Explosion
⫸ Free YouTube Subscription
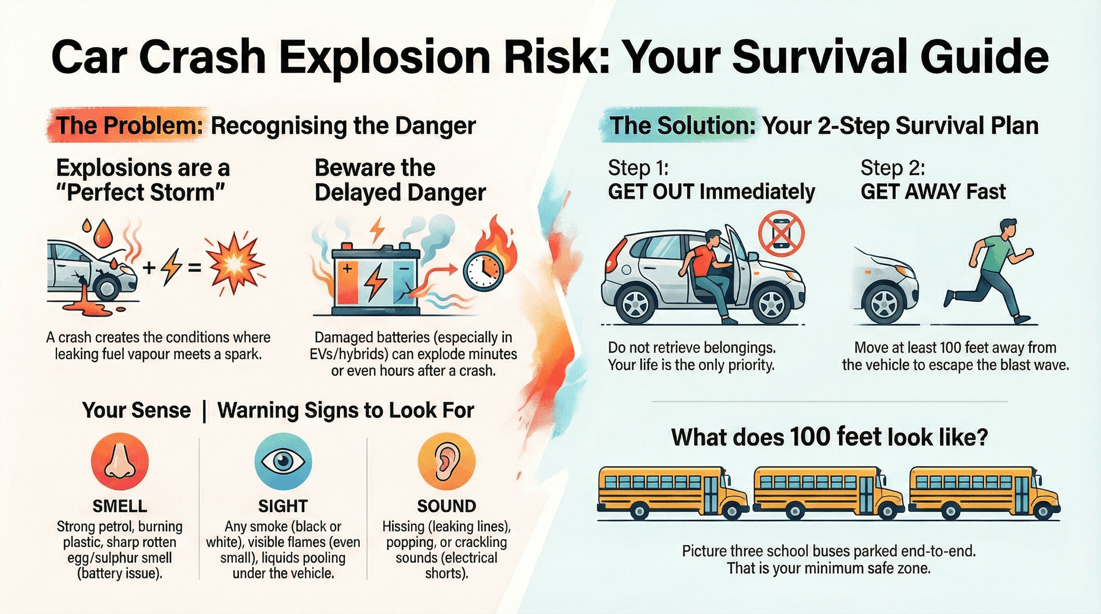
A car crash can be life-altering, but when it triggers an explosion, the danger becomes truly catastrophic. Explosions can happen in moments, fueled by leaking gasoline, damaged batteries, or sparks from metal and wiring. In the chaos that follows a severe accident, knowing what to do and where to go could be the difference between escaping unharmed and suffering devastating injury. Understanding how explosions happen and how to respond can help every driver stay safer on the road.
What causes a vehicle to explode after an accident? How can you spot the warning signs that a blast may be about to occur? What should you do immediately if you suspect a car fire is turning explosive? Where is the safest place to move once you've escaped the vehicle? How far should you stand from a burning car? What dangers can remain after the initial impact? Can leaking fluids or broken batteries cause a delayed explosion?
This page offers essential guidance for recognizing and responding to explosion risks after a crash. It explains how fuel vapors, heat, and structural damage interact to cause vehicle fires and explosions. It also shows how fast these events can unfold and what steps increase your chances of getting away safely. With clear explanations, visual demonstrations, and actionable safety tips, this guide helps drivers make smarter, faster decisions in high-risk situations. Being prepared for even rare emergencies like a car explosion is a powerful way to protect yourself, your passengers, and others on the road.
Stand as far away from the burning vehicle as possible (at least 100 feet), even further than you think is safe, as the accompanying videos will demonstrate.
⧋
☠️ Alert:
⧋