritizing pedestrian safety and convenience enhances the livability of urban areas, making them more attractive and accessible.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Uniform Traffic Laws : Traffic laws are designed to provide clear and consistent rules for all road users. Giving pedestrians the right of way creates a predictable and orderly traffic environment. Crosswalk Regulations : In many jurisdictions, pedestrians have the right of way at marked and unmarked crosswalks. This legal framework helps ensure that drivers yield to pedestrians, reducing the risk of accidents.
Traffic Flow and Efficiency
Reducing Conflicts : Granting pedestrians the right of way helps minimize conflicts between vehicles and pedestrians, contributing to smoother and safer traffic flow. Priority at Intersections : At intersections, giving pedestrians the right of way helps manage traffic flow more effectively, especially in areas with high pedestrian activity.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Protecting the Most Vulnerable : It is an ethical responsibility to protect the most vulnerable members of society, including pedestrians. Promoting Equity : Ensuring pedestrian safety and accessibility promotes equity, as walking is a primary mode of transportation for many people, including those who cannot afford a vehicle or prefer not to drive.
Practical Implications
Driver Responsibility : Drivers are required to be vigilant and yield to pedestrians, especially in areas where pedestrians are likely to be present, such as crosswalks, school zones, and residential neighborhoods. Pedestrian Awareness : Pedestrians, while having the right of way, must still exercise caution and be aware of their surroundings, particularly when crossing streets and navigating traffic. Infrastructure Improvements : Cities and municipalities are encouraged to invest in pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, such as well-marked crosswalks, pedestrian signals, and traffic calming measures, to enhance safety and accessibility.
Summary
? How can I improve pedestrian safety as a driver?
Stay Alert and Avoid Distractions
Avoid Phone Use : Do not use your phone or any other distractions while driving. Pay Attention to Surroundings : Always be aware of your surroundings, especially in areas with high pedestrian traffic.
Yield to Pedestrians
At Crosswalks : Always yield to pedestrians at marked and unmarked crosswalks. Intersections : Be prepared to stop for pedestrians when turning at intersections, even if they are crossing in unmarked crosswalks.
Obey Speed Limits
Residential Areas : Drive slowly in residential neighborhoods where children might be playing. School Zones : Adhere to lower speed limits in school zones and be extra cautious during school hours.
Improve Visibility
Use Headlights : Turn on your headlights in low visibility conditions such as dawn, dusk, rain, or fog to make yourself more visible to pedestrians. Clear Windows : Ensure your windshield, windows, and mirrors are clean for maximum visibility.
Be Extra Cautious at Night
Reduced Visibility : Pedestrians are harder to see at night, so drive slowly and be vigilant in poorly lit areas. Watch for Pedestrians in Dark Clothing : Pedestrians in dark clothing are less visible; keep an eye out for them.
Be Careful Near Public Transport Stops
Bus Stops and Train Stations : Slow down and be prepared to stop near bus stops and train stations, where pedestrians might suddenly cross the street.
Understand Pedestrian Signals
Pedestrian Crossing Signals : Learn and obey pedestrian crossing signals and be patient as pedestrians cross the street.
Be Prepared for Unexpected Pedestrian Behavior
Children and Elderly : Children and elderly pedestrians might not always follow expected patterns, so be extra cautious around them. Distracted Pedestrians : Be aware that some pedestrians might be distracted by their phones or other devices.
Observe Traffic Laws and Signs
Stop Signs and Traffic Lights : Always come to a complete stop at stop signs and obey traffic lights. Yield Signs : Yield to pedestrians when required by signs and road markings.
Use Designated Parking Areas
Avoid Illegal Parking : Do not park in crosswalks, on sidewalks, or blocking pedestrian pathways. Check for Pedestrians When Reversing : Always look out for pedestrians when backing out of parking spaces.
Practice Defensive Driving
Anticipate Pedestrian Movement : Always be ready for unexpected pedestrian movements. Maintain Safe Distance : Keep a safe distance from the car in front of you to ensure you have ample time to stop if needed.
Promote and Support Pedestrian Safety Initiatives
Community Involvement : Support local initiatives aimed at improving pedestrian infrastructure and safety. Advocate for Improvements : Advocate for better crosswalks, pedestrian signals, and other safety measures in your community.
Summary
? How can pedestrians stay safe around vehicles?
Be Visible
Wear Bright or Reflective Clothing : Especially at night or in low-light conditions, wear clothing that makes you more visible to drivers. Use Flashlights or Reflective Gear : Carry a flashlight or wear reflective accessories to increase visibility.
Stay Alert and Avoid Distractions
Avoid Using Phones : Keep your attention on the road and avoid distractions such as texting or listening to music with headphones. Be Aware of Your Surroundings : Stay alert to the movements of vehicles and other pedestrians.
Follow Pedestrian Signals and Signs
Obey Traffic Signals : Cross streets only at designated crosswalks and when the pedestrian signal indicates it's safe. Use Crosswalks : Always cross at marked crosswalks or intersections where drivers expect pedestrians.
Make Eye Contact with Drivers
Ensure Visibility : Before crossing the street, make eye contact with drivers to ensure they see you and are stopping.
Use Sidewalks and Paths
Walk on Sidewalks : Whenever available, use sidewalks instead of walking on the road. Walk Facing Traffic : If there are no sidewalks, walk on the side of the road facing oncoming traffic to see approaching vehicles.
Be Cautious at Intersections
Look Both Ways : Always look left, right, and left again before crossing, even if you have the right of way. Watch for Turning Vehicles : Be aware of vehicles making turns, especially at intersections.
Cross Quickly and Safely
Don’t Dawdle : Cross streets promptly and avoid lingering in the roadway. Use Pedestrian Islands : If available, use pedestrian islands or refuge areas to cross busy streets in stages.
Avoid Jaywalking
Cross at Designated Points : Cross streets at designated crosswalks or intersections, where drivers expect pedestrians.
Be Extra Cautious in Poor Visibility
Increase Visibility : Use extra caution and make yourself as visible as possible in fog, rain, or snow. Slow Down and Observe : Take your time and ensure drivers see you before you cross.
Be Aware of Blind Spots
Avoid Walking Behind Vehicles : Be especially cautious around large vehicles like trucks and buses, which have significant blind spots. Stay Out of Blind Spots : When near vehicles, try to stay in areas where you are visible to the driver.
Be Extra Careful Around Driveways and Parking Lots
Watch for Reversing Vehicles : Pay attention to vehicles reversing out of driveways or parking spaces. Be Aware of Slow-Moving Vehicles : In parking lots, vehicles might be moving slowly but can still pose a risk.
Teach Children About Pedestrian Safety
Supervise Young Children : Always hold hands with young children near traffic. Teach Safe Crossing : Educate children on how to cross streets safely and the importance of following traffic signals.
Plan Your Route
Use Pedestrian-Friendly Routes : Choose routes that have sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian signals. Avoid High-Traffic Areas : Whenever possible, avoid walking in high-traffic areas where pedestrian infrastructure is inadequate.
Summary
? What are the rules for pedestrians at traffic signals?
Pedestrian Signals
Begin Crossing : Pedestrians can start crossing the street when the "Walk" signal is illuminated. Stay Alert : While crossing, remain aware of your surroundings and look out for turning vehicles.
Do Not Start Crossing : If you have not yet started crossing, do not begin. Finish Crossing : If you are already in the crosswalk, continue to the other side quickly and safely.
Do Not Cross : Pedestrians should not start to cross the street when the "Don't Walk" signal is steady.
Traffic Signal Lights
Do Not Cross : Pedestrians should not cross the street when the signal light for vehicles is red unless there is a separate pedestrian signal indicating it is safe to do so.
Wait for Pedestrian Signal : Pedestrians should only cross when the pedestrian signal is green or when there is no pedestrian signal, and it is clear and safe to do so. Look for Turning Vehicles : Even if the light is green, pedestrians should be cautious of vehicles turning across their path.
Do Not Start Crossing : If you are already crossing, continue to the other side quickly and safely. Do not start crossing if the signal changes to yellow.
Countdown Timers
Use Timers Wisely : Some crosswalks have countdown timers that show how many seconds remain to cross. Pedestrians should only start crossing if they can safely reach the other side before the timer runs out.
Push Button Pedestrian Signals
Activate the Signal : If a pedestrian push button is available, press it to activate the pedestrian signal. Wait for the "Walk" signal before crossing.
Unsignalized Intersections
Yield to Vehicles : At intersections without signals, pedestrians should yield to vehicles and only cross when it is safe to do so. Use Caution : Always use extra caution and make eye contact with drivers to ensure they see you.
Mid-Block Crosswalks
Wait for the Signal : At mid-block crosswalks with pedestrian signals, wait for the "Walk" signal before crossing. Look Both Ways : Always look left, right, and left again before crossing, even if the signal indicates it is safe.
General Safety Tips
Make Eye Contact : Always try to make eye contact with drivers before crossing to ensure they see you. Avoid Distractions : Do not use phones or other distractions while crossing the street. Cross Quickly and Safely : Do not linger in the crosswalk. Cross at a steady pace and get to the other side as quickly as possible.