
SAFETY > EQUIPMENT
Equipment
🛈 Info:
? Questions:

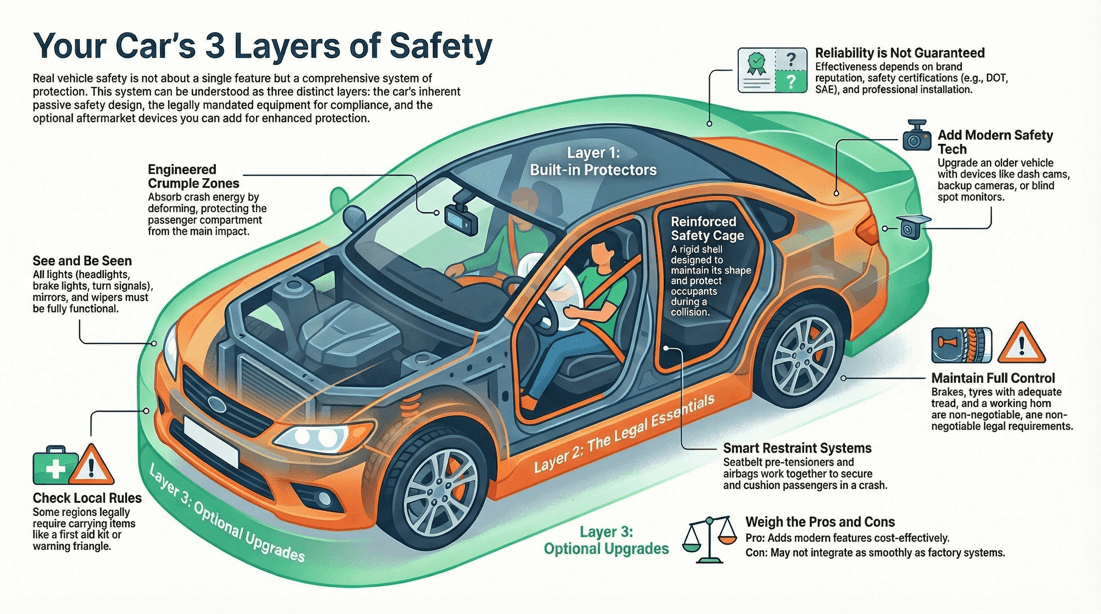
🛈 Passive car safety equipment
Airbags: Front, side, curtain, and knee airbags provide cushioning and reduce the risk of injury. Seatbelts with Pre-tensioners and Load Limiters: Tighten the seatbelt in a crash and then slightly release to prevent chest injuries. Crumple Zones: Absorb and dissipate crash energy to protect occupants. Reinforced Safety Cage: Maintains the integrity of the passenger compartment during a collision. Head Restraints: Reduce the risk of neck injuries in rear-end collisions. Child Safety Seats and LATCH System: Ensure proper installation and security of child seats. Automatic Door Locks: Lock the doors when the vehicle is in motion, enhancing security and reducing the risk of ejection during a crash.
Conclusion
? What safety equipment is legally required in my vehicle?
Seat Belts
Front and Rear Seat Belts: All seating positions must have seat belts. Child Restraints: Proper child seats for young passengers based on age and size.
Airbags
Driver and Front Passenger Airbags: Required in many newer vehicles. Side and Curtain Airbags: Increasingly required in newer models.
Lights
Headlights : Both high and low beams must be functional. Tail Lights and Brake Lights : Must be operational and clearly visible. Turn Signals : All indicators should work properly. Hazard Lights : Should be functional for use in emergencies. Reverse Lights : Should illuminate when the vehicle is in reverse gear.
Mirrors
Rearview Mirror: Must provide a clear view of the road behind. Side Mirrors: Both left and right side mirrors are typically required.
Windshield and Windows
Windshield Wipers : Must be functional and in good condition. Defrosters: Should be operational to clear fog or frost from the windshield. Safety Glass: Windshield and other windows should be made of safety glass to reduce injury in case of breakage.
Brakes
Service Brakes: The main braking system must be in good working order. Parking Brake: Should be functional and able to hold the vehicle on an incline.
Tires
Adequate Tread Depth : Tires must have sufficient tread to provide traction. Proper Inflation: Tires should be inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure.
Horn
Functional Horn: Must be in working condition to alert other drivers or pedestrians.
Exhaust System
Properly Maintained Exhaust: Should not emit excessive smoke or noise.
License Plates
Visible and Legible: Front and rear plates (where required) must be securely attached and clearly visible.
Registration and Inspection Stickers
Valid Stickers: Must display current registration and inspection stickers as required by local laws.
Safety Reflectors
Front and Rear Reflectors: Often required to improve visibility of the vehicle at night.
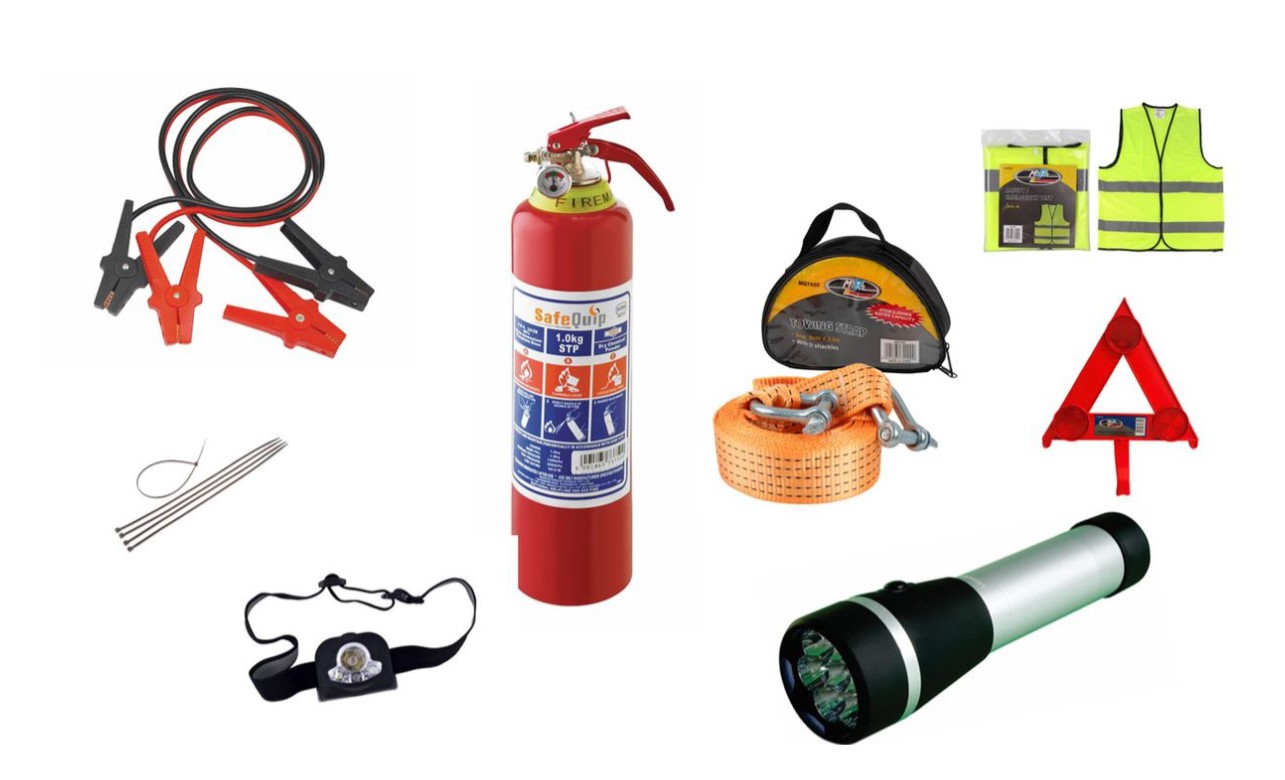
Fire Extinguisher
In Some Jurisdictions: Required for commercial vehicles or certain passenger vehicles.
First Aid Kit and Emergency Equipment
In Some Regions: Required equipment may include a first aid kit, reflective triangles , and a high-visibility vest.
Speedometer
Functional Speedometer: Must accurately display the vehicle's speed.
OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) System
Check Engine Light: Must be operational and used to indicate emissions and other vehicle issues.
? Are aftermarket safety devices reliable?
Quality and Reputation
Brand Reputation: Choose products from reputable brands with a track record of producing reliable safety equipment. User Reviews: Look for reviews and ratings from other users to gauge their experiences with the product.
Certification and Standards
Industry Standards: Ensure the product meets relevant safety standards and certifications (e.g., SAE, DOT, or ECE standards for automotive equipment). Independent Testing: Look for products that have been independently tested and verified for safety and performance.
Installation
Professional Installation: Consider having the device installed by a professional to ensure it is set up correctly and functions as intended. Manufacturer Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions carefully if you choose to install the device yourself.
Compatibility
Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the aftermarket device is compatible with your specific vehicle make and model. Integration with Existing Systems: Check if the device can integrate seamlessly with your vehicle’s existing safety systems without causing conflicts.
Maintenance and Support
Customer Support: Choose a manufacturer that offers good customer support and a warranty for their products. Regular Maintenance: Ensure that any aftermarket safety device is regularly maintained and checked for proper functioning.
Types of Aftermarket Safety Devices
Backup Cameras and Sensors: These can improve visibility and reduce the risk of backing accidents. Blind Spot Monitors : Help alert drivers to vehicles in their blind spots. Dash Cameras : Record driving footage, which can be useful in the event of an accident. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) : Such as lane departure warning, forward collision warning, and automatic emergency braking. Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) : Monitor tire pressure and alert the driver to potential issues.
Pros and Cons
Can enhance vehicle safety beyond the factory-installed systems. May offer advanced features not available in older vehicles. Can be cost-effective compared to upgrading to a newer vehicle.
May not integrate as seamlessly as factory-installed systems. Potential for compatibility issues or malfunctions if not properly installed. Quality and reliability can vary widely between different brands and products.