
DEFENSIVE > ESCAPE ROUTES > FRONT
Front
? Questions:
Gap :
2-second rule is the minimum following distance. Longer if momentum is greater such as carrying a heavy load. Not too much of a gap, otherwise others may constantly fill the gap. If a gap is filled, then slowly let the gap increase again, all the while keeping an eye on the vehicle ahead until you have a safe buffer zone. The closer the gap, the more focused, and less distracted your concentration needs to be. The worse the road surface , the longer the gap. The more restricted the view ahead, the longer the gap should be. If lane is congested, the bigger the gap should be because of the danger of a multiple car pile-up Where there is the danger from the rear , such as a driver on their cellphone , then try to control the space in front of you to be able to keep a minimum distance from the vehicle behind.
Stop :
Whenever you stop behind another vehicle, always leave enough of a gap in front that will allow you to escape to the side if necessary. As a rule of thumb, you should be able to see the bottom of the rear tires of the vehicle ahead above the hood of your vehicle.
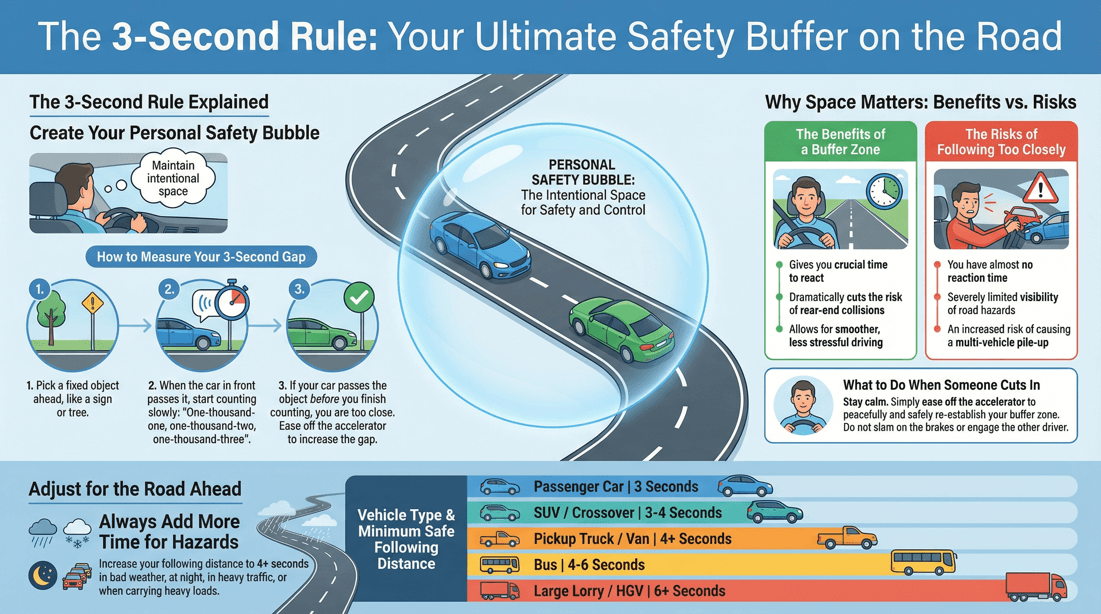
? Should the following distance be 2 or 3 seconds?
2-Second Rule
Minimum Safe Distance: The 2-second rule is often taught as the minimum safe following distance under ideal driving conditions (clear weather, good road conditions, and moderate traffic). It provides a basic buffer to react to the vehicle in front stopping suddenly. Ideal for: Urban or suburban driving where speeds are generally lower.
3-Second Rule
Increased Safety Margin: The 3-second rule gives drivers a greater margin of safety. This additional second can make a significant difference in reaction time and stopping distance, especially at higher speeds. Recommended for: Highway driving, where speeds are higher and stopping distances are longer. It is also beneficial in moderate traffic conditions.
Adjusting Following Distance
Bad Weather: Rain, snow, fog, or icy roads reduce traction and visibility, requiring a longer distance to stop safely. Night Driving: Reduced visibility at night makes it harder to see and react to road hazards. Heavy Traffic: In heavy traffic, sudden stops are more common, necessitating a greater following distance. Towing a Trailer or Heavy Load: Vehicles towing trailers or carrying heavy loads need more time to stop. Poor Road Conditions: Uneven or poorly maintained roads can affect vehicle control and stopping distance. Driver's Experience: Less experienced drivers might benefit from a greater following distance to give themselves more time to react.
Conclusion
2-Second Rule: Minimum safe distance under ideal conditions, better suited for lower speeds and urban driving. 3-Second Rule: Provides a safer margin, especially at higher speeds and on highways.
? How do I determine a 3-second following distance?
Steps to Determine a 3-Second Following Distance
Pick a Fixed Object: Choose a stationary object on the side of the road that you will pass, such as a sign, tree, or overpass. Start Counting: When the rear bumper of the vehicle in front of you passes the chosen fixed object, begin counting “One thousand one, one thousand two, one thousand three” at a normal pace. Check Your Position: If you reach the fixed object before you finish counting to three, you are following too closely and need to increase your distance. If you reach the object after counting to three, you have maintained a safe following distance.
Example
Identify a Marker: Notice a road sign ahead. Observe the Car Ahead: When the vehicle in front passes the road sign, start counting out loud: “One thousand one, one thousand two, one thousand three.” Assess Your Position: If you pass the road sign before finishing your count, slow down slightly to increase the distance. If you pass it after the count, you’re maintaining a safe distance.
Adjust for Conditions
Bad Weather: Increase your following distance to 4 or more seconds to account for reduced traction and visibility. Heavy Traffic: In stop-and-go traffic, keep a larger gap to accommodate sudden stops. Night Driving: Extend the following distance to account for reduced visibility. Towing or Heavier Loads: Increase your distance since heavier loads require more time to stop.
Benefits of the 3-Second Rule
Reaction Time: Provides adequate time to react if the vehicle in front of you suddenly stops or swerves. Stopping Distance: Ensures you have enough space to come to a complete stop without colliding with the car in front. Visibility: Maintains a clear view of the road ahead, allowing you to anticipate and respond to changes in traffic conditions.
Visual Guide
Daylight Example: When driving in daylight under normal conditions, you can easily use road markings, signs, or shadows to gauge your following distance. Night Example: At night, use the taillights of the car in front as your marker, ensuring you count the same way to maintain the distance.
Adjusting on the Fly
Speeding Up: If traffic speeds up, maintain your 3-second distance by gradually increasing your speed while continuing to use fixed objects to measure. Slowing Down: When slowing down, keep an eye on the vehicle in front and adjust your speed to maintain the 3-second buffer.
? What is a buffer zone in relation to my vehicle?
Key Aspects of a Buffer Zone:
Following Distance: The space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you. A good rule of thumb is the "three-second rule," where you should stay at least three seconds behind the vehicle ahead under normal driving conditions. Increase this distance in poor weather or heavy traffic. Side Space: The space on either side of your vehicle, which allows for safe lane changes and provides room to avoid obstacles or other vehicles suddenly moving into your lane. It's important to avoid driving in other vehicles' blind spots. Front and Rear Space: The space directly in front of and behind your vehicle. In heavy traffic, maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle ahead and being mindful of the vehicle behind you is crucial to avoid rear-end collisions. Escape Routes: The space around your vehicle that you could use to steer clear of an unexpected hazard. Maintaining a buffer zone on all sides of your vehicle ensures that you have options to maneuver in an emergency.
Benefits of Maintaining a Buffer Zone:
Increased Reaction Time: Gives you more time to respond to sudden stops, obstacles, or erratic driving by others. Collision Avoidance: Reduces the likelihood of rear-end collisions and sideswipes. Stress Reduction: Provides a more relaxed driving experience by reducing the need for sudden maneuvers or panic braking. Adaptability: Allows you to adjust your speed or position smoothly in response to changing road conditions.
How to Maintain a Buffer Zone:
Adjust Speed: Slow down or speed up as needed to maintain a safe distance from other vehicles. Change Lanes: If someone is tailgating you or if you find yourself too close to the vehicle in front, change lanes to increase your buffer. Be Aware of Blind Spots: Avoid lingering in other vehicles' blind spots and check your own blind spots before making lane changes. Plan Ahead: Anticipate the actions of other drivers, especially at intersections, roundabouts, and areas with heavy pedestrian traffic.
? Why is it important to keep a buffer zone in front of my vehicle?
Increased Reaction Time:
A buffer zone gives you more time to react to sudden changes in traffic, such as the vehicle ahead braking suddenly, a pedestrian crossing unexpectedly, or debris on the road. The more space you have, the more time you have to assess the situation and respond appropriately.
Collision Avoidance:
Maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle in front reduces the risk of rear-end collisions. If the vehicle ahead stops suddenly and you’re too close, you might not have enough time to stop safely, leading to a collision. A buffer zone minimizes this risk.
Smooth Driving:
A buffer zone allows you to adjust your speed gradually rather than making abrupt stops or sudden accelerations. This leads to a smoother driving experience, which is more comfortable for both you and your passengers.
Reduced Stress:
Driving too close to the vehicle in front can create a stressful situation, especially in heavy traffic. By keeping a buffer zone, you reduce the pressure to react quickly, leading to a more relaxed and controlled driving environment.
Adaptation to Road Conditions:
Different road conditions, such as wet, icy, or uneven surfaces, require more stopping distance. A buffer zone allows you to adapt to these conditions by giving you the extra space needed to stop or slow down safely.
Room for Error:
In case the vehicle ahead makes a mistake, such as swerving, braking hard, or stopping suddenly, having a buffer zone gives you the room to correct your course without incident.
Legal and Safe Driving Practices:
Many traffic laws require maintaining a safe following distance. Keeping a buffer zone helps you comply with these laws, avoiding potential fines or accidents.
Visibility:
A proper buffer zone improves your visibility of the road ahead, allowing you to see beyond the vehicle in front. This helps in anticipating traffic conditions and making informed driving decisions.
Avoiding "Tailgating":
Following too closely (tailgating) can lead to road rage or aggressive driving from the driver in front of you. Keeping a buffer zone reduces tension and helps maintain a courteous driving environment.
Emergency Situations:
In an emergency, such as a sudden vehicle malfunction or an unexpected obstacle, a buffer zone provides the necessary space to maneuver your vehicle out of harm's way.
? What are the risks of not maintaining a proper buffer zone?
Increased Risk of Rear-End Collisions:
Without a sufficient buffer zone, if the vehicle ahead of you suddenly brakes or stops, you may not have enough time to react and stop your vehicle safely, leading to a rear-end collision. Rear-end crashes are among the most common types of accidents and can result in significant vehicle damage and personal injuries.
Reduced Reaction Time:
When driving too close to the vehicle in front, your reaction time is significantly reduced. Any sudden change in the traffic flow, such as a vehicle abruptly changing lanes or a pedestrian crossing, can catch you off guard, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
Limited Visibility:
Being too close to the vehicle ahead reduces your ability to see what's happening further down the road. This can prevent you from anticipating traffic issues, road conditions, or hazards, leading to delayed or inappropriate reactions.
Aggressive Driving Behavior:
Driving too close to another vehicle often leads to tailgating, which can provoke aggressive or erratic driving behavior from both you and the driver in front. This can escalate into dangerous driving situations or road rage incidents.
Increased Stress and Fatigue:
Constantly driving close to the vehicle ahead can be stressful, requiring continuous focus and quick reflexes. Over time, this can lead to driver fatigue, reducing your overall alertness and increasing the risk of making mistakes.
Inability to Adjust to Road Conditions:
Different road conditions, such as wet, icy, or uneven surfaces, require more stopping distance. Without a proper buffer zone, you may be unable to adjust your speed or stopping distance in time, leading to a loss of control or a collision.
Potential for Multiple-Vehicle Collisions:
In situations where traffic comes to a sudden stop, not maintaining a buffer zone can lead to chain-reaction crashes involving multiple vehicles. If you rear-end the car in front of you, the impact might push that car into the vehicle ahead of it, creating a pile-up.
Legal and Financial Consequences:
Many jurisdictions have laws requiring drivers to maintain a safe following distance. If you're involved in an accident due to tailgating, you may be found at fault, resulting in fines, increased insurance premiums, and potential legal liability.
Reduced Escape Options:
A buffer zone provides you with the space needed to maneuver out of danger if something goes wrong, such as a vehicle malfunction or an obstacle appearing on the road. Without that space, your ability to avoid a crash is limited.
Compromised Passenger Safety:
In a rear-end collision, passengers in both vehicles are at risk of injury, particularly from whiplash or more severe trauma. Not maintaining a buffer zone increases the likelihood of such injuries to you, your passengers, and others on the road.
? How do I maintain a buffer zone in heavy traffic?
Adjust Your Speed:
Drive at a Speed Appropriate for the Traffic Flow: In heavy traffic, it’s essential to adjust your speed to match the flow of vehicles while maintaining a reasonable distance from the car ahead. Slow Down Gradually: Avoid sudden braking, which can cause chain reactions in heavy traffic. Instead, ease off the gas to create a more consistent and manageable gap.
Use the “Three-Second Rule”:
Pick a Fixed Point: When the vehicle in front of you passes a stationary object (like a sign or a tree), start counting “one thousand one, one thousand two, one thousand three.” Maintain at Least a Three-Second Gap: If you reach the object before finishing the count, you’re following too closely. In heavy traffic, this may be challenging, but strive to maintain as close to this gap as possible.
Stay Calm and Patient:
Avoid Aggressive Driving: In heavy traffic, it’s easy to become impatient and try to close gaps quickly. However, aggressive driving can lead to accidents. Stay Focused: Keep your attention on the road and be mindful of the changing traffic conditions. This will help you maintain a safe distance.
Anticipate Traffic Flow:
Look Ahead Beyond the Car in Front: Try to observe traffic conditions further ahead. This allows you to anticipate slowdowns and adjust your speed gradually, helping to maintain a buffer zone. Be Ready for Sudden Stops: Heavy traffic often involves stop-and-go conditions. Keep your foot ready to brake and avoid tailgating to ensure you have enough space to stop safely.
Use Your Mirrors:
Regularly Check Rear and Side Mirrors: This helps you stay aware of vehicles around you, so you can adjust your speed and position to maintain a buffer zone. Monitor Vehicles Behind You: If someone is tailgating you, try to increase your buffer zone with the vehicle in front of you, providing more space to maneuver if needed.
Avoid Unnecessary Lane Changes:
Stay in Your Lane: Constantly switching lanes can reduce your buffer zone and increase the risk of accidents. It’s safer to stay in your lane and maintain a consistent gap. Only Change Lanes When Necessary: If you must change lanes, do so carefully, ensuring you have enough space both in front of and behind your vehicle.
Communicate with Other Drivers:
Use Your Signals: Indicate your intentions early to give other drivers time to react, helping to maintain buffer zones around all vehicles. Make Eye Contact: In certain situations, making brief eye contact with other drivers can help you gauge their intentions and adjust your driving accordingly.
Leave Extra Space in Bad Weather:
Increase Your Buffer Zone: In adverse weather conditions like rain or fog, increase your following distance to account for longer stopping times and reduced visibility. Be Prepared for Sudden Stops: Wet or icy roads can increase stopping distances, so having a larger buffer zone is critical.
Plan Your Route to Avoid Congestion:
Use Traffic Apps: Utilize navigation apps to avoid heavily congested areas, where maintaining a buffer zone is more difficult. Travel During Off-Peak Hours: If possible, plan your trips during times when traffic is lighter.
Practice Defensive Driving:
Stay Aware of Your Surroundings: Constantly scan the road and be prepared for the unexpected. Defensive driving helps you maintain a buffer zone even in heavy traffic. Give Yourself an Out: Always position your vehicle in such a way that you have an escape route if the traffic situation suddenly changes.
? What should I do if another driver cuts into my buffer zone?
Stay Calm and Avoid Reacting Aggressively:
Resist the Urge to Tailgate: Don’t retaliate by tailgating the vehicle that cut you off. This increases the risk of a collision and doesn’t improve the situation. Take a Deep Breath: Stay composed and focus on driving safely.
Gradually Slow Down to Recreate the Buffer Zone:
Ease Off the Gas: Slowly reduce your speed to create more space between you and the vehicle that cut in front of you. Don’t Slam on the Brakes: A sudden stop could cause a rear-end collision if the vehicle behind you isn’t prepared.
Increase Your Following Distance:
Restore a Safe Distance: Aim to reestablish a safe following distance, ideally the three-second rule, or even more if traffic and road conditions require it. Be Patient: It may take a few moments, especially in heavy traffic, but keeping a safe distance is more important than staying close to the car that cut you off.
Monitor the Situation:
Watch the Car Ahead: Keep an eye on the actions of the vehicle that cut you off. If they’re driving erratically, it might be wise to give them even more space or change lanes when it’s safe. Stay Aware of Surroundings: Regularly check your mirrors to stay aware of the traffic behind you as you adjust your speed.
5. Don’t Engage with the Other Driver:
Avoid Eye Contact or Gestures: Engaging with the other driver, even if you’re upset, can escalate the situation and distract you from driving safely. Focus on Your Own Driving: Concentrate on maintaining control of your vehicle and keeping yourself safe.
Consider Changing Lanes (if safe and necessary):
Move to a Different Lane: If the driver who cut you off continues to drive erratically or too slowly, you might consider changing lanes to avoid potential problems. Ensure it’s safe to do so by checking your mirrors and blind spots. Only Change Lanes When Needed: Don’t make unnecessary lane changes; only do so if it significantly improves your safety or flow of traffic.
Use Defensive Driving Techniques:
Anticipate Potential Issues: Be aware that other drivers might cut into your buffer zone, especially in congested areas. Stay alert and prepared to adjust. Plan for an Out: Always have an escape route in mind in case of sudden changes in traffic flow.
? How does a buffer zone help with sudden stops?
Provides Reaction Time
Reaction Time: When the vehicle in front of you suddenly stops, the buffer zone gives you enough time to perceive the stop, react by moving your foot from the accelerator to the brake, and begin slowing down. Reduced Risk of Collision: The more distance you maintain, the less likely you are to collide with the vehicle in front of you if it stops unexpectedly.
Allows Safe Braking Distance
Braking Distance: This is the distance your vehicle travels from the time you apply the brakes until it comes to a complete stop. A buffer zone ensures that you have enough space to bring your car to a stop without hitting the vehicle ahead. Preventing Rear-End Collisions: In sudden stop situations, having a sufficient buffer zone can be the difference between stopping safely and causing a rear-end collision.
Compensates for Road Conditions
Adverse Weather: In conditions like rain, snow, or ice, your vehicle’s braking distance increases. A larger buffer zone is necessary to account for the reduced traction and longer stopping times. Visibility Issues: Poor visibility due to fog, heavy rain, or darkness can slow your reaction time. A buffer zone helps by giving you more space to react when you can’t see as well.
Reduces Stress and Panic
Calm Driving: Maintaining a buffer zone can reduce the stress and panic that often accompanies sudden stops. Knowing you have enough space to stop safely allows for more composed and controlled driving. Avoiding Abrupt Maneuvers: If you don’t have enough space, you might be forced to make sudden, aggressive maneuvers (like swerving) to avoid a collision, which can be dangerous.
Gives Room for Evasive Action
Swerving or Changing Lanes: If you need to avoid an obstacle or if the vehicle ahead stops very suddenly, a buffer zone provides the space needed to swerve or change lanes safely without hitting other vehicles.
Prevents Chain-Reaction Accidents
Multi-Vehicle Collisions: In heavy traffic, sudden stops by one vehicle can cause a chain-reaction crash. A buffer zone reduces the likelihood that you will be involved in such an accident, and it also helps prevent contributing to it by giving you the space to stop safely.
How Much Buffer Zone Is Needed?
Two-Second Rule: A general guideline is to maintain a distance of at least two seconds behind the vehicle in front of you. In poor conditions, increase this to four seconds or more. Larger Vehicles and Heavier Loads: If you’re driving a larger vehicle or carrying a heavy load, increase the buffer zone since these factors typically require more time and space to stop.
Summary
? How does the type of vehicle affect the buffer zone?
Passenger Cars
Standard Buffer Zone: For most passenger cars, the standard buffer zone is about 2-3 seconds of following distance in normal conditions. Braking Capabilities: Passenger cars typically have good braking capabilities, allowing them to stop relatively quickly. However, in wet or slippery conditions, even these vehicles need a larger buffer zone.
SUVs and Crossovers
Increased Weight: SUVs and crossovers are generally heavier than standard passenger cars, which means they require more distance to stop. Higher Center of Gravity: These vehicles are also more prone to rollovers in emergency maneuvers, so maintaining a larger buffer zone (3-4 seconds) is advisable to avoid sudden sharp turns or stops. Recommended Buffer Zone: At least 3 seconds in normal conditions, increasing to 4 seconds or more in poor conditions.
Trucks and Vans
Much Heavier: Trucks and vans, especially when loaded, are significantly heavier, requiring a much longer distance to come to a complete stop. Longer Stopping Distances: The extra weight means more momentum, which takes longer to slow down. A buffer zone of at least 4 seconds is recommended, even in ideal conditions. Cargo Considerations: If the vehicle is carrying a heavy or unstable load, increasing the buffer zone further is necessary to account for the shifting weight and potential for extended braking distances.
Motorcycles
Quicker Acceleration and Braking: Motorcycles can stop more quickly than most cars due to their lighter weight, but they are also more vulnerable in a collision. Safety Buffer: Motorcyclists should maintain a buffer zone of at least 3-4 seconds to allow ample time to react to sudden stops or obstacles. Visibility Concerns: Motorcycles are less visible to other drivers, so a larger buffer zone helps ensure enough space for sudden maneuvers and enhances safety.
Large Trucks (e.g., Semi-Trucks, 18-Wheelers)
Significant Weight and Momentum: Large trucks require much longer distances to stop due to their size and weight, especially when fully loaded. Extended Buffer Zone: A following distance of at least 6 seconds is often recommended for large trucks in ideal conditions, with more space needed in adverse weather or traffic conditions. Braking Lag: The air brake systems in large trucks can have a slight delay, further necessitating a larger buffer zone.
Buses
Heavier with Passengers: Buses, particularly those carrying passengers, have a longer stopping distance due to their size and weight. Passenger Safety: A larger buffer zone is also critical to ensure a smooth stop that doesn't jostle passengers. Recommended Buffer Zone: At least 4-6 seconds, depending on road conditions and traffic.
Towing a Trailer or Caravan
Increased Stopping Distance: Vehicles towing trailers or caravans need more time to stop due to the added weight and the potential for trailer sway. Buffer Zone for Towing: A buffer zone of 5-6 seconds or more is advisable to account for the additional load and potential handling difficulties. Stability Concerns: The trailer or caravan might affect the vehicle’s handling, especially during braking, making a larger buffer zone even more critical.
Summary
? Can a buffer zone help avoid accidents on the highway?
Provides Adequate Reaction Time
Faster Speeds Require More Space: On the highway, vehicles travel at higher speeds, which reduces the time you have to react to sudden changes in traffic conditions. A buffer zone gives you the time needed to perceive hazards, such as sudden stops or lane changes, and react appropriately. Prevents Chain-Reaction Collisions: In high-speed environments, a sudden stop by one vehicle can lead to a chain-reaction collision involving multiple cars. A buffer zone reduces the likelihood that you’ll be involved in such incidents by giving you ample space to brake safely.
Allows Safe Braking Distance
Stopping Distance: The faster you’re going, the longer it takes to come to a complete stop. A buffer zone ensures that you have enough distance to slow down or stop without hitting the vehicle in front of you, even in emergencies. Compensates for Different Braking Capabilities: Vehicles have varying stopping distances based on their type, weight, and braking system. A buffer zone accounts for these differences, helping you avoid rear-end collisions.
Helps Avoid Aggressive Maneuvers
Reduces Need for Sudden Lane Changes: Maintaining a buffer zone reduces the likelihood that you’ll need to make abrupt lane changes to avoid slower traffic or obstacles, which can be dangerous at high speeds. Encourages Smooth Driving: A buffer zone allows for smoother acceleration and deceleration, reducing the risk of losing control of your vehicle during sudden maneuvers.
Improves Visibility
Better View of the Road Ahead: A sufficient buffer zone improves your ability to see beyond the vehicle directly in front of you, allowing you to anticipate and prepare for upcoming traffic slowdowns, accidents, or road debris. Avoids Blind Spots: By keeping a safe distance, you’re less likely to be in another driver’s blind spot, and you can more easily spot vehicles merging onto the highway or changing lanes.
Adapts to Changing Road Conditions
Weather and Road Surface: On highways, road conditions can change rapidly due to weather, construction, or accidents. A buffer zone gives you the flexibility to adapt your speed and position safely in response to these changes. Nighttime and Low Visibility: In conditions of reduced visibility, such as nighttime or fog, a buffer zone is even more critical, as it compensates for the decreased reaction time and limited sight distance.
Mitigates Risks from Distracted Drivers
Other Drivers’ Behavior: On highways, you have less control over the actions of other drivers. A buffer zone provides a margin of safety if another driver suddenly brakes, swerves, or fails to maintain a consistent speed. Reduces Risk of Tailgating: By maintaining a buffer zone, you discourage tailgating, which is a common cause of accidents on highways.
Helps with Emergency Situations
Time to Respond to Emergencies: In the event of a sudden emergency, such as a blown tire, animal crossing, or debris on the road, a buffer zone gives you the crucial time needed to take evasive action or stop safely. Space for Emergency Vehicles: On highways, emergency vehicles often need to pass through traffic quickly. A buffer zone allows you to maneuver your vehicle safely out of the way without causing a hazard.