External
⫸ Free YouTube Subscription
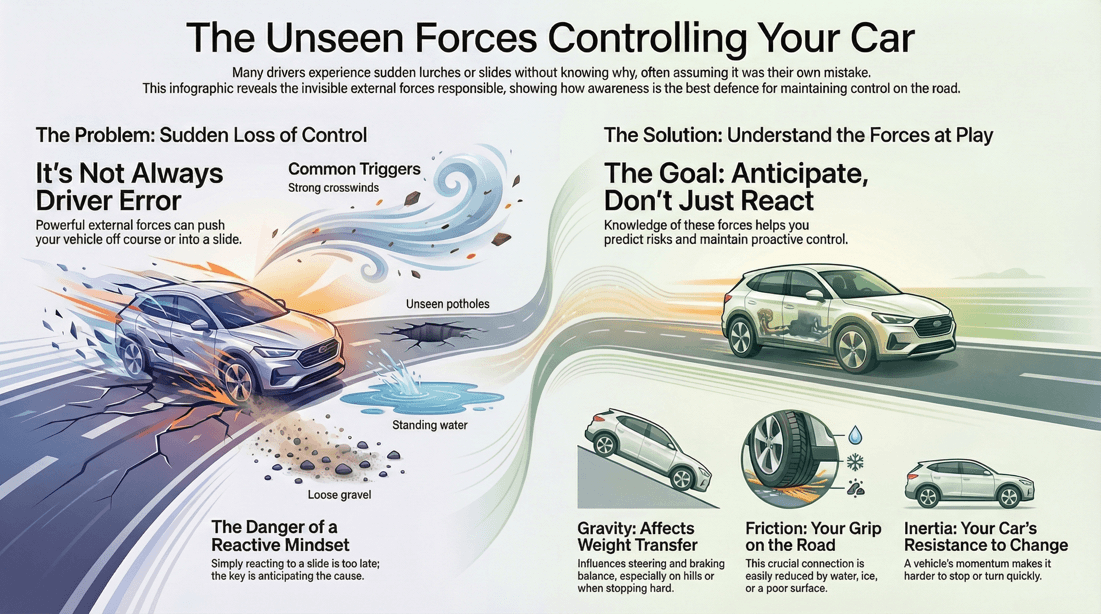
External forces are one of the most overlooked dangers drivers face on the road. These outside influences can affect how your vehicle handles, responds, and stays under control. From changing surfaces to shifting weight, staying safe often depends on how well you recognize and adapt to these conditions.
What are external forces in driving? How do external forces affect vehicle stability? What role do external factors play in unexpected skids or slides? Can a driver anticipate when external forces will become a risk? What should you do when your vehicle responds differently than expected?
This page helps drivers understand how external forces impact safety and control in real-world driving. By identifying the influence of these forces and learning how to respond effectively, drivers can reduce the risk of collisions, maintain control in challenging situations, and improve their overall awareness behind the wheel.
Any external force on a vehicle in motion that is powerful enough can induce a slide into the vehicle.
Such an external force can come from a variety of sources, too numerous to enumerate. However, the list below shows some of the more common categories that these causes would fall into:
⧋
🛈 Info:
⧋