
Medical
? Questions:
⮟ What are the long-term consequences of drug-impaired driving? ⮟ Can I be charged with impaired driving even if my drug use is legal? ⮟ Can prescription or over-the-counter drugs affect driving? ⮟ Is driving under the influence of marijuana as dangerous as alcohol? ⮟ Can combining drugs and alcohol increase driving impairment?

Medical Conditions ( Inspira Health ):
Epilepsy. Stroke or other neurological condition. Loss of consciousness. Vertigo. Diabetes. Vision loss. Heart conditions. Sleep disorders.

Medication ( FDA ):
Sleepiness or drowsiness. Blurred vision. Dizziness. Retarded movement. Fainting. Inability to focus or pay attention. Nausea. Excitability. Street drugs, e.g., Marijuana.
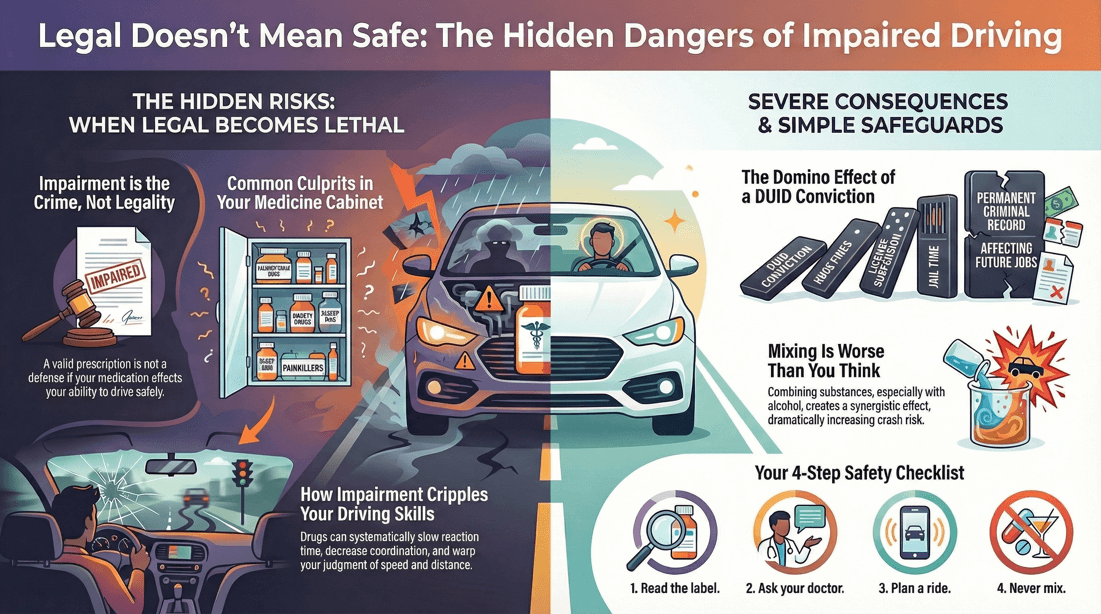
Opioid pain relievers. Prescription drugs for anxiety (for example, benzodiazepines) Anti-seizure drugs (antiepileptic drugs). Antipsychotic drugs. Some antidepressants. Products containing codeine. Some cold remedies and allergy products, such as antihistamines (both prescription and Over the Counter). Sleeping medication, even the following day. Muscle relaxants. Medicines that treat or control symptoms of diarrhea. Medicines that treat or prevent symptoms of motion sickness. Diet pills, “stay awake” drugs, and other medications with stimulants (e.g., caffeine, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine). Allergy medicines. Cannabidiol (CBD) products.

? Is driving under the influence of drugs illegal?
Legal Prohibitions
Most countries and states have laws that specifically prohibit driving under the influence of drugs (DUID). These laws typically cover a broad range of substances, including illegal drugs like marijuana, cocaine, and methamphetamine, as well as prescription medications and over-the-counter drugs that can impair driving.
Impairment-Based Laws
In many jurisdictions, it's illegal to drive if you are impaired by any substance that affects your ability to operate a vehicle safely. This includes not only illegal drugs but also legal medications if they cause drowsiness, dizziness, or other impairments.
Zero Tolerance for Certain Drugs
Some areas have zero-tolerance laws, which mean that any detectable amount of certain illegal drugs in your system while driving can lead to a DUI charge, regardless of whether you appear impaired.
Field Sobriety and Drug Tests
Law enforcement officers may use field sobriety tests, breathalyzers, or drug tests (like blood or urine tests) to determine if a driver is under the influence of drugs. Refusing to take these tests can result in penalties, including license suspension.
Prescription Drugs
Even if a drug is legally prescribed to you, it is illegal to drive if it impairs your ability to do so safely. Prescription medications with warnings about operating machinery or driving should be taken seriously.
Marijuana Laws
With the legalization of marijuana in some places, it's important to note that driving under the influence of marijuana is still illegal. Like alcohol, marijuana can impair reaction times, coordination, and judgment.
Consequences of DUID
Penalties for driving under the influence of drugs can include fines, license suspension, mandatory drug education or treatment programs, and even jail time. These penalties often become more severe with repeat offenses or if the impaired driving results in an accident or injury.
Combined Influence
Driving under the influence of a combination of drugs and alcohol can result in more severe charges and penalties, as the combined effects can significantly impair driving ability.
? What are the penalties for drug-impaired driving?
Fines
First Offense : Fines for a first-time offense can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the jurisdiction and circumstances of the offense. Subsequent Offenses : For repeat offenders, fines increase significantly and can reach several thousand dollars.
License Suspension or Revocation
First Offense : Drug-impaired drivers often face license suspension for a period of several months to a year, depending on local laws. Repeat Offenders : Subsequent offenses can lead to longer suspensions, and in some cases, permanent revocation of the driver’s license.
Jail or Prison Time
First Offense : Some jurisdictions impose short jail sentences, often ranging from a few days to several months, for first-time drug-impaired driving offenses. Repeat Offenses or Aggravating Circumstances : Penalties can escalate to several years in prison, especially if the offense involves injury, death, or repeated offenses.
Probation
In some cases, a driver may be sentenced to probation instead of, or in addition to, jail time. This typically involves regular check-ins with a probation officer and adherence to strict rules, such as refraining from drug use and attending drug treatment programs.
Mandatory Drug Education and Treatment Programs
Offenders are often required to complete a drug education or rehabilitation program as part of their sentence. These programs are designed to address substance abuse issues and reduce the likelihood of reoffending.
Ignition Interlock Devices
Some jurisdictions may require the installation of an ignition interlock device (IID) on your vehicle, even for drug-impaired driving. While these devices are more commonly associated with alcohol DUIs, some courts may impose this requirement to prevent further impaired driving.
Increased Insurance Premiums
Drug-impaired driving convictions usually result in significantly higher car insurance premiums, as insurers view convicted drivers as high-risk. In some cases, insurance companies may even refuse to cover the driver.
Community Service
Courts may impose community service hours as part of the penalty, especially for first-time offenders or in cases where the driver caused no harm but was still impaired.
Vehicle Impoundment or Forfeiture
In some cases, particularly with repeat offenders, the court may order the impoundment or forfeiture of the vehicle used during the offense.
Criminal Record
A conviction for drug-impaired driving often results in a permanent criminal record, which can have long-term consequences, including difficulty finding employment, housing, or qualifying for loans.
Civil Liability
If the impaired driving results in an accident, injury, or death, the driver may face civil lawsuits. Victims or their families can sue for damages, including medical bills, lost wages, pain and suffering, and more.
Enhanced Penalties for Aggravating Factors
Causing Injury or Death : If the drug-impaired driving leads to an accident that causes injury or death, the driver may face enhanced penalties, including longer prison sentences and higher fines. Driving with Minors : Driving under the influence of drugs with a child in the vehicle can lead to additional charges, such as child endangerment, which carry their own set of penalties.
Permanent Driving Record
A drug-impaired driving conviction is usually noted on your driving record, which can lead to long-term consequences even after the legal penalties have been served.
Conclusion
? What are the long-term consequences of drug-impaired driving?
Criminal Record
Permanent Record : A conviction for drug-impaired driving usually results in a permanent criminal record, which can follow you for the rest of your life. This can affect your reputation, personal relationships, and opportunities in many areas of life. Difficulty Expunging : In many jurisdictions, it can be difficult, if not impossible, to expunge or remove a DUI conviction from your record, making it a lasting part of your criminal history.
Employment Challenges
Job Applications : Many employers conduct background checks, and a conviction for drug-impaired driving can limit your employment prospects, particularly in fields that require driving or have strict policies regarding criminal behavior. Professional Licenses : A conviction may affect your ability to obtain or maintain professional licenses (e.g., medical, legal, commercial driving licenses), especially in industries that require high levels of trust and responsibility. Job Loss : If you rely on driving for work (e.g., delivery, trucking, sales), a suspended or revoked license could lead to job loss or difficulty finding similar employment.
Insurance Consequences
Higher Premiums : A drug-impaired driving conviction typically leads to skyrocketing car insurance premiums. Insurers consider you a high-risk driver, and you may be required to carry high-risk insurance, such as SR-22 insurance. Loss of Coverage : In some cases, your insurance company may cancel your policy entirely, making it difficult to find affordable coverage.
Loss of Driving Privileges
License Suspension or Revocation : A conviction for drug-impaired driving can lead to the suspension or revocation of your driver’s license. In some cases, you may have to go through a lengthy process to reinstate your driving privileges. Impact on Daily Life : Losing your license can significantly affect your ability to carry out daily tasks, such as commuting to work, running errands, or taking care of family responsibilities, potentially leading to further complications in your personal and professional life.
Financial Burden
Legal Fees and Fines : Even after the initial court case is over, the costs associated with drug-impaired driving can add up. This includes legal fees, fines, and the cost of mandatory drug treatment programs. Long-Term Financial Strain : Increased insurance premiums, job loss, and potential civil lawsuits can place a long-term strain on your finances, affecting your ability to save, invest, or pay off debts.
Civil Liability
Lawsuits : If your drug-impaired driving results in an accident, injury, or death, you may face civil lawsuits from victims or their families. You could be liable for significant damages, including medical bills, lost wages, pain and suffering, and more. Loss of Assets : Civil judgments can lead to garnishment of wages, liens on property, or even the loss of personal assets to cover the costs of damages awarded in a lawsuit.
Reputation and Social Stigma
Social Consequences : A conviction for drug-impaired driving can harm your reputation in your community and among friends and family. You may face social stigma, judgment, or exclusion from social and professional circles. Impact on Relationships : The strain caused by legal issues, financial burdens, and the stigma of a conviction can negatively affect personal relationships, including with family members, friends, and romantic partners.
Restricted Travel
International Travel : A drug-impaired driving conviction can limit your ability to travel internationally. Some countries may deny entry to individuals with a criminal record, making it difficult to travel for work or leisure. Visa and Residency Issues : For non-citizens, a drug-impaired driving conviction can affect visa renewals, residency applications, or even lead to deportation, depending on the severity of the offense.
Health and Substance Abuse Issues
Addiction : A conviction for drug-impaired driving often points to an underlying substance abuse issue. Left unaddressed, drug addiction can continue to affect your life long after the legal penalties are over. Mandatory Treatment : You may be required to complete a drug rehabilitation program as part of your sentence, which, while beneficial, can be time-consuming and expensive.
Impact on Family and Dependents
Family Strain : The financial and emotional strain of a drug-impaired driving conviction can significantly affect your family, particularly if you lose your job or face jail time. Child Custody Issues : If your conviction is serious, it may also affect your ability to gain or maintain custody of your children, as courts take impaired driving offenses seriously in custody decisions.
Conclusion
? Can I be charged with impaired driving even if my drug use is legal?
Key Points to Consider:
Impairment, Not Legality : The focus of impaired driving laws is on your ability to drive safely, not whether the drug is legal. Even if you have a valid prescription or are using a drug that is legal in your area, you can still be considered impaired if the substance affects your motor skills, reaction time, judgment, or coordination. Prescription and Over-the-Counter Medications : Many prescription and over-the-counter medications, such as painkillers, sedatives, antihistamines, and sleep aids, can impair your ability to drive. These drugs often come with warnings about operating heavy machinery (including cars) due to their potential to cause drowsiness, dizziness, or slow reaction times. Medical Marijuana : Even in places where marijuana is legal for medical or recreational use, driving while under its influence is still illegal. Marijuana can impair judgment, coordination, and reaction time, all of which are critical for safe driving. Zero-Tolerance Policies : Some jurisdictions have zero-tolerance policies for certain drugs, meaning that any detectable amount of the substance in your system while driving could result in charges, even if you do not feel impaired. Drug Recognition Experts (DREs) : Law enforcement officers trained as Drug Recognition Experts may assess your impairment based on behavioral signs, field sobriety tests, and chemical testing. If they determine you are impaired, you can be charged with a DUI, regardless of whether the drug is legal or prescribed.
Conclusion
? How do police test for drug impairment?
Observation of Behavior
Initial Traffic Stop : When an officer suspects a driver may be impaired, they will first look for signs of intoxication, such as erratic driving, speeding, swerving, or failing to obey traffic laws. Interaction with Driver : Once the driver is stopped, the officer will observe their behavior, looking for physical signs of drug impairment, such as bloodshot eyes, slurred speech, lack of coordination, unusual behavior, or the smell of drugs.
Field Sobriety Tests (FSTs)
Standardized Tests : Officers typically use a series of standardized field sobriety tests designed to assess coordination, balance, and mental focus. These tests are similar to those used for alcohol impairment but can indicate drug impairment as well.\ Horizontal Gaze Nystagmus (HGN) Test : The officer observes the driver’s eyes as they follow a moving object, looking for involuntary jerking of the eyes, which can indicate impairment. Walk-and-Turn Test : The driver is asked to walk heel-to-toe along a straight line, turn around, and walk back. This test checks balance, coordination, and the ability to follow instructions. One-Leg Stand Test : The driver is asked to stand on one leg while counting aloud. This test assesses balance, coordination, and attention. Non-Standardized Tests : In some cases, officers may use other observational techniques, such as asking the driver to recite the alphabet backward or perform simple mental tasks.
Drug Recognition Expert (DRE) Evaluation
DRE Protocol : If the officer believes the driver is impaired by drugs, they may call in a Drug Recognition Expert (DRE). DREs are specially trained law enforcement officers who can identify drug impairment through a 12-step evaluation process. This evaluation includes: Breath Alcohol Test : To rule out alcohol as the cause of impairment. Interview with the Arresting Officer : To gather details about the driver’s behavior and driving. Preliminary Examination : To assess the driver’s general condition, including checking for signs of injury or medical conditions that might mimic impairment. Eye Examinations : The DRE looks for signs of impairment in the eyes, such as pupil size, reaction to light, and signs of nystagmus (involuntary jerking). Divided Attention Tests : Similar to the FSTs, these tests assess the driver’s ability to divide their attention between physical and mental tasks. Vital Signs Check : The DRE may measure the driver’s pulse, blood pressure, and temperature, which can be affected by drug use. Dark Room Examinations : The DRE assesses the driver’s pupils under different lighting conditions, which can reveal the effects of drugs that affect pupil size (e.g., opioids or stimulants). Muscle Tone Evaluation : Certain drugs can cause muscles to be unusually relaxed or rigid. Toxicology : The DRE may request a blood, urine, or saliva test to confirm the presence of drugs.
Chemical Tests
Blood Tests : Blood tests are the most accurate method for detecting drugs in a driver’s system. If the officer suspects drug impairment, they may take the driver to a medical facility for a blood draw. The blood sample is then analyzed for the presence of drugs, including illegal substances, prescription medications, and over-the-counter drugs. Urine Tests : Urine tests are commonly used to detect drugs, although they are less accurate than blood tests. They can indicate recent drug use but may not always correlate with current impairment, as some drugs stay in the system for days or weeks. Saliva Tests : Saliva (or oral fluid) tests are increasingly being used by law enforcement to detect drugs. These tests are quicker and less invasive than blood tests and can detect recent drug use within a few hours. Breath Tests for Drugs : While breath tests are primarily used for alcohol detection, new technologies are being developed to test for certain drugs via breath analysis. However, these are still in the experimental phase and not widely used.
Mobile Drug Testing Units
Roadside Drug Testing Kits : Some jurisdictions use portable drug testing kits at the roadside to screen drivers for drug use. These devices, often saliva-based, can provide rapid results for drugs like marijuana, cocaine, methamphetamines, and opioids. Preliminary Drug Testing Devices : These devices allow officers to test for drugs at the scene, though positive results typically require confirmation through more thorough laboratory testing.
Implied Consent Laws
Legal Requirement to Submit : In many places, drivers are required by law to submit to chemical testing (blood, urine, saliva) if suspected of impaired driving. Refusing these tests can result in additional penalties, such as license suspension or fines.
Conclusion
? How do drugs impair driving?
Slowed Reaction Time
Effect : Drugs, particularly depressants like opioids, alcohol, and some prescription medications, can slow your reaction time. This means it takes longer to respond to unexpected events, such as a car stopping suddenly in front of you or a pedestrian stepping into the road.
Impaired Judgment and Decision-Making
Effect : Drugs can impair your ability to make good decisions while driving. This includes judging distances, assessing road conditions, and evaluating the actions of other drivers. Stimulants, hallucinogens, and marijuana are known to impair judgment, leading to risky driving behaviors.
Decreased Coordination
Effect : Driving requires fine motor coordination to steer, brake, accelerate, and shift gears. Drugs such as alcohol, sedatives, and certain prescription medications can affect your motor coordination, making it difficult to perform these tasks effectively.
Drowsiness and Fatigue
Effect : Many drugs, especially those with sedative effects (like sleeping pills, antihistamines, or tranquilizers), can cause drowsiness, which impairs your alertness and ability to stay awake while driving. This increases the risk of accidents due to falling asleep at the wheel or losing focus.
Distorted Perception
Effect : Certain drugs, such as marijuana, hallucinogens (e.g., LSD or psilocybin), and even some prescription medications, can distort your perception of time, space, and speed. This can lead to difficulty judging distances, staying in your lane, or determining the speed of other vehicles.
Reduced Attention and Focus
Effect : Drugs like marijuana, opioids, and alcohol can reduce your ability to focus on multiple tasks at once, such as watching the road, monitoring your speed, and checking your mirrors. Distracted driving is a major cause of accidents, and drug use exacerbates this risk.
Impaired Vision
Effect : Many drugs can cause blurred vision, altered depth perception, or sensitivity to light. For example, alcohol and stimulants can impair vision, making it difficult to see clearly or adjust to changing light conditions (e.g., bright sunlight or night driving).
Memory Impairment
Effect : Certain drugs, particularly sedatives, tranquilizers, and alcohol, can impair short-term memory, making it difficult to remember road signs, directions, or the flow of traffic.
Heightened Emotional Responses
Effect : Drugs like stimulants (e.g., cocaine or methamphetamine) or hallucinogens can lead to heightened emotions, including anxiety, aggression, or paranoia. This can cause erratic driving, road rage, or overreactions to normal driving situations.
Loss of Consciousness
Effect : Some drugs, particularly in high doses, can cause you to lose consciousness or become unresponsive. This is extremely dangerous while driving, as it can lead to accidents, collisions, or veering off the road.
Types of Drugs and Their Effects:
Depressants (Alcohol, Opioids, Benzodiazepines) : Slow reaction time, impair coordination, cause drowsiness, and reduce focus. Stimulants (Cocaine, Amphetamines) : Increase risk-taking, cause overconfidence, impair judgment, and can lead to aggressive driving. Marijuana : Slows reaction time, impairs judgment, and distorts perception of time and space. Hallucinogens (LSD, Psilocybin) : Distort reality, impair perception, and affect mental clarity. Prescription Medications : Many, such as painkillers, sedatives, and muscle relaxants, can impair driving similarly to illegal drugs.
Conclusion
? What types of drugs impair driving?
Illegal Drugs
Marijuana (Cannabis): Impairs motor coordination, reaction time, and judgment. It can make it difficult to stay in your lane or respond to unexpected events on the road. Cocaine: Causes erratic driving behavior, aggressiveness, and impaired judgment. It can lead to overconfidence and risky driving. Methamphetamine: Results in aggressive driving, overconfidence, and erratic behavior. It also causes extreme fatigue once the drug wears off, which can be dangerous. Heroin: Slows down brain function, impairs reaction times, and reduces the ability to think clearly or make quick decisions.
Prescription Medications
Opioids (e.g., Oxycodone, Hydrocodone): Cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired cognitive function, making it dangerous to drive. Benzodiazepines (e.g., Valium, Xanax): Used to treat anxiety or sleep disorders, these drugs can cause significant drowsiness, slower reaction times, and impaired coordination. Antidepressants: Some antidepressants can cause drowsiness, blurred vision, and dizziness, affecting driving abilities. Sleep Aids (e.g., Ambien, Lunesta): Even if taken the night before, these medications can cause drowsiness and impair cognitive function the next day. Muscle Relaxants: Drugs like cyclobenzaprine can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired motor coordination.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Antihistamines (e.g., Diphenhydramine/Benadryl): Used for allergies and colds, these can cause drowsiness and slower reaction times. Cold and Flu Medications: Many contain ingredients like decongestants or antihistamines that can impair driving by causing drowsiness or dizziness. Motion Sickness Medications (e.g., Dimenhydrinate/Dramamine): Can cause drowsiness and impaired coordination.
Stimulants
ADHD Medications (e.g., Adderall, Ritalin): While these can improve focus, they can also lead to anxiety, restlessness, and impaired judgment if misused or taken in high doses. Caffeine: While not illegal, excessive consumption of caffeine can cause jitteriness, anxiety, and impaired coordination.
Psychedelic Drugs
LSD, Psilocybin (Mushrooms), and MDMA (Ecstasy): These drugs can cause hallucinations, impaired perception of time and space, and poor judgment, making driving extremely dangerous.
Inhalants
Nitrous Oxide, Glue, and Paint Thinners: Inhalants can cause dizziness, euphoria, and impaired motor function, leading to poor driving performance.
Combination of Drugs
Polydrug Use: Taking multiple drugs simultaneously, such as combining alcohol with prescription medications or illegal drugs, can drastically increase impairment and the risk of an accident.
Key Points to Remember:
Even if a drug is legal, prescribed, or over-the-counter, it can still impair your driving ability. It's crucial to read labels and consult with a healthcare provider if you're unsure about the effects of a medication on your ability to drive. Never drive if you feel drowsy, dizzy, or impaired in any way after taking a drug.
? Can prescription or over-the-counter drugs affect driving?
Common Effects of Prescription and OTC Drugs on Driving:
Drowsiness : Many medications, especially those for allergies, colds, anxiety, or sleep disorders, can cause drowsiness or make you feel unusually tired. This can slow your reaction times and impair your ability to make quick decisions on the road. Dizziness and Lightheadedness : Some drugs can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, which may affect your balance, coordination, and perception, making it difficult to maintain control of your vehicle. Blurred Vision : Certain medications can cause blurred vision, making it hard to see clearly and react to road signs, signals, and other vehicles. Impaired Judgment and Focus : Some drugs can alter your mental state, affecting your ability to concentrate, make sound decisions, and react appropriately to traffic situations. Slower Reaction Time : Drugs that sedate or relax your muscles can also slow your reaction time, making it harder to respond quickly to sudden changes, such as a pedestrian crossing or a car braking suddenly in front of you. Nausea : Some medications can cause nausea or stomach discomfort, which can be distracting and uncomfortable, leading to a reduced focus on driving. Increased Risk of Accidents : Combining multiple medications or mixing them with alcohol can intensify these side effects, greatly increasing the risk of accidents.
Examples of Medications that Can Impair Driving:
Antihistamines (e.g., Diphenhydramine/Benadryl): Commonly used for allergies, these can cause significant drowsiness. Benzodiazepines (e.g., Valium, Xanax): Prescribed for anxiety or sleep disorders, these can slow reaction time and impair coordination. Opioids (e.g., Oxycodone, Hydrocodone): Pain medications that can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion. Sleep Aids (e.g., Ambien, Lunesta): Can cause next-day drowsiness and impaired cognitive function. Muscle Relaxants (e.g., Cyclobenzaprine): Can lead to drowsiness and impaired motor skills. Antidepressants : Some can cause drowsiness, blurred vision, and dizziness. Cold and Flu Medications : Many contain sedating ingredients that can affect alertness and coordination.
What You Should Do:
Read Labels : Always read the labels on your medications to check for warnings about drowsiness or other side effects that might impair driving. Consult Your Doctor or Pharmacist : If you're unsure about how a medication might affect your driving, consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for advice. Avoid Mixing Medications : Be cautious about taking multiple medications, especially if they have similar side effects, as this can intensify impairment. Avoid Driving If Impaired : If you feel drowsy, dizzy, or otherwise impaired, it’s best to avoid driving altogether. Consider alternative transportation options, such as a taxi, ride-sharing service, or public transport.
? How long do drugs stay in your system and affect driving?
Alcohol
Detection Window : 12-24 hours in the bloodstream, longer in urine and hair. Impact on Driving : Alcohol can impair driving for several hours after consumption, even if you feel sober. Reaction times, judgment, and coordination can be significantly affected.
Cannabis (Marijuana)
Detection Window : Up to 30 days in urine, a few days in blood, and several hours in saliva. Impact on Driving : The psychoactive effects, like impaired judgment and slowed reaction time, can last from 4-6 hours, though residual effects may linger for up to 24 hours.
Prescription Opioids
Detection Window : 2-4 days in urine, up to 24 hours in blood. Impact on Driving : Opioids can impair driving for 4-6 hours after ingestion, with side effects like drowsiness and dizziness potentially lasting longer.
Benzodiazepines (e.g., Valium, Xanax)
Detection Window : 3-6 weeks in urine, up to 48 hours in blood. Impact on Driving : These can impair cognitive and motor functions for 6-12 hours, though effects like drowsiness may persist for up to 24 hours.
Stimulants (e.g., Cocaine, Amphetamines)
Detection Window : 2-3 days in urine, up to 48 hours in blood. Impact on Driving : Stimulants can cause overconfidence, erratic behavior, and impaired judgment. Effects last 1-2 hours, but residual effects may persist longer.
Over-the-Counter Medications (e.g., Antihistamines)
Detection Window : Typically 1-2 days in urine. Impact on Driving : Effects like drowsiness and blurred vision can last for 4-6 hours, depending on the medication and dosage.
Sleep Aids (e.g., Ambien, Lunesta)
Detection Window : 1-2 days in urine. Impact on Driving : These can impair driving for 8 hours or more, with some users experiencing residual drowsiness or confusion the next day.
Muscle Relaxants
Detection Window : 1-3 days in urine. Impact on Driving : Effects can last 4-6 hours, with lingering drowsiness potentially affecting driving ability for longer.
Antidepressants
Detection Window : Varies widely (some up to several weeks in urine). Impact on Driving : Some antidepressants can cause drowsiness, dizziness, or blurred vision, with effects that might impair driving for several hours after taking the medication.
Factors Affecting How Long Drugs Stay in Your System:
Metabolism : Faster metabolisms process drugs more quickly. Body Fat : Some drugs, especially those stored in fat cells, may linger longer in individuals with higher body fat. Age : Older adults may process drugs more slowly, leading to longer periods of impairment. Liver and Kidney Function : Impaired liver or kidney function can slow drug metabolism, extending the duration of effects. Frequency of Use : Regular use of a drug can lead to accumulation in the system, prolonging the time it affects driving.
Summary
? How can I avoid driving while impaired by drugs?
Know the Effects of Your Medications
Read Labels : Always read the labels of prescription and over-the-counter medications to understand potential side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, or impaired judgment. Ask Your Doctor or Pharmacist : If you're unsure about how a medication might affect your ability to drive, consult with a healthcare professional.
Plan Ahead
Use Public Transportation : If you know you’ll be taking medication or using substances that might impair you, plan to use public transportation, rideshare services, or have someone else drive. Stay Home : If possible, avoid going out if you’re under the influence of any substance that could impair your driving.
Avoid Mixing Substances
Be Cautious with Alcohol and Drugs : Combining alcohol with prescription, over-the-counter, or recreational drugs can significantly increase impairment. Follow Guidelines : Adhere strictly to prescribed dosages and avoid any unapproved combinations of medications.
Monitor Your Reaction
Test at Home : If you’re starting a new medication, test your reaction at home before driving. Pay attention to how it affects your alertness and coordination. Time Your Doses : Take medications well in advance of when you need to drive, allowing time for any side effects to subside.
Use Alternative Transportation
Designated Driver : Arrange for a sober friend or family member to drive if you need to travel. Rideshare Services : Use Uber, Lyft, or other rideshare options to avoid driving yourself. Public Transit : Opt for buses, trains, or other forms of public transportation when impaired.
Set Reminders
Medication Reminders : Set alarms or use apps to remind you when you’re due to take medication, helping you manage timing and avoid driving during peak side effect periods. Note Your Driving Schedule : Align your driving schedule with times when you know you’ll be unimpaired.
Stay Informed
Know Your Limits : Understand how your body reacts to certain substances and respect those limits. Stay Updated on Laws : Be aware of local laws regarding drug use and driving, as penalties for impaired driving can be severe.
Have a Backup Plan
Emergency Contacts : Keep a list of contacts you can call if you find yourself in a situation where you’ve taken something that might impair your driving. Reschedule Plans : If you find yourself unexpectedly impaired, be willing to change your plans or delay your trip.
Monitor Your Health
Regular Check-ups : Regularly visit your healthcare provider to discuss how your medications and overall health might affect your driving. Adjustments as Needed : If you notice new side effects or increased sensitivity to a medication, talk to your doctor about possible adjustments.
Educate Yourself and Others
Spread Awareness : Share information about the dangers of drug-impaired driving with friends and family to help everyone stay safe. Stay Updated on Research : Keep up with new studies and information regarding drug interactions and their effects on driving.
? Can I use medical marijuana and drive?
Legal Considerations
State Laws : In many places, even if medical marijuana is legal, driving under the influence of any drug, including marijuana, is illegal. This includes states where marijuana is legal for both medical and recreational use. Impairment Laws : Most states have laws that prohibit driving while impaired, regardless of whether the impairment is caused by alcohol, prescription drugs, or medical marijuana.
Effect on Driving Ability
Impairment Risks : Medical marijuana can impair your motor skills, reaction time, and judgment, which can make driving dangerous. Even if you feel okay, your ability to drive safely may be compromised. THC Levels : Some states have specific limits on the amount of THC (the psychoactive component of marijuana) that can be in your blood while driving. If you exceed these levels, you can be charged with driving under the influence (DUI).
Medical Marijuana and DUI Charges
Zero Tolerance : Some jurisdictions have zero-tolerance policies for driving with any detectable level of THC in your system. DUI Penalties : If you're caught driving under the influence of marijuana, you may face DUI charges, which can result in fines, license suspension, and even jail time, depending on the severity of the offense and your driving record.
Safe Practices
Know Your Limits : Understand how medical marijuana affects you. If you feel any impairment, do not drive. Wait It Out : The effects of marijuana can last several hours. If you’ve consumed medical marijuana, wait until you are no longer feeling its effects before getting behind the wheel. Use Alternative Transportation : If you need to use medical marijuana and are not sure how it will affect your driving, consider using public transportation, rideshares, or getting a ride from someone else.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Discuss with Your Doctor : If you're prescribed medical marijuana, talk to your doctor about its potential impact on your ability to drive. Follow Recommendations : Adhere to any advice your healthcare provider gives you regarding the timing of doses and driving.
Employer and Insurance Implications
Workplace Policies : Some employers have strict policies about drug use, including medical marijuana, especially for jobs that require driving. Insurance Coverage : A DUI for driving under the influence of marijuana can affect your insurance rates and coverage.
Know the Science
Understanding Impairment : Different strains of marijuana can have varying effects. Some may impair you more than others, even if they're medically prescribed. Effects of Combining Substances : Using medical marijuana along with other medications can increase impairment. Be aware of how these interactions might affect your driving.
? Is driving under the influence of marijuana as dangerous as alcohol?
Impairment Effects
Alcohol : Alcohol significantly impairs cognitive functions, motor skills, reaction time, and judgment. It increases the likelihood of risky behaviors, such as speeding and aggressive driving. Marijuana : Marijuana primarily affects motor coordination, reaction time, and attention. It can make tasks that require quick decision-making, like driving, more difficult. However, marijuana users often compensate by driving more slowly and cautiously, though this doesn't eliminate the risk.
Risk of Accidents
Alcohol : Driving under the influence of alcohol is strongly linked to an increased risk of accidents, particularly fatal ones. Alcohol-related crashes are a leading cause of death on the roads. Marijuana : Studies show that marijuana use before driving is associated with an increased risk of accidents, but the risk is generally lower than that for alcohol. However, the combination of marijuana and alcohol greatly increases the likelihood of a crash.
Legal Consequences
Alcohol : Laws regarding driving under the influence of alcohol are strict, with legal blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limits in place. Exceeding these limits can result in DUI charges, fines, license suspension, and even imprisonment. Marijuana : Many states and countries have set limits on THC levels in the bloodstream, similar to alcohol. Driving with THC levels above the legal limit can lead to DUI charges, although enforcement can be more complicated due to variations in how THC affects different individuals.
Public Perception
Alcohol : The dangers of driving under the influence of alcohol are widely recognized and heavily emphasized in public safety campaigns. Marijuana : While awareness of the dangers of driving under the influence of marijuana is increasing, some people mistakenly believe it's safer to drive after using marijuana compared to alcohol.
Combined Use
Alcohol and Marijuana : Using both substances together has a compounded effect on impairment, making it much more dangerous to drive. The combination of alcohol and marijuana increases the risk of an accident significantly more than using either substance alone.
Research and Data
Alcohol : Decades of research have established a clear connection between alcohol consumption and impaired driving. Statistics show a high percentage of road fatalities involve alcohol. Marijuana : Research on marijuana and driving is more recent and still developing. While there is evidence of impairment, the exact level of risk is still being studied, particularly because marijuana affects individuals differently.
Conclusion
? Can combining drugs and alcohol increase driving impairment?
Synergistic Effects
When drugs and alcohol are combined, they often interact in a way that amplifies their effects. For example, alcohol is a depressant, and when combined with other depressants like sedatives or opioids, it can severely impair motor skills, reaction time, and cognitive functions. Even when alcohol is combined with stimulants like cocaine or amphetamines, the mixed effects can lead to overconfidence, erratic driving behavior, and delayed reaction times, all of which increase the risk of an accident.
Impaired Judgment and Coordination
Alcohol alone impairs judgment, making it difficult for drivers to accurately assess situations and make safe decisions. Drugs such as marijuana, prescription medications, or illegal substances can also impair coordination, focus, and reaction time. When combined, these impairments are magnified, making it much harder to control the vehicle, stay in the correct lane, follow traffic signals, and respond to unexpected events on the road.
Increased Risk of Accidents
Studies have shown that drivers under the influence of both drugs and alcohol are far more likely to be involved in serious or fatal accidents compared to those under the influence of either substance alone. The combination often leads to more severe impairments in motor control, cognitive functioning, and perception, all of which are critical for safe driving.
Legal Consequences
Driving under the influence of both drugs and alcohol can result in more severe legal penalties. In many jurisdictions, the presence of multiple impairing substances can lead to higher fines, longer license suspensions, and more significant criminal charges.
Unpredictable Effects
The effects of combining drugs and alcohol can be unpredictable, especially since different drugs interact with alcohol in different ways. For example, mixing alcohol with prescription drugs like benzodiazepines can cause extreme drowsiness and loss of motor control, while combining alcohol with stimulants can lead to risky and aggressive driving behavior.
Conclusion
? How do drugs affect inexperienced drivers differently?
Lack of Experience with Vehicle Control
Inexperienced drivers may still be learning how to control a vehicle under normal conditions. The impairing effects of drugs, such as slower reaction times, impaired coordination, and reduced motor skills, can be more detrimental because these drivers haven't yet developed strong driving habits or instincts. Experienced drivers might have better-developed reflexes and muscle memory for driving, allowing them to compensate slightly for impairments (though they are still at risk).
Poor Judgment and Decision-Making
Drugs impair cognitive functions like judgment and decision-making. Inexperienced drivers are already more prone to making poor decisions due to their lack of road experience. When drugs further impair these abilities, it can lead to dangerous situations, such as misjudging the speed of other vehicles or the distance required to stop safely. Experienced drivers may have a better understanding of road situations and might anticipate potential hazards, though drug impairment still poses a significant risk.
Increased Risk of Overconfidence
Drugs, particularly stimulants or certain recreational substances, can lead to overconfidence. Inexperienced drivers may overestimate their ability to handle the vehicle under the influence, leading to risky behaviors like speeding, aggressive driving, or taking unnecessary risks. Experienced drivers might recognize the impairing effects sooner, though they can also fall victim to overconfidence.
Greater Susceptibility to Distraction
Inexperienced drivers are more easily distracted because they are still mastering the basic skills of driving. Drugs can exacerbate this by impairing focus and attention. For example, marijuana can cause a lack of concentration, while stimulants might cause jitteriness and erratic focus. Experienced drivers might be better at filtering out distractions, but drug use can still diminish their focus and awareness.
Lack of Familiarity with Drug Effects
Inexperienced drivers might not fully understand how different drugs affect their body and mind, making them more vulnerable to unexpected impairments. They might not recognize the signs of impairment or know when it’s unsafe to drive. Experienced drivers might be more aware of their limits, though they are not immune to the effects.
Reduced Ability to Handle Unexpected Situations
In emergencies or unexpected situations, inexperienced drivers may not have the quick reflexes or problem-solving skills needed to respond safely. Drugs further slow their reaction times and impair their ability to think clearly, increasing the likelihood of accidents. Experienced drivers may have better problem-solving skills, but drugs can still impair their ability to react quickly and appropriately.
Higher Risk of Legal Consequences
Inexperienced drivers might not be aware of the legal risks associated with drug-impaired driving. They could be more likely to make mistakes that attract law enforcement attention, such as erratic driving or failure to obey traffic signals. Experienced drivers might understand the legal implications better, though they can still face severe penalties if caught driving under the influence.