
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS > CROSSING
Crossing
🛈 Info:
? Questions:

📹 Corner
📹 Near Miss
⚠️ 📹 Accident
⚠️ 📹 Not Stopping
📹 Speed
📹 Rear
🛈 How to use a pedestrian crossing
General Steps for Using Any Pedestrian Crossing
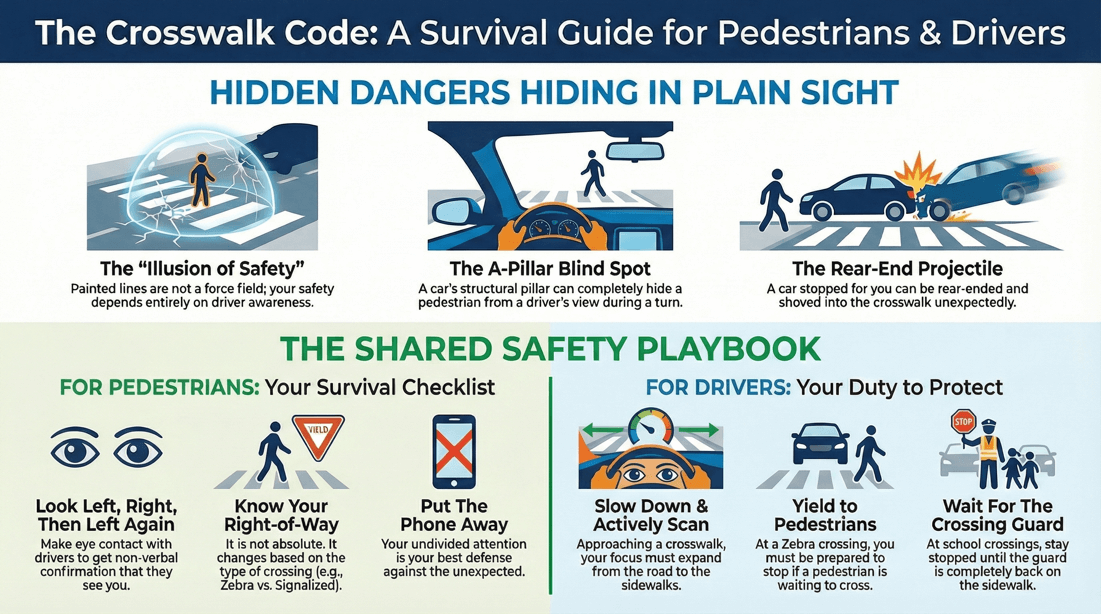
Always use a designated pedestrian crossing whenever possible. Avoid crossing in the middle of the road or between parked cars.
Stop at the curb or edge of the road. Look left, right, and left again to check for oncoming traffic. Ensure it is safe to cross before stepping onto the road.
If there is a pedestrian signal, wait for the "Walk" signal before crossing. Do not start crossing if the signal is flashing "Don't Walk" or is solid red.
Cross the road quickly and avoid lingering in the crossing area. Stay alert and continue looking for oncoming traffic as you cross. Walk, do not run, to reduce the risk of tripping or falling.
Remain within the marked lines of the crosswalk. Avoid crossing diagonally or outside the designated area.
Specific Steps for Different Types of Pedestrian Crossings
Approach the Crossing : Stand at the edge of the crossing. Make Eye Contact : Ensure that drivers see you and are stopping. Cross When Safe : When vehicles have stopped, proceed across the crossing.
Press the Button : Press the button to activate the pedestrian signal. Wait for the Green Man : Wait for the "Walk" signal to appear. Cross When Safe : Cross the road when the signal is green, and the traffic has stopped.
Press the Button : Press the button to activate the pedestrian signal. Wait for the Green Man : The signal will change based on pedestrian presence and traffic flow. Cross When Safe : Cross when the "Walk" signal is illuminated.
Press the Button : Press the button to activate the signal. Wait for the Signal : Wait for the green pedestrian and bicycle signal. Cross Together : Pedestrians and cyclists can cross simultaneously when the signal is green.
Wait for the Crossing Guard : Follow the instructions of the crossing guard. Cross When Directed : Cross the road when the guard indicates it is safe.
Use the Path : Follow the designated path to cross above or below the road. Stay Alert : Be cautious of other pedestrians and cyclists.
Additional Tips
Avoid Distractions : Do not use your phone or other distractions while crossing. Use Crosswalks at Intersections : Cross at intersections with traffic lights or pedestrian signals whenever possible. Be Extra Cautious at Night : Wear bright or reflective clothing and use well-lit crossings at night. Teach Children Safe Practices : Ensure children know and follow these steps.
? What are the different types of pedestrian crossings?
Zebra Crossings:
Description: Marked by black and white stripes on the road, typically with pedestrian priority. Features: Often accompanied by Belisha beacons (flashing amber lights) to alert drivers. Usage: Pedestrians have the right of way once they step onto the crossing.
Pelican Crossings (Pedestrian Light-Controlled):
Description: Signal-controlled crossing with traffic lights that pedestrians activate by pressing a button. Features: Lights for pedestrians and vehicles, with a flashing amber phase allowing vehicles to proceed if the crossing is clear. Usage: Pedestrians wait for the green walking signal to cross.
Puffin Crossings (Pedestrian User-Friendly Intelligent):
Description: Signal-controlled crossing similar to pelican crossings but with sensors to detect pedestrian presence. Features: No flashing amber phase; lights change based on pedestrian movement, improving safety and efficiency. Usage: Pedestrians wait for the green walking signal, which adjusts based on their presence.
Toucan Crossings (Two-Can-Cross):
Description: Signal-controlled crossing shared by pedestrians and cyclists. Features: Wider than standard crossings, with lights for both pedestrians and cyclists. Usage: Both pedestrians and cyclists wait for the green signal to cross.
Pegasus Crossings (Equestrian):
Description: Crossing designed for horse riders, as well as pedestrians and cyclists. Features: Buttons positioned higher for riders, with horse symbols on the signals. Usage: Riders, pedestrians, and cyclists wait for the green signal to cross.
School Crossings (Lollipop Crossings):
Description: Managed by a school crossing patrol officer with a stop sign, usually during school hours. Features: Officer stops traffic to allow children to cross safely. Usage: Pedestrians follow the instructions of the crossing patrol officer.
Subways and Overpasses:
Description: Crossings that go under or over busy roads, avoiding direct interaction with traffic. Features: Tunnels or bridges with ramps or stairs for pedestrian access. Usage: Pedestrians use the designated paths to cross safely without interacting with road traffic.
Marked Crosswalks (Standard Crosswalks):
Description: Basic road markings indicating a crossing area, often at intersections. Features: May include additional signage but not necessarily controlled by signals. Usage: Pedestrians have the right of way, but caution is needed as these crossings rely on driver compliance.
Uncontrolled Crossings:
Description: Crossings marked only by road markings or signs, without traffic signals or active controls. Features: May include warning signs for drivers but rely on mutual awareness between drivers and pedestrians. Usage: Pedestrians should exercise caution and ensure vehicles are stopping before crossing.
Hawk Beacons (High-Intensity Activated Crosswalk):
Description: A pedestrian-activated crossing system with unique signaling. Features: When activated, signals flash yellow, turn solid yellow, and then red, allowing pedestrians to cross. Usage: Pedestrians press a button to activate the signal and wait for the walk sign.
Raised Crosswalks:
Description: Elevated sections of the road designed to slow down traffic and enhance pedestrian visibility. Features: Often combined with zebra markings and signage. Usage: Pedestrians cross on the raised platform, benefiting from reduced vehicle speeds.
? Can pedestrians cross anywhere?
Designated Crosswalks and Intersections:
Use Crosswalks: Pedestrians are encouraged and often required to cross at designated crosswalks, whether marked or unmarked, especially at intersections. Traffic Signals: Follow traffic signals at intersections. Cross only when the pedestrian signal indicates it is safe to do so.
Jaywalking:
Definition: Jaywalking refers to crossing the street outside of designated crosswalks or against traffic signals. Legality: Jaywalking is illegal in many places and can result in fines or other penalties.
Pedestrian Rights and Responsibilities:
Right of Way: In most jurisdictions, pedestrians have the right of way at marked crosswalks and intersections with pedestrian signals. However, they must also ensure it is safe to cross. Responsibility: Pedestrians must not suddenly leave a curb or other safe place and walk or run into the path of a vehicle that is close enough to be a hazard.
Mid-Block Crossings:
Legal but Risky: In some places, pedestrians may legally cross mid-block if there are no nearby intersections or crosswalks. However, they must yield the right of way to vehicles. Safety Considerations: Crossing mid-block can be dangerous due to limited visibility and the potential for higher vehicle speeds.
Rural and Suburban Areas:
Limited Crosswalks: In rural or suburban areas with fewer crosswalks, pedestrians must exercise extra caution and choose safe crossing points with good visibility.
School Zones and Residential Areas:
Additional Crossings: School zones and residential areas often have additional marked crosswalks, and drivers are typically required to yield to pedestrians in these zones.
Pedestrian Bridges and Underpasses:
Use Alternatives: Where available, use pedestrian bridges or underpasses to cross busy roads or highways safely.
Avoiding Dangerous Crossings:
High-Speed Roads: Avoid crossing highways or high-speed roads outside of designated pedestrian crossings. Limited Visibility: Avoid crossing at locations with limited visibility, such as curves or near obstructions.
Following Local Laws:
Variations by Jurisdiction: Rules regarding pedestrian crossings can vary by country, state, or city. It's important to be aware of and follow local laws and regulations.
General Guidelines for Pedestrians:
Be Alert: Always stay alert and avoid distractions like phones or headphones when crossing the street. Look Both Ways: Look left, right, and left again before crossing, even if you have the right of way. Use Signals: Follow pedestrian traffic signals where available. Visible Clothing: Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially when walking at night or in low-light conditions. Cross Quickly and Safely: Cross quickly and directly, avoiding unnecessary time on the roadway.
? What are the rules for using a pedestrian crossing?
General Rules for All Crossings
Always look left, right, and left again before crossing. Continue to be alert while crossing the street.
Use the designated crosswalk area to cross the road. Avoid crossing diagonally unless it is a marked or signaled diagonal crossing.
Make eye contact with drivers to ensure they see you. Wear bright or reflective clothing, especially in low-light conditions.
Do not use phones, headphones, or other distractions while crossing.
Rules for Specific Types of Crossings
Zebra Crossings:
Right of Way: Pedestrians have the right of way once they step onto the crossing. Wait for Traffic to Stop: Ensure vehicles have stopped before stepping onto the crossing. Cross Quickly: Do not linger on the crossing; cross promptly and safely.
Pelican Crossings (Pedestrian Light-Controlled):
Press the Button: Activate the pedestrian signal by pressing the button. Wait for the Green Signal: Cross only when the pedestrian light is green. Flashing Amber Phase: If the light starts flashing amber, vehicles may move if the crossing is clear, so continue crossing quickly and safely.
Puffin Crossings (Pedestrian User-Friendly Intelligent):
Press the Button: Activate the pedestrian signal by pressing the button. Wait for the Green Signal: Cross when the pedestrian light turns green. Sensors: The crossing time is adjusted based on pedestrian presence, so do not rush if the signal is still green.
Toucan Crossings (Two-Can-Cross):
Shared Use: These crossings are for both pedestrians and cyclists. Press the Button: Activate the signal by pressing the button. Wait for the Green Signal: Cross when the light turns green for both pedestrians and cyclists.
Pegasus Crossings (Equestrian):
Press the Button: Riders and pedestrians press the appropriate button to activate the signal. Wait for the Green Signal: Cross when the pedestrian and horse rider signals turn green. Higher Buttons: Use the higher button if you are on horseback.
School Crossings (Lollipop Crossings):
Follow the Patrol Officer: Cross only when the school crossing patrol officer signals that it is safe. Wait for Traffic to Stop: Ensure all vehicles have stopped before stepping onto the road.
Marked Crosswalks (Standard Crosswalks):
Follow Traffic Rules: Cross at marked crosswalks, especially at intersections with traffic lights. Yield to Vehicles: If there are no signals, ensure vehicles are stopping before crossing.
Hawk Beacons (High-Intensity Activated Crosswalk):
Press the Button: Activate the beacon by pressing the button. Wait for the Signals: Follow the sequence of lights: flashing yellow, solid yellow, and then red. Cross on Red: Cross when the vehicle light is red, ensuring it is safe to do so.
Additional Safety Tips:
Cross at Designated Points: Always use marked crossings where available. Use Pedestrian Bridges and Underpasses: Where available, use these facilities to cross busy roads or highways safely. Crossing in Groups: When crossing with children or groups, ensure everyone is aware of the rules and crosses together.
? Who has the right of way at pedestrian crossings?
Zebra Crossings:
Pedestrians: Have the right of way once they step onto the crossing. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians who are on the crossing.
Pelican Crossings (Pedestrian Light-Controlled):
Pedestrians: Have the right of way and should cross when the pedestrian light is green. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians during the green walk signal.
Drivers: Can proceed if the crossing is clear but must yield to any pedestrians still crossing.
Puffin Crossings (Pedestrian User-Friendly Intelligent):
Pedestrians: Have the right of way and should cross when the pedestrian light is green. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians during the green walk signal. Sensors: Adjust crossing times based on pedestrian presence, ensuring safe crossing.
Toucan Crossings (Two-Can-Cross):
Pedestrians and Cyclists: Have the right of way and should cross when the light is green. Drivers: Must stop and yield to both pedestrians and cyclists during the green signal.
Pegasus Crossings (Equestrian):
Pedestrians and Horse Riders: Have the right of way and should cross when the light is green. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians and horse riders during the green signal.
School Crossings (Lollipop Crossings):
Pedestrians: Have the right of way when the school crossing patrol officer signals it is safe to cross. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians when signaled by the patrol officer.
Marked Crosswalks (Standard Crosswalks):
Pedestrians: Have the right of way when the pedestrian light is green. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians during the green walk signal.
Pedestrians: Have the right of way if they are already on the crossing. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians already on or entering the crosswalk.
Hawk Beacons (High-Intensity Activated Crosswalk):
Pedestrians: Have the right of way when the vehicle light is red. Drivers: Must stop and yield to pedestrians during the red signal.
General Guidelines:
Pedestrians: Should always ensure that it is safe to cross, even when they have the right of way. Drivers: Must remain vigilant and yield to pedestrians at all types of crossings, as required by local laws and signals.
Local Variations:
Legal Requirements: The specifics of right of way can vary based on local traffic laws and regulations, so it's important to be familiar with the rules in your area. Signs and Signals: Always pay attention to local signs, signals, and road markings that may provide specific instructions for right of way at crossings.
? What should drivers do when approaching a pedestrian crossing?
General Actions for All Crossings
Reduce Speed: Approach pedestrian crossings at a reduced speed to allow time to react to any pedestrians who may be crossing.
Be Vigilant: Pay close attention to the road, sidewalks, and surroundings for any signs of pedestrians intending to cross. Avoid Distractions: Do not use mobile phones or engage in other distractions when approaching a crossing.
Right of Way: Be prepared to stop and give pedestrians the right of way if they are already on or about to enter the crossing.
Specific Actions for Different Types of Crossings
Stop if Necessary: Stop and allow pedestrians to cross if they are on the crossing or waiting to cross. Observe Pedestrian Intentions: Look for pedestrians approaching the crossing and be ready to stop.
Follow Traffic Lights: Red Light: Stop when the traffic light is red, allowing pedestrians to cross. Flashing Amber Light: Proceed with caution if the crossing is clear, but yield to any pedestrians still on the crossing.
Observe Traffic Lights: Red Light: Stop when the light is red. Green Light for Pedestrians: Ensure no pedestrians are still crossing before proceeding when the light turns green for vehicles.
Toucan Crossings (Two-Can-Cross):
Respect Signals: Red Light: Stop and allow both pedestrians and cyclists to cross when the light is red. Green Light for Pedestrians and Cyclists: Ensure the crossing is clear before proceeding.
Obey Traffic Signals: Red Light: Stop and yield to pedestrians and horse riders when the light is red. Green Light for Pedestrians and Riders: Make sure the crossing is clear before moving.
Follow Patrol Officer’s Instructions: Stop When Signaled: Stop and wait for the school crossing patrol officer to allow children and other pedestrians to cross. Remain Stopped: Stay stopped until the patrol officer has returned to the sidewalk and signaled it is safe to proceed.
Yield at Intersections: Traffic Signals: Stop when the pedestrian light is green, allowing pedestrians to cross. Uncontrolled Crosswalks: Yield to pedestrians already on or about to enter the crosswalk.
Observe Beacon Signals: Yellow Flashing Light: Slow down and prepare to stop. Red Light: Stop and allow pedestrians to cross. Dark Phase: Proceed with caution if the beacon is not activated.
Additional Tips for Drivers
Anticipate Pedestrian Behavior: Be aware that pedestrians may not always be predictable; be ready to stop suddenly if necessary. Use Mirrors: Regularly check mirrors for pedestrians who may be crossing behind or beside your vehicle. Adjust for Conditions: In poor weather or low visibility, reduce speed further and be extra vigilant for pedestrians. Respect School Zones: Extra caution is needed in school zones, where children may be crossing unpredictably.
? What should pedestrians do if there is no designated crossing?
Choose a Safe Crossing Point:
Visibility: Select a crossing point where you and oncoming drivers have a clear view of each other. Avoid crossing near bends, hills, or other obstacles that limit visibility. Straight Path: Cross the road in a straight line rather than diagonally, as this minimizes the time spent in the roadway.
Assess Traffic:
Look Both Ways: Look left, right, and left again to check for oncoming traffic. Continue to look as you cross. Judge Speed and Distance: Assess the speed and distance of any approaching vehicles. Ensure there is enough time to cross safely before any vehicles reach you.
Wait for a Gap:
Wait for a Safe Gap: Wait until there is a sufficient gap in traffic from both directions to cross safely. Avoid Running: Do not run across the road, as it may be harder for drivers to predict your movements.
Make Your Intentions Clear:
Be Visible: Make eye contact with drivers if possible to ensure they see you and understand your intention to cross. Raise Your Hand: In some regions, raising your hand can signal to drivers that you intend to cross.
Cross Quickly and Safely:
Stay Alert: Continue to look both ways as you cross. Do not assume that drivers will stop. Do Not Hesitate: Cross the road confidently and at a steady pace. Hesitating or stopping in the middle of the road can confuse drivers.
Crossing Multiple Lanes:
Cross One Lane at a Time: If crossing a multi-lane road, treat each lane as a separate crossing. Ensure each lane is clear before proceeding. Use Medians: If there is a median or island, use it as a safe stopping point if needed.
Crossing in Poor Conditions:
Extra Caution: Be extra cautious in poor weather conditions (rain, fog, snow) as visibility is reduced, and stopping distances for vehicles are longer. Reflective Clothing: Wear bright or reflective clothing to increase visibility, especially at night or in low-light conditions.
Avoid Distracted Walking:
No Distractions: Do not use mobile phones, headphones, or other distractions while crossing the road. Stay focused on the traffic.
Follow Local Laws:
Legal Considerations: Be aware of and follow any local laws or regulations regarding pedestrian crossings. In some areas, jaywalking (crossing outside of a designated crosswalk) may be illegal and subject to fines.
Seek Assistance if Needed:
Help for Vulnerable Pedestrians: Children, elderly individuals, or those with disabilities may require assistance to cross safely. Seek help if needed.
Summary Checklist for Safe Road Crossing:
Choose a visible, safe crossing point. Look left, right, and left again. Wait for a safe gap in traffic. Make your intentions clear to drivers. Cross quickly and safely, continuing to look both ways. Use medians or islands for multi-lane roads. Exercise extra caution in poor conditions. Avoid distractions. Follow local laws. Seek assistance if necessary.
? How do pedestrian signals work?
Components of Pedestrian Signals
Typically depicted by a walking person symbol or the word "WALK." Indicates it is safe for pedestrians to start crossing.
Usually shown by an upraised hand symbol or the words "DON'T WALK." Indicates pedestrians should not start crossing.
The upraised hand symbol flashes. Indicates pedestrians should not start crossing if they haven't already, but those already in the crosswalk should continue to the other side.
Shows the number of seconds remaining for pedestrians to complete their crossing. Often used alongside the flashing "DON'T WALK" signal.
Types of Pedestrian Signals
Integrated into regular traffic lights at intersections. Controlled by the same system that manages vehicle traffic lights.
Pedestrians press a button to request a walk signal. The system adjusts the traffic light cycle to provide a walk signal.
Provide sound cues for visually impaired pedestrians. May include beeping sounds or spoken messages indicating when to walk and when to wait.
Include tactile features and audible instructions. Help visually and hearing-impaired pedestrians navigate crossings.
Operation of Pedestrian Signals
Pedestrian signals are synchronized with vehicle traffic lights to ensure safety. When vehicle traffic in one direction is stopped, the corresponding pedestrian signal allows crossing.
The "WALK" signal is illuminated, indicating it is safe for pedestrians to start crossing. This phase is typically short and may be followed by the flashing "DON'T WALK" signal.
The "DON'T WALK" signal begins to flash, indicating pedestrians should not start crossing if they haven't already. Pedestrians already in the crosswalk should continue to the other side. Often accompanied by a countdown timer showing the remaining seconds to cross.
The "DON'T WALK" signal is steady, indicating it is not safe to start crossing. Vehicles may be moving, and pedestrians should wait for the next "WALK" signal.
Pedestrian-Activated Signals
Pedestrians press a button to request a crossing signal. The system will prioritize the pedestrian request in the next traffic light cycle.
There may be a short wait time for the traffic light cycle to change and provide a walk signal. The system ensures a safe gap in vehicle traffic before allowing pedestrians to cross.
Some systems provide auditory or visual confirmation that the button press has been registered.
Safety Considerations
Pedestrians should wait for the "WALK" signal before starting to cross. Crossing during the "DON'T WALK" phase can be dangerous and illegal.
If the "WALK" signal changes to flashing "DON'T WALK" while crossing, pedestrians should continue to the other side. Do not stop in the middle of the crosswalk.
Even with a "WALK" signal, watch for vehicles making turns across the crosswalk. Make eye contact with drivers to ensure they see you.
Summary
? What if a pedestrian crossing signal is malfunctioning?
For Pedestrians
Determine if the signal is completely off, stuck on a particular signal (e.g., "DON'T WALK" or flashing), or behaving erratically.
Observe the flow of vehicle traffic and look for gaps or opportunities to cross safely. Check if the vehicle traffic signals are functioning normally and use them as a guide.
Cross with Care: Cross only when you have a clear view of approaching traffic from both directions and can determine it is safe to cross.
Be vigilant and ready to stop if a vehicle does not yield.
Ensure drivers can see you by making eye contact and using hand signals if necessary to indicate your intention to cross.
If the malfunctioning signal is at an intersection with multiple crossings, consider using another crossing point with a functioning signal.
If you are unsure or feel unsafe, ask for assistance from other pedestrians, nearby people, or a crossing guard if available.
For Drivers
Slow down when approaching a pedestrian crossing with a malfunctioning signal. Be prepared for unexpected pedestrian movements.
Always yield to pedestrians who are already in the crosswalk or are clearly intending to cross.
Be attentive to pedestrians who may signal their intent to cross with hand gestures or by making eye contact.
Allow extra time for pedestrians to cross safely and be prepared to stop.
Reporting the Malfunction
Note the specific issue with the signal, such as whether it is completely off, stuck, or displaying incorrect signals.
Record the exact location of the malfunctioning signal, including the intersection or crosswalk and nearby landmarks.
Report the malfunction to the relevant local authorities, such as the city's transportation department, public works department, or local police. Many cities have non-emergency hotlines or online reporting systems for such issues. Provide as much detail as possible to help expedite the repair process.
Temporary Measures
Temporary Signs: In some cases, authorities may place temporary signs or barriers to alert drivers and pedestrians to the malfunction. Manual Control: Traffic personnel may be dispatched to manage the intersection manually until repairs are made.
Summary
? How can pedestrian crossings be made safer?
Engineering Solutions
High-Visibility Markings: Use bright, reflective paint and patterns like zebra stripes to make crosswalks more visible. Advance Stop Lines: Place stop lines further back from crosswalks to give pedestrians more space and improve visibility.
Street Lighting: Install adequate lighting at and around pedestrian crossings to improve visibility at night. In-Roadway Lights: Embed lights in the road surface at crosswalks that activate when pedestrians are present.
Speed Tables: Elevate crosswalks to the level of the sidewalk, which can slow down vehicles and make pedestrians more visible.
Medians: Install refuge islands in the middle of wide roads to provide a safe stopping point for pedestrians crossing multiple lanes.
Speed Humps and Bumps: Use speed humps and bumps near pedestrian crossings to slow down vehicle traffic. Narrowed Lanes: Narrow lanes or use curb extensions (bulb-outs) to reduce vehicle speeds and shorten crossing distances for pedestrians.
Longer Walk Phases: Extend the duration of pedestrian walk signals to allow more time for crossing, especially for the elderly and disabled. Leading Pedestrian Intervals (LPI): Provide pedestrians with a head start by giving them a walk signal before vehicles get a green light.
Bridges and Tunnels: Construct overpasses or underpasses for pedestrians to completely separate them from vehicle traffic in high-traffic areas.
Technological Enhancements
Sensors and Cameras: Use sensors or cameras to detect pedestrians and automatically trigger crossing signals. Smart Signals: Implement adaptive traffic signals that adjust based on real-time pedestrian and vehicle traffic.
Clear Timing Information: Install countdown timers at pedestrian signals to inform pedestrians of the remaining time to cross safely. Audible Signals: For the Visually Impaired: Use audible signals to provide crossing information for visually impaired pedestrians.
Enforcement and Education
Traffic Law Enforcement: Implement strict enforcement of traffic laws related to pedestrian crossings, such as yielding to pedestrians and speed limits. Fines and Penalties: Impose fines and penalties for violations to deter dangerous driving behavior.
Education Programs: Educate drivers and pedestrians about the importance of crosswalk safety through public campaigns, schools, and community programs. Safety Workshops: Conduct workshops and training sessions for pedestrians, especially vulnerable groups like children and the elderly.
Neighborhood Watch Programs: Encourage community involvement in monitoring and promoting pedestrian safety. Feedback Mechanisms: Provide channels for the public to report safety issues and suggest improvements.
Policy and Planning
Inclusive Design: Adopt policies that prioritize the safety of all road users, including pedestrians, cyclists, and public transit users. Integrated Planning: Plan urban environments with pedestrian safety in mind, integrating safe crossings into broader transportation and land use planning.
Child Safety: Implement programs to create safe walking routes for children going to and from school.