
SAFETY > FIRE
Fire
☠️ Alert:
? Questions:

☠️ Dangers associated with vehicle fires
Risk of injury or death : Vehicle fires can cause serious injury or even death. The flames and heat can quickly engulf the entire vehicle, making it difficult to escape. Smoke inhalation : Smoke from a vehicle fire can be toxic and cause serious health problems, such as respiratory damage or carbon monoxide poisoning. Explosion : A vehicle fire can cause an explosion if there is a fuel leak or if the fire reaches the fuel tank. This can cause serious injuries or fatalities. Property damage : Vehicle fires can also cause significant property damage, including damage to other vehicles, buildings, and other structures. Traffic congestion and delays : Vehicle fires can cause traffic congestion and delays, which can create additional safety hazards for drivers and emergency responders. Environmental damage : Vehicle fires can also cause environmental damage, as burning materials can release pollutants and toxic chemicals into the air and water.
? What causes vehicle fires?
Electrical Issues: Short circuits, faulty wiring, or malfunctioning electrical components can generate heat and ignite nearby materials. Fuel System Problems: Leaking fuel lines, fuel pump failures, or fuel tank punctures can lead to the ignition of fuel vapors. Engine Overheating: Excessive heat buildup in the engine compartment, often due to coolant leaks, cooling system malfunctions, or running the engine hard in high temperatures. Exhaust System Failures: Over time, exhaust system components can degrade or become damaged, potentially leading to hot exhaust gases igniting nearby materials. Catalytic Converter Issues: Malfunctioning catalytic converters can overheat and ignite debris or flammable materials in the exhaust system. Brake System Problems: Brakes that are stuck or dragging can generate excessive heat, which can lead to fires if not addressed promptly. Flammable Fluid Leaks: Fluids such as oil, coolant, brake fluid, or transmission fluid leaking onto hot engine components can ignite. Collision or Impact: Crashes or collisions can damage fuel lines, electrical systems, or other components, leading to fires immediately or over time due to compromised safety features. Spontaneous Combustion: Rarely, certain materials or conditions within a vehicle can lead to spontaneous combustion, though this is extremely uncommon. Arson or Deliberate Acts: In some cases, vehicle fires may be intentionally set.
? How can vehicle fires be prevented?
Regular Maintenance : Keep up with scheduled maintenance checks, including inspections of the electrical system, fuel system, brakes , and engine components. Monitor Fluids : Check for leaks regularly and promptly repair any leaks in the fuel, oil, coolant, brake fluid, or transmission fluid systems. Electrical System Checks: Inspect wiring, fuses, and electrical connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Ensure any aftermarket electrical accessories are installed properly and do not overload the electrical system. Cooling System Maintenance: Keep the cooling system in good condition, including checking coolant levels and ensuring proper functioning of the radiator, water pump, and thermostat. Exhaust System Inspection: Look for signs of damage or deterioration in the exhaust system and promptly repair or replace any damaged components. Avoid Overloading: Do not overload your vehicle beyond its designated weight limits, as excessive weight can strain components and increase the risk of fires, especially in the brakes and tires. Safe Refueling Practices: When refueling, turn off the engine and avoid spilling fuel. Tighten the gas cap securely after refueling to prevent fuel leaks. Proper Parking : Avoid parking over dry grass or other flammable materials. When parking, ensure the vehicle's exhaust system is clear of tall grass or debris that could ignite from hot exhaust gases. Carry a Fire Extinguisher : Keep a fire extinguisher designed for automotive use in your vehicle and know how to use it properly. Watch for Warning Signs: Be aware of warning signs such as unusual odors, smoke, or dashboard warning lights indicating potential problems. If you notice anything unusual, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic.
? What are the signs of a potential vehicle fire?
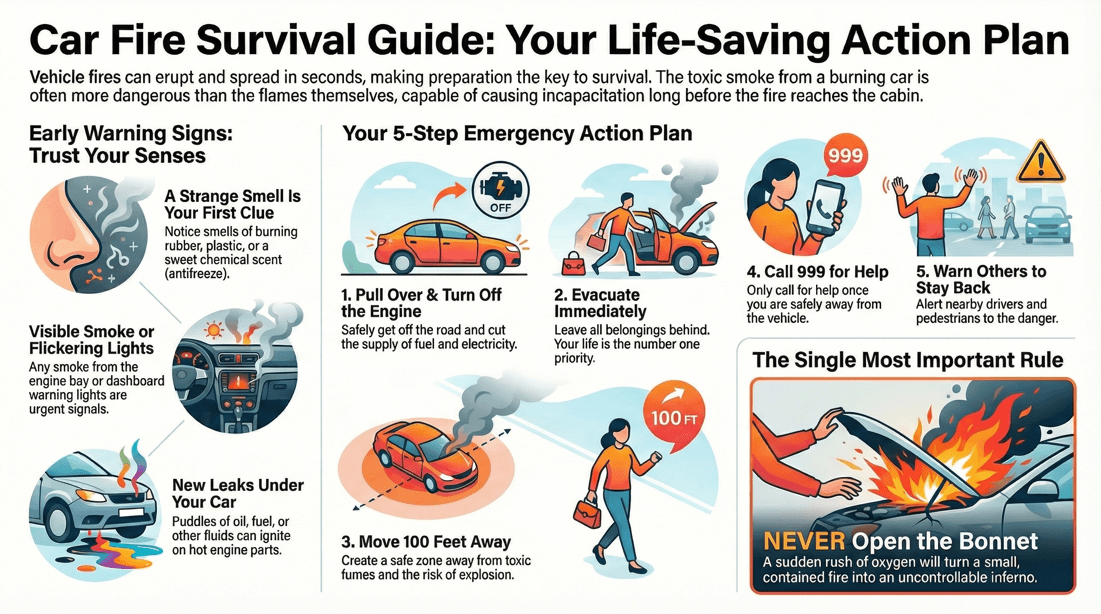
Smoke or Flames: Visible smoke coming from under the hood, dashboard, or any part of the vehicle, or flames visible through windows or vents. Unusual Odors: Strong smell of burning rubber, plastic, electrical wiring, or other materials inside or outside the vehicle. Dashboard Warning Lights : Warning lights such as the check engine light, oil pressure warning light, or battery warning light may illuminate if there is a fire-related issue. Sparks or Electrical Issues: Sparks or electrical problems, such as flickering lights , may indicate an electrical fire hazard. Hot or Overheated Parts: Excessive heat or overheating of engine components, brakes , wheels , or exhaust system, which may be accompanied by unusual sounds. Fluid Leaks : Leaking fluids, particularly flammable ones like gasoline or oil, which can increase the risk of fire. Fuses Blowing: Frequent blowing of fuses or tripping of circuit breakers may indicate an electrical issue that could lead to a fire. Smoking Under the Hood: Smoke coming from under the hood, particularly when the vehicle is running or shortly after it has been turned off.
? What should I do if my vehicle catches fire?
Pull Over Safely: Immediately move your vehicle to the side of the road or to a safe location away from traffic. Turn off the engine. Evacuate Immediately: Get yourself and any passengers out of the vehicle as quickly as possible. Exit through the doors, not through windows unless absolutely necessary. Stay Away: Move at least 100 feet away from the burning vehicle and any other vehicles, bystanders, or structures. Keep a safe distance to avoid inhaling toxic fumes or being near potential explosions. Call Emergency Services: Dial emergency services (911 or the local emergency number) to report the fire. Provide your location, the type of vehicle, and any other relevant details. Do Not Open the Hood: Opening the hood can provide more oxygen to the fire and make it worse. It's best to keep the hood closed and wait for professional firefighters to handle the situation. Use a Fire Extinguisher (if safe): If you have a fire extinguisher and are trained to use it, attempt to extinguish the fire from a safe distance. Aim the extinguisher at the base of the flames. Only attempt this if the fire is small and manageable. Warn Others: Alert nearby pedestrians and motorists about the fire to prevent them from approaching the vehicle. Wait for Assistance: Wait in a safe location until firefighters arrive and handle the fire. Follow any instructions given by emergency responders.
? Can vehicle fires be extinguished with a fire extinguisher?
Type of Fire Extinguisher : Use a fire extinguisher that is suitable for Class B (flammable liquids such as gasoline, oil) and Class C (electrical fires) fires. ABC-rated fire extinguishers are typically recommended as they cover multiple fire classes. Location of Fire: Aim the extinguisher nozzle at the base of the flames, not directly into the smoke or flames. This helps to smother the fire by removing its oxygen supply.
Pull: Pull the pin or safety clip from the extinguisher handle. Aim: Aim the nozzle at the base of the fire from a safe distance (around 6 to 8 feet). Squeeze: Squeeze the handle to discharge the extinguishing agent. Sweep: Sweep the nozzle from side to side, covering the base of the fire until it appears to be out. Safety Distance: Maintain a safe distance from the fire while using the extinguisher. If the fire starts to spread or becomes uncontrollable, evacuate immediately and call emergency services. Evacuation: Even if you manage to partially extinguish the fire, evacuate the area and wait for professional firefighters to ensure the fire is completely out. Recharge or Replace: After using a fire extinguisher, even partially, it should be recharged or replaced to ensure it's ready for future emergencies.