
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS > DRUNKS
Drunks
☠️ Alert:
💡 Tips:
? Questions:
⮟ How can drunk pedestrians be made aware of their surroundings? ⮟ What should drivers do if they encounter a drunk pedestrian? ⮟ What are the best ways to prevent drunk pedestrians from being injured? ⮟ Are there any specific programs or initiatives to address the issue of drunk pedestrians? ⮟ What role do law enforcement and emergency services play in dealing with drunk pedestrians? ⮟ How can technology help address the problem of drunk pedestrians? ⮟ What are the best practices for pedestrians to avoid walking drunk?

☠️ Drunk pedestrian behavior
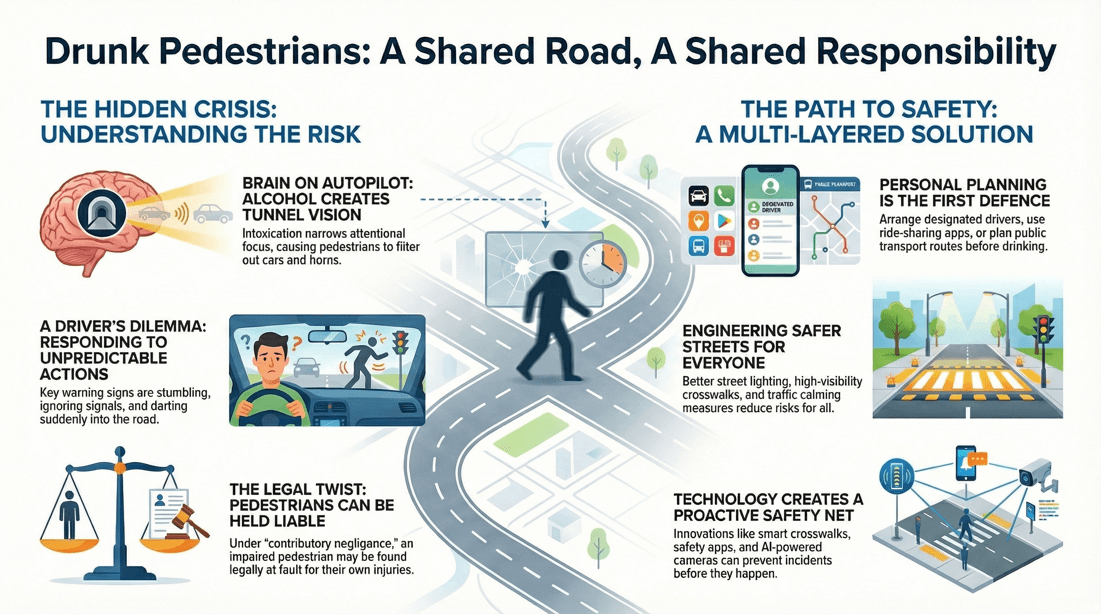
Impaired Judgment and Decision-Making
Risky Crossings: Drunk pedestrians may attempt to cross streets in unsafe locations, such as between parked cars or mid-block, rather than using designated crosswalks. Ignoring Traffic Signals: They may disregard traffic signals and cross against the light, increasing the risk of accidents. Poor Route Choices: They might choose more dangerous routes, such as walking along highways or other areas with high-speed traffic.
Decreased Physical Coordination and Balance
Stumbling and Falling: Impaired balance and motor skills can lead to stumbling, tripping, or falling, which increases the risk of injury. Difficulty Walking Straight: Drunk pedestrians often have trouble walking in a straight line, making their movements unpredictable for drivers.
Reduced Awareness and Reaction Time
Delayed Reactions: Alcohol slows reaction times, making it harder for pedestrians to respond quickly to oncoming traffic or other hazards. Inattention: Drunk pedestrians may be less aware of their surroundings, failing to notice vehicles, obstacles, or other dangers.
Erratic and Unpredictable Behavior
Sudden Movements: They may make sudden, unexpected movements, such as darting into the road or changing direction without warning. Unpredictable Stops: They might stop abruptly in the middle of the street or sidewalk, creating hazards for both vehicles and other pedestrians.
Aggressive or Reckless Actions
Confrontational Attitude: Alcohol can lower inhibitions and increase aggression, leading to confrontational behavior with drivers, other pedestrians, or law enforcement. Vandalism or Property Damage: In some cases, drunk pedestrians might engage in reckless behavior, such as damaging property or disrupting traffic.
Poor Decision-Making Regarding Safety
Ignoring Personal Safety: Drunk pedestrians may not consider personal safety, leading to risky behaviors such as sitting or lying down in the street. Entering Hazardous Areas: They might wander into construction zones, restricted areas, or other dangerous locations.
Visual and Cognitive Impairment
Difficulty Recognizing Hazards: Impaired vision and cognitive function can make it harder to identify and avoid potential hazards, such as oncoming vehicles or uneven sidewalks. Misjudging Distances: Alcohol can affect depth perception, leading to misjudgments about the speed and distance of approaching vehicles.
Social and Environmental Factors
Peer Influence: Drunk pedestrians may be influenced by peers, engaging in risky group behaviors, such as running across streets together or encouraging reckless actions. Environmental Familiarity: In unfamiliar environments, drunk pedestrians may have more difficulty navigating safely, increasing the risk of accidents.
Summary
💡 Tips regarding drunk pedestrians
For Drunk Pedestrians:
Plan Ahead: Arrange for a safe transportation option before consuming alcohol. Use ride-sharing services, public transport, or designated drivers. Stay with Friends: Walk in groups whenever possible. Friends can help keep each other safe and make more responsible decisions. Stick to Well-Lit, Familiar Routes: Choose well-lit paths and familiar routes to reduce the risk of accidents and make navigation easier. Use Pedestrian Crossings: Always use designated crosswalks and follow traffic signals. Avoid jaywalking or crossing streets mid-block. Wear Bright or Reflective Clothing: Increase visibility to drivers by wearing bright or reflective clothing, especially at night. Stay Alert: Even while intoxicated, try to stay as alert as possible. Avoid distractions like using your phone while walking.
For Friends and Bystanders:
Look Out for Each Other: Keep an eye on friends who have been drinking. Ensure they have a safe way to get home and don’t wander off alone. Intervene if Necessary: If you see someone who is clearly intoxicated and trying to walk in a dangerous area, offer assistance or call for help. Contact Authorities if Needed: If you encounter a drunk pedestrian who appears to be a danger to themselves or others, don’t hesitate to contact local authorities for assistance.
For Drivers:
Be Extra Cautious: Drive cautiously in areas where there may be intoxicated pedestrians, especially near bars, clubs, and event venues during late hours. Watch for Erratic Behavior: Be on the lookout for pedestrians who might be behaving unpredictably or stumbling. Slow Down in Pedestrian Areas: Reduce speed in pedestrian-heavy areas, particularly at night when visibility is lower.
For Community and Urban Planning:
Improve Lighting: Ensure streets and sidewalks are well-lit to help pedestrians see hazards and make themselves visible to drivers. Install Barriers: Use barriers or fencing to prevent pedestrians from entering particularly dangerous areas, such as highways or construction zones. Enhance Crosswalks: Make crosswalks more visible with reflective materials, better signage, and pedestrian-activated crossing signals. Public Awareness Campaigns: Run campaigns to educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated and encourage the use of safe transportation options.
For Businesses and Venues:
Provide Transportation Options: Offer information about ride-sharing, taxis, and public transport options to patrons. Designated Driver Programs: Promote designated driver programs or provide incentives for patrons who agree to be the designated driver for their group. Monitor and Assist: Staff at bars and clubs should monitor patrons for signs of extreme intoxication and assist them in getting home safely if needed.
General Safety Tips:
Use Technology: Utilize apps that offer ride-sharing or pedestrian safety features. Some apps provide walking routes that avoid high-risk areas. Carry Identification: Always carry some form of identification and emergency contact information. Stay Hydrated and Nourished: Eating food and drinking water can help mitigate some of the effects of alcohol, though it won't eliminate impairment.
Summary
? What risks do drunk pedestrians face?
Increased Risk of Traffic Accidents
Erratic Behavior: Drunk pedestrians may walk unpredictably, suddenly darting into traffic or crossing streets in unsafe places. Ignoring Traffic Signals: They might ignore traffic signals and cross the road against the light, putting themselves in danger from oncoming vehicles. Misjudging Speed and Distance: Alcohol can impair depth perception, leading to misjudgments about the speed and distance of approaching vehicles.
Falls and Physical Injuries
Stumbling and Tripping: Impaired balance and coordination increase the likelihood of stumbling or tripping over obstacles. Slower Reaction Times: Reduced reaction times can make it harder to avoid hazards or regain balance after a stumble. Severe Injuries: Falls while intoxicated can result in more severe injuries, such as fractures, head injuries, and cuts.
Decreased Awareness and Response to Surroundings
Inattention to Hazards: Drunk pedestrians may be less aware of their surroundings, including potential hazards like uneven sidewalks, construction zones, or approaching vehicles. Delayed Reactions: Slower cognitive and physical reactions can prevent timely responses to sudden dangers.
Increased Vulnerability to Crime
Target for Crime: Drunk pedestrians are more vulnerable to theft, assault, or other crimes due to impaired judgment and reduced situational awareness. Reduced Ability to Defend Themselves: Impairment can also reduce their ability to effectively defend themselves or escape dangerous situations.
Poor Decision-Making and Risky Behavior
Choosing Dangerous Routes: Drunk pedestrians might choose risky routes, such as walking along highways or through poorly lit areas. Ignoring Personal Safety: They may engage in risky behaviors, like walking in the middle of the road or sitting/lying down in dangerous locations.
Hypothermia or Exposure
Inappropriate Clothing: Drunk individuals might be dressed inappropriately for the weather, increasing the risk of hypothermia or heat-related illnesses. Falling Asleep Outdoors: Alcohol can cause drowsiness, leading some to fall asleep outdoors in potentially dangerous environments.
Legal and Financial Consequences
Public Intoxication: In some areas, drunk pedestrians may be cited or arrested for public intoxication or disorderly conduct. Fines and Penalties: Crossing streets improperly or causing traffic disruptions can result in fines and legal penalties.
Strain on Emergency Services
Increased Emergency Calls: Drunk pedestrians are more likely to require assistance from emergency services, whether due to accidents, medical issues, or involvement in altercations. Resource Allocation: This can strain resources and divert attention from other emergencies.
Impact on Mental Health
Embarrassment and Regret: Incidents involving public intoxication can lead to feelings of embarrassment, regret, and anxiety. Injury-Related Trauma: Serious injuries can have long-lasting physical and psychological effects.
Summary
? What are the legal implications for drunk pedestrians?
Public Intoxication Laws
Arrests and Citations: Many jurisdictions have laws against public intoxication. Drunk pedestrians may be arrested or cited if they are found to be intoxicated in public spaces. Fines: Penalties for public intoxication often include fines, which can vary based on the severity of the offense and local laws.
Disorderly Conduct
Behavioral Offenses: Drunk pedestrians engaging in disruptive, aggressive, or dangerous behavior can be charged with disorderly conduct. This includes actions like disturbing the peace or causing public disturbances. Legal Consequences: Disorderly conduct charges can lead to fines, community service, probation, or even jail time, depending on the severity and jurisdiction.
Traffic Violations
Jaywalking: Crossing streets illegally (jaywalking) while intoxicated can result in fines or citations. Jaywalking includes crossing outside of designated crosswalks or against traffic signals. Obstructing Traffic: Pedestrians who impede traffic flow or create hazards for drivers by walking or standing in the roadway can be cited for obstructing traffic.
Liability in Accidents
Contributory Negligence: If a drunk pedestrian is involved in an accident, they may be found partially or fully liable for their injuries due to contributory negligence. This can affect their ability to receive compensation. Civil Lawsuits: Pedestrians who cause accidents or injuries to others while intoxicated may face civil lawsuits from affected parties seeking damages.
Health and Safety Ordinances
Loitering and Trespassing: Drunk pedestrians loitering in certain areas or trespassing on private property can face legal actions, including fines and possible arrest. Public Safety Laws: Some areas have specific ordinances aimed at protecting public safety, which can be invoked if a drunk pedestrian poses a risk to themselves or others.
Increased Scrutiny from Law Enforcement
Enhanced Monitoring: Areas with high rates of public intoxication may see increased law enforcement presence, leading to more frequent stops and checks of individuals suspected of being intoxicated. Detainment for Safety: In some cases, law enforcement may detain intoxicated individuals for their safety, particularly if they are unable to care for themselves.
Impact on Criminal Record
Permanent Record: Arrests or citations for public intoxication and related offenses can become part of a person's criminal record, potentially affecting future employment opportunities, travel, and other aspects of life. Repeat Offenses: Repeat offenses can lead to harsher penalties, including increased fines, longer jail sentences, and mandatory rehabilitation programs.
Community Service and Rehabilitation Programs
Alternative Sentences: Some jurisdictions may offer alternative sentences, such as community service or enrollment in rehabilitation programs, for first-time offenders or minor infractions. Mandatory Programs: In cases of chronic public intoxication, courts may mandate participation in alcohol education or treatment programs as part of the sentencing.
Impact on Insurance Claims
Insurance Coverage: In accidents involving drunk pedestrians, insurance companies may scrutinize claims more closely, potentially denying coverage or reducing compensation if the pedestrian's intoxication contributed to the incident.
Social and Economic Consequences
Financial Burden: Fines, legal fees, and potential job loss due to criminal records can impose significant financial burdens on individuals. Social Stigma: Being publicly intoxicated and facing legal consequences can lead to social stigma and strained personal relationships.
Summary
? How can drunk pedestrians be made aware of their surroundings?
Personal Responsibility
Plan Ahead: Arrange for a designated driver, use public transportation, or book a ride-sharing service before drinking. Stay with Friends: Walk with a group or a sober friend who can help navigate and ensure everyone stays safe. Set Limits: Limit alcohol consumption to a level where personal awareness and motor skills remain relatively intact. Avoid Distractions: Refrain from using mobile phones or engaging in other distractions while walking.
Community and Urban Planning
Well-Lit Paths: Ensure that streets and sidewalks are well-lit to improve visibility for both pedestrians and drivers. Clear Signage: Use clear and visible signage to direct pedestrians to safe crossing points and pathways. Safety Barriers: Install barriers or railings to prevent pedestrians from wandering into dangerous areas, such as highways or construction zones. Designated Walkways: Create designated pedestrian walkways that are separated from vehicular traffic.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Educational Programs: Implement programs to educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated and safe practices. Media Campaigns: Use social media, posters, and public service announcements to raise awareness about pedestrian safety for those who have been drinking. Venue Partnerships: Partner with bars and clubs to promote safe transportation options and distribute safety information.
Technology Solutions
Safety Apps: Utilize smartphone apps that provide safe walking routes, reminders to stay alert, and easy access to ride-sharing services. GPS and Location Sharing: Use GPS and location-sharing features to keep track of friends and ensure they are taking safe routes. Wearable Devices: Encourage the use of wearable devices with safety features, such as fall detection and emergency alerts.
Infrastructure Enhancements
Improved Crosswalks: Enhance crosswalks with reflective materials, better lighting, and pedestrian-activated crossing signals. Pedestrian Islands: Install pedestrian islands in busy streets to provide a safe space for crossing. Traffic Calming Measures: Implement measures such as speed bumps and raised crosswalks to slow down traffic in pedestrian-heavy areas.
Intervention Strategies
Bystander Assistance: Encourage sober individuals to assist drunk pedestrians in navigating safely and ensuring they reach their destinations. Law Enforcement Support: Increase law enforcement presence in areas with high rates of public intoxication to monitor and assist drunk pedestrians. Venue Policies: Establish policies in bars and clubs to monitor intoxicated patrons and offer assistance, such as calling a taxi or arranging for a ride.
Emergency Preparedness
Emergency Contact Information: Ensure that drunk pedestrians have emergency contact information readily available. First Aid Training: Promote first aid training within communities to help bystanders assist intoxicated individuals who may be injured.
Health and Safety Initiatives
Access to Water and Food: Provide access to water and food at venues serving alcohol to help mitigate the effects of intoxication. Regular Breaks: Encourage regular breaks from drinking to allow for assessment of one’s own condition and awareness.
Summary
? What should drivers do if they encounter a drunk pedestrian?
Slow Down and Be Cautious
Reduce Speed: Slow down immediately upon noticing a drunk pedestrian. This gives you more time to react if they move unpredictably. Increase Following Distance: Maintain a safe distance from other vehicles to allow for sudden stops or maneuvers.
Stay Alert and Focused
Stay Vigilant: Keep an eye on the pedestrian’s movements and be prepared for erratic behavior. Avoid Distractions: Ensure full attention on the road by avoiding distractions such as phone use or adjusting in-car settings.
Use Defensive Driving Techniques
Prepare to Stop: Be ready to stop or change direction if the pedestrian suddenly enters your path. Use Horn if Necessary: If the pedestrian is unaware of your presence, a short beep of the horn can alert them without startling them excessively.
Maintain Clear Visibility
Use Headlights: Ensure your headlights are on, especially at night or in poor visibility conditions, to improve your visibility to the pedestrian. Avoid High Beams: High beams can startle or disorient a drunk pedestrian, leading to unpredictable movements.
Communicate with Other Drivers
Signal Intentions: Use turn signals and brake lights to communicate your actions to other drivers. Hazard Lights: If you need to stop or slow down significantly, use your hazard lights to alert drivers behind you.
Navigate Safely Around the Pedestrian
Pass with Care: If it’s safe to do so, carefully pass the pedestrian, ensuring a wide berth. Avoid Sudden Movements: Make gradual and deliberate movements to avoid startling the pedestrian.
Report to Authorities if Necessary
Call for Help: If the pedestrian is endangering themselves or others, call local authorities. Provide clear information about their location and behavior. Stay on Scene: If it’s safe and necessary, stay on the scene to guide authorities and ensure the pedestrian’s safety.
Be Prepared for Unexpected Situations
Emergency Braking: Be prepared for sudden stops if the pedestrian moves into your path unexpectedly. Plan an Escape Route: Always have an escape route in mind, such as the shoulder of the road, in case you need to avoid a collision.
Offer Assistance if Safe
Assess the Situation: If it’s safe to do so, consider offering assistance to the pedestrian, such as calling a taxi or helping them to a safer location. Avoid Confrontation: Ensure that your interaction is non-confrontational and prioritizes the pedestrian’s safety.
Educate Yourself on Local Laws
Know the Laws: Familiarize yourself with local traffic laws regarding interactions with pedestrians, including drunk pedestrians. Follow Protocol: Adhere to legal requirements for reporting and responding to incidents involving impaired individuals.
Summary
? What are the best ways to prevent drunk pedestrians from being injured?
Personal Responsibility
Designated Driver: Arrange for a sober friend or family member to drive. Ride-Sharing Services: Use apps like Uber or Lyft to get home safely. Public Transport: Utilize buses, trains, or taxis.
Buddy System: Always walk with friends who can help keep each other safe. Check-In: Regularly check in with your group to ensure everyone is accounted for.
Moderate Drinking: Set and stick to a limit for alcohol consumption. Stay Hydrated: Drink water between alcoholic beverages to stay more alert.
Community and Urban Planning
Well-Lit Streets: Ensure streets and sidewalks are well-lit to improve visibility. Enhanced Crosswalks: Use lighting and reflective materials to make crosswalks more visible.
Pedestrian Paths: Create designated pedestrian paths away from high-traffic areas. Barriers: Install barriers to prevent pedestrians from wandering into dangerous areas.
Clear Signage: Use clear and visible signs to guide pedestrians to safe crossings. Pedestrian Signals: Implement pedestrian-activated crossing signals to ensure safe crossing.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Awareness Campaigns: Launch campaigns to educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated. School Programs: Educate students about the importance of responsible drinking and pedestrian safety.
Information Distribution: Partner with bars, clubs, and restaurants to provide information about safe transportation options. Safe Ride Programs: Encourage venues to offer discounts or incentives for using ride-sharing services.
Technological Solutions
Navigation Apps: Use apps that offer safe walking routes and alert friends to your location. Emergency Contacts: Apps that allow quick access to emergency contacts and services.
Smart Wearables: Use wearables with features like fall detection and emergency alerts. Reflective Gear: Wear clothing and accessories that enhance visibility, such as reflective vests or armbands.
Law Enforcement and Emergency Services
Hotspot Monitoring: Increase police presence in areas with high rates of public intoxication to monitor and assist drunk pedestrians. Community Policing: Encourage law enforcement to engage with the community and provide assistance to those in need.
Quick Response Teams: Ensure emergency services are equipped and trained to respond quickly to incidents involving intoxicated pedestrians. Public Safety Campaigns: Run campaigns to remind the public to call emergency services if they see someone in danger.
Health and Safety Initiatives
Rehabilitation Services: Provide access to programs and services for those struggling with alcohol abuse. Support Groups: Encourage participation in support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous.
Food and Drink Options: Ensure venues offer food and non-alcoholic beverages to help mitigate the effects of alcohol. Water Stations: Install water stations in public areas to help pedestrians stay hydrated.
Infrastructure Enhancements
Raised Crosswalks: Install raised crosswalks to slow down traffic and improve pedestrian safety. Pedestrian Islands: Provide safe spaces for pedestrians to wait while crossing busy streets.
Speed Bumps: Install speed bumps in pedestrian-heavy areas to slow down vehicles. Reduced Speed Limits: Implement lower speed limits in areas with high foot traffic.
Community Engagement
Community Involvement: Engage residents in monitoring and reporting unsafe behaviors. Volunteer Patrols: Organize volunteer patrols to assist and guide intoxicated individuals.
Policy Making: Work with local governments to create policies and regulations that enhance pedestrian safety. Funding for Safety Projects: Secure funding for projects aimed at improving pedestrian infrastructure and safety.
Summary
? How can public spaces be designed to improve safety for all pedestrians, including those under the influence?
Enhanced Lighting
Street Lighting: Ensure streets, sidewalks, and crosswalks are well-lit to improve visibility. Motion-Activated Lights: Use motion-activated lighting in less-trafficked areas to conserve energy while maintaining safety.
Clear and Safe Walkways
Wide Sidewalks: Design sidewalks wide enough to accommodate groups and reduce congestion. Pedestrian-Only Zones: Create areas where motor vehicles are prohibited to reduce the risk of accidents. Barrier Separation: Use barriers to separate pedestrian paths from vehicle lanes, particularly in high-traffic areas.
Improved Crosswalks and Intersections
High-Visibility Crosswalks: Use reflective paint and enhanced lighting at crosswalks to increase visibility. Pedestrian Islands: Install pedestrian islands in the middle of wide roads to provide safe resting points for those crossing. Raised Crosswalks: Implement raised crosswalks to slow down vehicles and give pedestrians priority.
Traffic Calming Measures
Speed Bumps and Humps: Install speed bumps in areas with high pedestrian traffic to slow down vehicles. Narrow Lanes: Design narrower traffic lanes to naturally reduce vehicle speeds. Roundabouts: Use roundabouts instead of traditional intersections to slow down traffic and reduce collision points.
Accessible and Intuitive Signage
Clear Signage: Use large, easily readable signs to guide pedestrians safely through public spaces. Universal Symbols: Employ universally recognized symbols to ensure comprehension by all, regardless of language or literacy levels. Digital Signage: Consider digital signs that can display real-time information and alerts.
Public Transportation Integration
Transit Stops: Design transit stops with shelters, lighting, and clear paths to nearby crosswalks and sidewalks. Real-Time Updates: Provide real-time updates on transit schedules to reduce the need for pedestrians to wander or wait in unsafe areas.
Green Spaces and Rest Areas
Parks and Plazas: Incorporate green spaces and plazas to provide safe, pleasant areas for pedestrians to relax. Benches and Rest Areas: Place benches and rest areas at regular intervals along walkways.
Technology and Smart Infrastructure
Smart Crosswalks: Implement crosswalks with embedded lights that activate when pedestrians are present. Surveillance Cameras: Use cameras to monitor high-risk areas and deploy resources quickly in case of emergencies. Pedestrian Signals: Utilize pedestrian-activated crossing signals to ensure safe crossing times.
Education and Awareness Campaigns
Public Education: Run campaigns to educate the public about pedestrian safety, including the risks associated with walking under the influence. Community Involvement: Engage local communities in safety initiatives and encourage reporting of unsafe conditions.
Support Services and Facilities
Emergency Call Boxes: Install emergency call boxes in strategic locations for quick access to help. First Aid Stations: Provide first aid stations in large public areas to address minor injuries quickly. Public Restrooms: Ensure accessible and clean public restrooms are available to reduce the need for pedestrians to wander into unsafe areas.
Safe and Accessible Infrastructure
ADA Compliance: Ensure all pedestrian pathways comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards to accommodate individuals with disabilities. Ramp Access: Provide ramps and smooth surfaces for wheelchair users and those with mobility issues.
Community Design Principles
Eyes on the Street: Design spaces that encourage natural surveillance by residents and businesses. Mixed-Use Development: Create mixed-use areas that encourage foot traffic and reduce the likelihood of isolated areas. Walkability: Prioritize walkability in urban design, making it easy and safe for people to walk to various destinations.
Summary
? Are there any specific programs or initiatives to address the issue of drunk pedestrians?
Educational Campaigns
"Walk Sober" Campaigns: These campaigns, often run by local governments or non-profits, educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated. They use posters, social media, and public service announcements to spread the message. Media Outreach: Utilizing TV, radio, and social media platforms to educate the public about the risks associated with being a drunk pedestrian.
Safe Routes to School: This program promotes safe walking routes for children and often includes education about the dangers of alcohol and pedestrian safety. Community Workshops: Conduct workshops and seminars in community centers to raise awareness about pedestrian safety and responsible drinking.
Infrastructure Improvements
Safer Crosswalks: Installing high-visibility crosswalks, pedestrian islands, and pedestrian-activated signals to ensure safer crossing points. Lighting Improvements: Adding more streetlights in areas with high foot traffic to improve visibility for both pedestrians and drivers.
Speed Bumps and Reduced Speed Limits: Implementing these in areas with heavy pedestrian traffic to slow down vehicles and make it safer for pedestrians.
Law Enforcement and Policy Initiatives
Sobriety Checkpoints: Police set up checkpoints to catch drunk drivers, which can also help identify intoxicated pedestrians and guide them to safety. Increased Patrols in High-Risk Areas: Deploying more police officers in areas with high rates of public intoxication to monitor and assist intoxicated pedestrians.
Stricter Alcohol Control Laws: Implementing and enforcing laws around public intoxication and open containers to reduce the number of drunk pedestrians. Penalties for Drunk Walking: Some places impose fines or other penalties for public intoxication to discourage walking while drunk.
Technological Solutions
Safety Apps: Apps that offer safe walking routes, connect with ride-sharing services, and provide emergency contact features. Wearable Devices: Devices that can detect intoxication levels and alert users or emergency contacts if they are in danger.
Partnerships and Collaborations
Safe Ride Programs: Partnerships with bars and restaurants to offer free or discounted rides home for patrons who have been drinking. Staff Training: Training staff to recognize intoxicated patrons and encourage them to use safe transportation options.
Discounts and Promotions: Offering discounts or promotions for ride-sharing services during peak drinking times to encourage people to avoid walking home drunk.
Community Engagement and Support
Community Patrols: Encouraging local residents to participate in patrols and report unsafe conditions or intoxicated individuals in need of help.
Alcohol Support Groups: Providing access to support groups and counseling services for individuals struggling with alcohol addiction. Temporary Shelters: Offering shelters or safe spaces for intoxicated individuals who are unable to get home safely.
Research and Data Collection
Pedestrian Safety Studies: Conducting research to understand the patterns and causes of pedestrian injuries related to alcohol. Data-Driven Approaches: Using data to identify high-risk areas and times, allowing for targeted interventions and resource allocation.
Summary
? What role do law enforcement and emergency services play in dealing with drunk pedestrians?
Law Enforcement
Patrols: Regular patrols in areas with high foot traffic, particularly near bars, clubs, and entertainment districts, to monitor and assist intoxicated pedestrians. Sobriety Checkpoints: Setting up checkpoints to identify and manage intoxicated individuals, ensuring they do not endanger themselves or others. Public Education: Conducting community outreach programs to educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated and promoting safe behaviors.
Assistance: Providing direct assistance to intoxicated pedestrians, such as guiding them to safe areas or arranging transportation home. Deterrence: Using visible police presence to deter risky behaviors, such as jaywalking or wandering into traffic. Collaboration with Local Businesses: Working with bars and restaurants to manage patrons and encourage the use of safe transportation options.
Public Intoxication Laws: Enforcing laws related to public intoxication to reduce the number of drunk pedestrians on the streets. Penalties and Citations: Issuing fines or citations to individuals who engage in dangerous behaviors while intoxicated. Zero Tolerance Policies: Implementing strict enforcement measures in high-risk areas to prevent incidents involving drunk pedestrians.
Emergency Services
Emergency Medical Services (EMS): Providing immediate medical assistance to intoxicated pedestrians who are injured or in distress. Fire and Rescue: Responding to accidents involving drunk pedestrians, such as vehicle collisions, to provide rapid intervention and rescue services.
Safe Transport: Arranging transportation for intoxicated individuals who are unable to get home safely, often in collaboration with law enforcement or community programs. Temporary Shelter: Providing access to temporary shelters or safe spaces for intoxicated individuals to sober up.
Harm Reduction: Implementing harm reduction strategies, such as offering water, blankets, or first aid, to intoxicated individuals on the street. Medical Evaluations: Conducting medical evaluations to determine if intoxicated individuals need further medical treatment or monitoring.
Collaboration Between Law Enforcement and Emergency Services
Joint Operations: Conducting joint operations to address public intoxication, such as combined patrols and checkpoint operations. Communication: Maintaining open lines of communication between law enforcement and emergency medical services to ensure a coordinated response to incidents involving intoxicated pedestrians.
Cross-Training: Providing cross-training for police officers and emergency responders on how to handle intoxicated individuals effectively and safely. Awareness Programs: Implementing training programs focused on recognizing the signs of severe intoxication and the appropriate interventions.
Incident Reporting: Sharing data on incidents involving drunk pedestrians to identify patterns and high-risk areas. Strategic Planning: Using data analysis to develop targeted strategies for reducing the incidence of drunk pedestrian-related accidents and injuries.
Community and Public Partnerships
Partnerships with NGOs: Collaborating with non-governmental organizations that focus on alcohol abuse prevention and pedestrian safety. Local Business Involvement: Encouraging local businesses to participate in safe transportation programs and to promote responsible drinking.
Educational Initiatives: Launching public awareness campaigns that highlight the risks of walking while intoxicated and promote safe alternatives. Event-Based Outreach: Conducting outreach activities during major events and holidays when public intoxication is more likely to occur.
Summary
? How can technology help address the problem of drunk pedestrians?
Mobile Apps and Digital Solutions
Navigation Assistance: Apps that provide safe walking routes, avoid high-risk areas, and offer real-time alerts about potential dangers. Emergency Contact Features: Apps that allow users to quickly contact emergency services or designated safety contacts if they are in trouble.
Instant Booking: Apps that allow users to easily book ride-sharing services like Uber or Lyft, ensuring they have a safe transportation option if they’re intoxicated. Discounts and Promotions: Partnering with ride-sharing apps to offer discounts or promotions specifically for users who need a safe ride home.
Sobriety Monitors: Apps that track alcohol consumption and provide alerts when users reach potentially dangerous levels of intoxication.
Wearable Technology
Fall Detection: Wearables equipped with sensors that detect falls or sudden movements and alert emergency contacts or services. Intoxication Monitoring: Devices that measure blood alcohol content (BAC) and provide real-time feedback on intoxication levels.
Reflective Gear: Wearable items such as vests or armbands with reflective materials to increase visibility to drivers, especially at night.
Infrastructure and Smart City Solutions
Embedded Lights: Crosswalks with embedded LED lights that activate when pedestrians are present, making them more visible and alerting drivers. Pedestrian Detection: Systems that detect pedestrians approaching crosswalks and adjust traffic signals to give them ample time to cross safely.
Adaptive Traffic Signals: Traffic signals that adapt to real-time conditions and prioritize pedestrian crossings, especially in areas with high foot traffic. Surveillance Cameras: Cameras equipped with AI to monitor and analyze pedestrian behavior, detecting risky actions and alerting authorities if needed.
Communication and Alert Systems
Real-Time Alerts: Systems that provide real-time alerts about road conditions, traffic changes, or safety warnings through public announcement systems in urban areas.
Automated Alerts: Systems that send automated alerts to pedestrians about nearby hazards or unsafe conditions via text messages or app notifications.
Data Analytics and Research
Predictive Analytics: Using data analytics to predict high-risk times and locations for intoxicated pedestrian accidents and deploying resources accordingly. Behavioral Insights: Analyzing data on pedestrian behavior to develop targeted interventions and safety measures.
Heat Maps: Creating heat maps of pedestrian traffic and incidents involving intoxicated pedestrians to identify problem areas and improve safety measures.
Community Engagement and Education
Safety Simulations: Using virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) simulations to educate the public about the dangers of walking while intoxicated. Educational Apps: Developing educational apps that provide information on pedestrian safety and responsible drinking.
Awareness Campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms to run campaigns that raise awareness about the risks of walking while intoxicated and promote safe behavior.
Integrated Support Services
Integrated Platforms: Platforms that integrate information from law enforcement, emergency services, and public health to provide a coordinated response to incidents involving drunk pedestrians.
Crowdsourced Alerts: Apps or platforms that allow community members to report unsafe conditions or intoxicated individuals in need of help.
Summary
? What are the best practices for pedestrians to avoid walking drunk?
Plan Ahead
Designate a Driver: Arrange for a sober friend or family member to be your designated driver before you start drinking. Ride-Sharing Services: Use ride-sharing apps or public transportation to ensure a safe way home if you’re planning to drink.
Check Schedules: Plan your trip around public transportation schedules to avoid being stranded. Know Your Routes: Familiarize yourself with transit routes and stops to avoid confusion when intoxicated.
Set Up Safe Alternatives
Pre-Book Rides: Schedule a taxi or ride-sharing service in advance if you anticipate needing one. Use Fare Programs: Take advantage of programs that offer discounted or free rides for those who are intoxicated.
Designated Zones: Stay in areas with easy access to transportation or safe havens where you can wait for a ride.
Make Responsible Choices
Know Your Limits: Be aware of how much alcohol you can consume before it affects your ability to make safe decisions. Stay Hydrated: Drink water or non-alcoholic beverages between alcoholic drinks to stay hydrated and reduce intoxication.
Travel in Groups: Walk with friends or acquaintances to ensure mutual safety and support. Stay in Well-Lit Areas: Stick to well-lit, populated areas if you must walk, to increase visibility and reduce risks.
Use Technology Wisely
Emergency Contacts: Use apps that allow you to quickly contact friends, family, or emergency services if needed. Location Sharing: Share your location with trusted individuals so they can monitor your safety.
Real-Time Updates: Use apps that provide updates on public transportation, ride-sharing availability, and safety alerts.
Know and Avoid Risks
Avoid Hazardous Areas: Stay away from areas known for high traffic, crime, or other safety hazards. Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Stay alert to your environment, even if you feel you are in a safe place.
Know the Laws: Be aware of local laws regarding public intoxication and the potential legal consequences of walking while drunk.
Seek Assistance When Needed
Reach Out: If you find yourself unable to get home safely, ask for assistance from friends, family, or local services. Use Public Facilities: Seek out public facilities or businesses that can offer temporary shelter or assistance.
Notify Authorities: If you see someone who appears to be in danger due to intoxication, notify local authorities or emergency services.
Community and Social Responsibility
Advocate for Safety: Encourage friends and family to adopt safe practices and make responsible choices regarding alcohol consumption and transportation. Support Safe Ride Programs: Participate in or support programs and initiatives that offer safe transportation options for intoxicated individuals.
Engage with Campaigns: Support and participate in community campaigns that raise awareness about the risks of walking while intoxicated and promote safe behaviors.
Summary
? Who is at fault if a drunk pedestrian is hit by a car?
Legal and Jurisdictional Factors
Pedestrian Rights: Laws regarding pedestrian rights and responsibilities vary by location. Some places may hold pedestrians responsible for crossing roads unsafely or being intoxicated. Driver Responsibilities: Drivers are generally required to exercise caution and avoid hitting pedestrians, regardless of the pedestrian’s state.
Shared Responsibility: In many jurisdictions, fault can be shared between the pedestrian and the driver based on their actions. Comparative negligence laws may reduce the driver's liability if the pedestrian was significantly at fault.
Pedestrian Behavior
Crosswalks: If the pedestrian was crossing at a crosswalk or designated crossing point, the driver may have a higher level of responsibility. Jaywalking: If the pedestrian was jaywalking or crossing at an unsafe location, this could impact the determination of fault.
Contributory Negligence: Intoxication can be considered as contributory negligence, potentially impacting the pedestrian's claim for damages. It may be argued that their impaired state contributed to the accident.
Driver Behavior
Speed Limits: Drivers must adhere to speed limits and drive cautiously, especially in areas with heavy pedestrian traffic. Distracted Driving: If the driver was distracted, speeding, or failing to observe traffic signals, they may be held liable even if the pedestrian was intoxicated.
Reasonable Measures: Drivers are expected to take reasonable measures to avoid accidents. This includes being alert and prepared to react to unexpected situations, such as a pedestrian stumbling into the road.
Accident Investigation
Official Findings: Police reports can provide an initial assessment of the accident and factors contributing to it. These reports often play a significant role in determining fault.
Witness Statements: Eyewitness accounts and surveillance footage can help clarify the circumstances of the accident and the behavior of both parties. Physical Evidence: Examining the scene, vehicle damage, and pedestrian injuries can offer insights into how the accident occurred.
Legal Proceedings
Liability Determination: Insurance companies will investigate the accident to determine fault and liability. This may include reviewing police reports, witness statements, and other evidence.
Civil Suits: If the parties involved cannot reach a resolution through insurance, they may pursue civil litigation. Courts will consider all evidence and apply relevant laws to determine fault and damages.
Mitigating Factors
Lighting and Visibility: Poor lighting, weather conditions, and visibility can affect fault determination. If the pedestrian was in a poorly lit area, this might influence the outcome.
Sudden Appearances: If the pedestrian suddenly appeared in front of the vehicle and the driver had no time to react, this could affect the determination of fault.