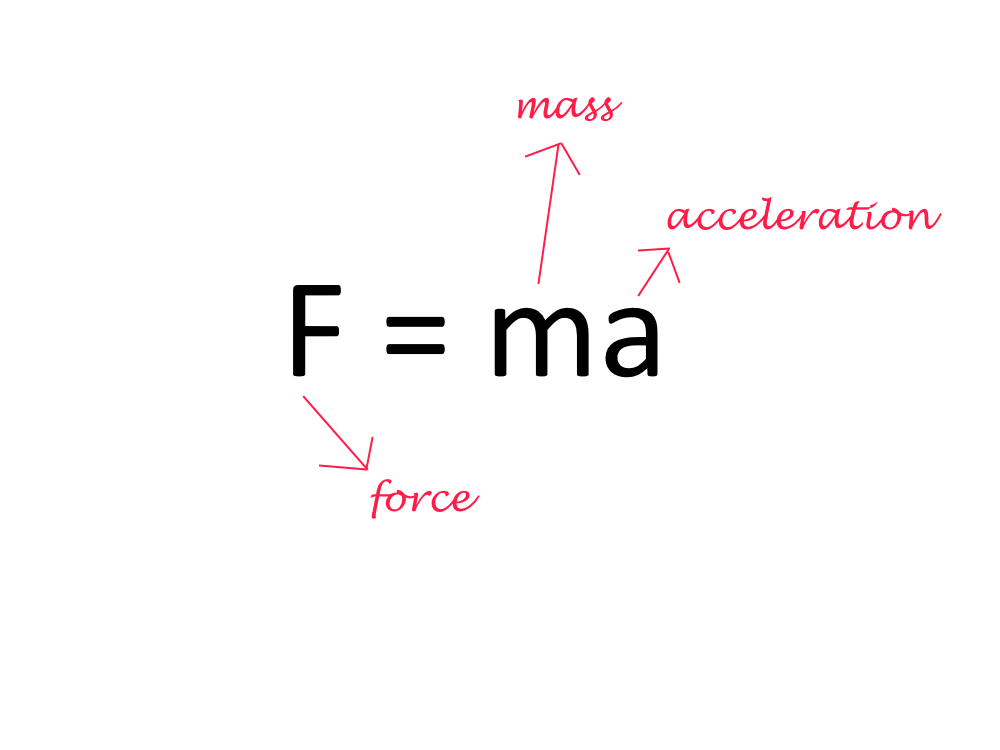Force
⫸ Free YouTube Subscription
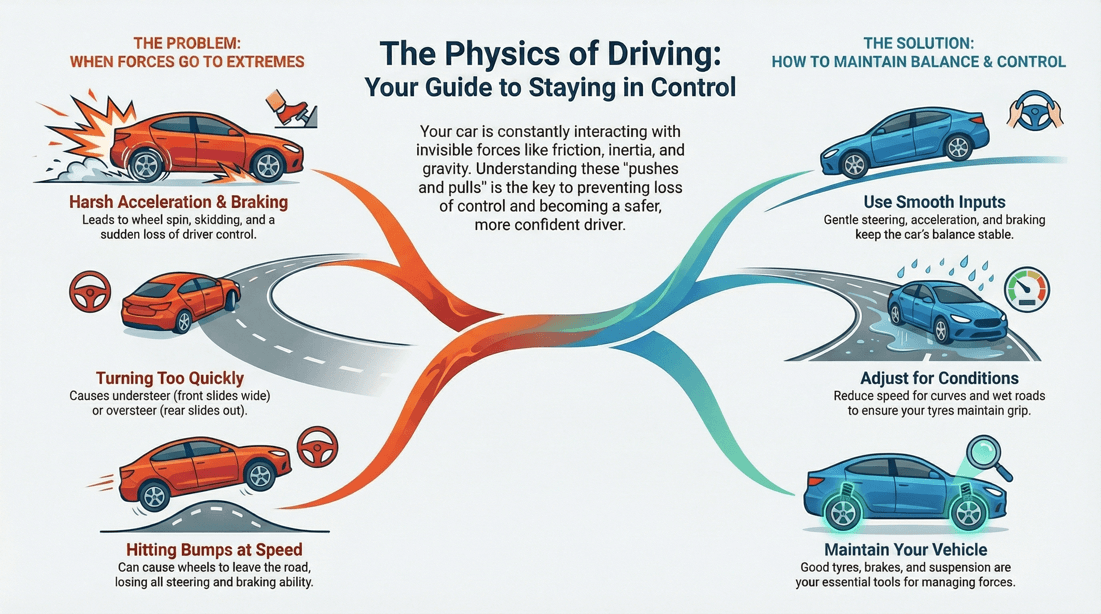
Your car is constantly at the mercy of invisible forces that can either keep you safe or put you in danger. From the moment you start the engine to every turn, brake, or swerve, physics is in control. Understanding how force affects your vehicle’s movement is essential for safer driving and better decision-making, especially when conditions change suddenly. Whether you're driving through a curve, braking in traffic, or accelerating on a slippery surface, the forces acting on your vehicle determine how it responds.
What forces act on a car while it is moving? How does centrifugal force affect your control when turning at speed? Why does braking too hard cause your vehicle to nosedive or skid? What happens when you accelerate quickly on a slippery surface? How do friction and weight distribution influence your ability to steer and stop safely? Why does your car behave differently at high speeds or in wet weather? How can understanding vehicle dynamics help prevent loss of control?
This page clearly explains the role of force in everyday driving and emergency situations. It explores how traction, inertia, momentum, and weight transfer influence your vehicle's handling and stability. By learning how these forces work and how to respond to them, you'll become a more confident driver, better equipped to stay safe in unexpected situations.
In Physics, force is defined as:
"The push or pull on an object with mass causes it to change its velocity."
Force is an external agent capable of changing a body's state of rest or motion. It has a magnitude and a direction.
In general, unless it is an attempt to avoid a dangerous situation, we want to avoid extremes in forces in the directions outlined below.
⧋
🛈 Info:
⧋