Clutch
🛈 Info:
💡 Tips:
? Question:
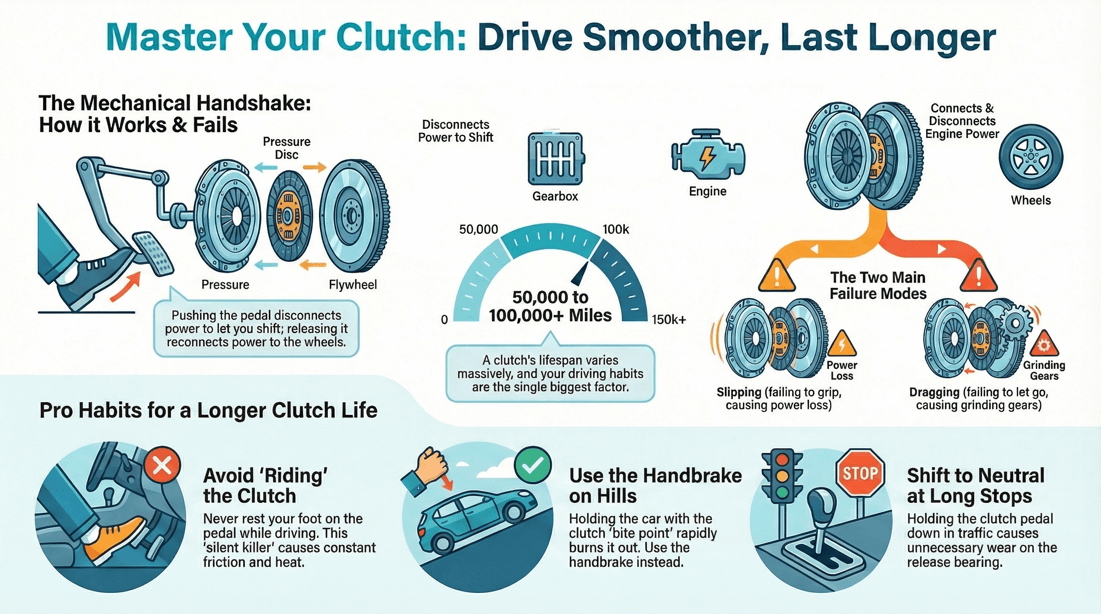
🛈 How a car clutch works
Key Components of a Clutch:
Clutch Pedal : The pedal that you press to engage or disengage the clutch. Flywheel : A heavy, spinning wheel connected to the engine's crankshaft that provides rotational energy. Clutch Disc (or Clutch Plate) : A friction disc located between the flywheel and the pressure plate. Pressure Plate : A spring-loaded plate that presses the clutch disc against the flywheel. Release Bearing (or Throw-out Bearing) : A bearing that pushes against the pressure plate to disengage the clutch. Clutch Fork : A lever that moves the release bearing when you press the clutch pedal.
How the Clutch Works:
When your foot is off the clutch pedal, the clutch is engaged. The pressure plate pushes the clutch disc against the flywheel, creating friction. This friction allows the engine’s power to be transmitted through the clutch disc to the transmission, and then to the wheels, propelling the vehicle.
When you press the clutch pedal, it moves the clutch fork, which in turn pushes the release bearing against the pressure plate. This action releases the pressure on the clutch disc, separating it from the flywheel. With the clutch disc disengaged from the flywheel, the engine is no longer connected to the transmission, allowing you to change gears or come to a stop without stalling the engine.
When the clutch is disengaged, the transmission is momentarily disconnected from the engine. This allows you to shift gears without causing damage to the transmission. After you select a new gear, releasing the clutch pedal re-engages the clutch disc with the flywheel, smoothly transmitting the engine’s power to the wheels at the new gear ratio.
To start moving from a stop, you slowly release the clutch pedal while simultaneously applying the accelerator. As the clutch disc gradually engages with the flywheel, it transfers power to the transmission and wheels, allowing the vehicle to move forward. Smoothly coordinating the clutch release and throttle application prevents the car from stalling and ensures a smooth start.
Types of Clutches:
Single-Plate Clutch : The most common type in passenger vehicles, where one clutch disc engages with the flywheel. Multi-Plate Clutch : Used in high-performance cars or motorcycles, where multiple clutch discs provide more friction surface for better power transfer. Wet Clutch : Operates in a bath of oil, often found in motorcycles and some high-performance vehicles, providing smoother operation and cooling. Dry Clutch : Not immersed in oil, common in most passenger vehicles, offering a direct connection between the engine and transmission.
Common Clutch Issues:
Clutch Slippage : Occurs when the clutch disc does not fully engage with the flywheel, causing a loss of power. This can be due to worn-out clutch discs, a weak pressure plate, or oil contamination. Clutch Drag : Happens when the clutch does not fully disengage, making it difficult to change gears. This could be caused by a faulty release bearing, misadjusted clutch linkage, or air in the hydraulic system. Clutch Judder : A jerky or shuddering sensation when engaging the clutch, often caused by worn or damaged clutch components.
Summary:
💡 Tips on using the clutch
Engage the Clutch Smoothly
Tip : When starting from a stop, slowly and gradually release the clutch pedal while simultaneously pressing the accelerator. This smooth coordination will prevent the car from jerking or stalling. Why : A smooth engagement ensures that the clutch disc meshes properly with the flywheel, allowing for a smooth transfer of power.
Avoid Riding the Clutch
Tip : Do not keep your foot on the clutch pedal while driving, except when changing gears. Resting your foot on the clutch pedal can cause partial engagement, leading to premature wear. Why : Riding the clutch generates unnecessary friction, which can overheat and wear out the clutch components.
Use the Clutch for Gear Changes Only
Tip : Only press the clutch when you need to change gears or come to a stop. Don’t use the clutch to control your speed; use the brakes instead. Why : Using the clutch unnecessarily puts extra strain on the clutch system and can lead to quicker wear and potential failure.
Downshift Appropriately
Tip : When downshifting, match the engine speed to the lower gear by using a technique called “rev-matching” (blipping the throttle) before re-engaging the clutch. Why : This helps to prevent the car from jerking when the lower gear engages, reducing stress on the clutch and transmission.
Avoid Holding the Clutch at the Bite Point
Tip : Don’t hold the clutch halfway down (at the bite point) for too long. Either fully engage or disengage the clutch. Why : Holding the clutch at the bite point for extended periods can cause excessive wear on the clutch disc and pressure plate.
Practice Hill Starts with the Handbrake
Tip : When starting on a hill, use the handbrake to prevent rolling back. Release the handbrake as you smoothly engage the clutch and press the accelerator. Why : This technique helps you avoid rolling back and reduces stress on the clutch, especially during uphill starts.
Use the Clutch Sparingly in Traffic
Tip : In stop-and-go traffic, try to anticipate when you’ll need to stop and shift to neutral instead of holding the clutch down for extended periods. Why : Keeping the clutch disengaged for too long can cause unnecessary wear on the release bearing.
Shift Gears at the Right RPM
Tip : Shift gears at the appropriate engine speed (RPM) for your vehicle. Typically, this is around 2,000-3,000 RPM for gasoline engines and 1,500-2,500 RPM for diesel engines. Why : Shifting at the right RPM ensures smooth gear changes and reduces the load on the clutch and engine.
Be Gentle with the Clutch in Cold Weather
Tip : In cold weather, be gentle when engaging the clutch as the components may be stiffer until they warm up. Why : Cold weather can make the clutch mechanism less responsive, so gentle engagement helps prevent unnecessary strain.
Regular Clutch Maintenance
Tip : Have your clutch system checked regularly as part of your vehicle’s maintenance routine, including checking the clutch fluid if your vehicle uses a hydraulic clutch. Why : Regular maintenance can identify potential issues early and ensure the clutch operates smoothly and reliably.
Summary:
? Do all cars have a clutch?
Manual Transmission Cars
Clutch : Yes, all manual transmission cars have a clutch. The driver operates it with a pedal to manually engage and disengage the engine from the transmission. Operation : The clutch pedal must be pressed to change gears or start/stop the vehicle without stalling.
Automatic Transmission Cars
Clutch : Automatic transmission cars do not have a traditional clutch pedal that the driver operates. However, they do have an internal clutch mechanism or a torque converter that handles gear changes automatically. Operation : The driver does not need to manually engage or disengage the clutch, as the transmission does this automatically.
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
Clutch : Dual-clutch transmissions use two clutches but do not have a clutch pedal. The system automatically controls the clutches for seamless gear shifts. Operation : The DCT system allows for rapid gear changes without the driver needing to operate a clutch pedal.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
Clutch : CVTs typically do not have a traditional clutch mechanism. Instead, they use a belt and pulley system to provide an infinite number of gear ratios. Operation : CVTs do not require a clutch pedal, and the transmission adjusts gear ratios smoothly without distinct gear shifts.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Clutch : Electric vehicles generally do not have a clutch. EVs often use a single-speed transmission, which eliminates the need for a clutch altogether. Operation : Since there are no gears to shift, there is no need for a clutch in most electric vehicles.
Summary:
Manual Transmission Cars : Have a traditional clutch operated by a pedal. Automatic, DCT, and CVT Cars : Do not have a clutch pedal, but may have an internal clutch mechanism or alternative system for shifting gears. Electric Vehicles : Typically do not have a clutch due to their single-speed transmission.
? What are the signs of a worn-out clutch?
Slipping Clutch
Symptom : The engine revs increase, but the vehicle doesn't accelerate correspondingly. You may notice this especially when accelerating, climbing hills, or carrying heavy loads. Cause : The clutch disc is no longer gripping the flywheel effectively, often due to wear or oil contamination.
Difficulty Shifting Gears
Symptom : It becomes hard to shift gears, particularly when moving into first gear or reverse. The gearshift may feel stiff or resistant. Cause : A worn-out clutch disc, misaligned linkage, or issues with the hydraulic system (if applicable) can prevent the clutch from fully disengaging, making gear changes difficult.
Soft or Spongy Clutch Pedal
Symptom : The clutch pedal feels softer or spongier than usual, and you may need to press it all the way to the floor to disengage the clutch. Cause : Air in the hydraulic clutch system, worn-out clutch fluid, or a failing master or slave cylinder can cause this issue.
Noisy Clutch Operation
Symptom : Unusual noises such as squealing, grinding, or rattling when the clutch pedal is pressed or released. Cause : This could be due to a worn-out release bearing, misaligned clutch components, or a damaged pressure plate.
Clutch Pedal Vibrations (Clutch Judder)
Symptom : The clutch pedal vibrates or shudders when you engage or release it, particularly when starting from a stop. Cause : Clutch judder can result from a warped flywheel, uneven clutch disc wear, or contamination on the clutch surfaces (e.g., oil or grease).
Burning Smell
Symptom : A distinct burning smell, especially after heavy use of the clutch (e.g., in stop-and-go traffic or during aggressive driving). Cause : This odor often indicates that the clutch is slipping, causing excessive heat and wear on the clutch disc.
Clutch Pedal Feels Higher or Lower than Usual
Symptom : The engagement point of the clutch pedal has changed, either higher or lower than normal. Cause : A change in the engagement point can signal wear in the clutch disc, pressure plate, or a problem with the hydraulic system.
Poor Acceleration
Symptom : The vehicle does not accelerate as expected when you release the clutch, even though the engine speed increases. Cause : A slipping clutch may not be fully transferring the engine's power to the wheels, resulting in poor acceleration.
Car Jerks or Stalls During Gear Changes
Symptom : The car may jerk or even stall when you shift gears, indicating that the clutch is not engaging smoothly. Cause : This can happen due to a worn clutch disc or pressure plate, or because of improper clutch adjustment.
Hydraulic Fluid Leaks (for Hydraulic Clutches)
Symptom : You may notice fluid leaks under the vehicle near the clutch pedal area or master/slave cylinder. Cause : Leaks in the hydraulic system can reduce the effectiveness of the clutch and make the pedal feel soft or spongy.
Summary:
? How long does a clutch typically last?
Driving Habits
Aggressive Driving : Frequent hard acceleration, high RPM gear changes, and excessive clutch slipping can cause the clutch to wear out faster. Smooth Driving : Gentle gear changes and avoiding unnecessary clutch use can extend clutch life.
Type of Driving
City Driving : Stop-and-go traffic with frequent gear changes and clutch use can lead to quicker wear. Highway Driving : Fewer gear changes and less clutch use in highway driving can result in a longer-lasting clutch.
Vehicle Type and Load
Heavy Vehicles : Vehicles carrying heavy loads or towing trailers put more strain on the clutch, leading to faster wear. Performance Cars : High-performance vehicles with more powerful engines may also experience faster clutch wear.
Clutch Quality
OEM vs. Aftermarket : High-quality original equipment manufacturer (OEM) clutches may last longer than cheaper aftermarket options. Material : The material of the clutch disc and pressure plate also affects durability.
Maintenance
Proper Maintenance : Regular inspections, maintaining the hydraulic system (if applicable), and addressing any issues promptly can extend clutch life. Neglect : Ignoring signs of clutch wear or fluid leaks can lead to premature failure.
Driving Environment
Hilly or Mountainous Terrain : Driving in areas with steep inclines often requires more clutch use, leading to faster wear. Flat Terrain : Driving in flat areas typically results in less clutch strain.
Driving Skill
Experienced Drivers : Drivers who are skilled in using the clutch correctly, such as avoiding riding the clutch or holding it at the bite point, can significantly extend clutch life. New or Inexperienced Drivers : Those still learning may unintentionally cause more wear by not using the clutch smoothly.
Summary:
? What causes a clutch to wear out?
Riding the Clutch
What It Is : Keeping your foot on the clutch pedal while driving, even when it's not necessary. Effect : This causes the clutch to partially engage, leading to continuous friction between the clutch disc and flywheel, which accelerates wear.
Frequent Clutch Slipping
What It Is : Allowing the clutch to slip too much during acceleration, especially when starting from a stop or on inclines. Effect : Slipping generates excessive heat, which can damage the clutch disc, pressure plate, and flywheel, causing premature wear.
Aggressive Driving
What It Is : Rapid acceleration, hard shifting, and high RPM gear changes. Effect : Aggressive driving puts extra stress on the clutch, leading to faster wear, especially in high-performance or heavily loaded vehicles.
Heavy Loads and Towing
What It Is : Regularly driving with heavy loads or towing trailers. Effect : The extra weight requires more power to move the vehicle, causing the clutch to work harder and wear out faster.
Improper Gear Selection
What It Is : Shifting into the wrong gear, such as starting in a higher gear (e.g., second or third) instead of first. Effect : This can cause the clutch to struggle and slip as it tries to move the vehicle, leading to excessive wear.
Stop-and-Go Traffic
What It Is : Constant starting, stopping, and gear changing in heavy traffic. Effect : This increases the frequency of clutch use, leading to faster wear, particularly if the clutch is not fully disengaged during stops.
Holding the Clutch at the Bite Point
What It Is : Keeping the clutch at the biting point for extended periods, such as when waiting at traffic lights or on inclines. Effect : Holding the clutch at the bite point causes continuous friction, generating heat and wearing out the clutch components.
Poor Driving Technique
What It Is : Inexperienced or untrained drivers may misuse the clutch, such as not fully pressing the pedal during gear changes or releasing it too quickly. Effect : This can cause the clutch to engage and disengage improperly, leading to increased wear and potential damage.
Contaminated Clutch Surfaces
What It Is : Oil, grease, or other fluids leaking onto the clutch disc or flywheel. Effect : Contamination reduces the friction needed for the clutch to engage properly, causing it to slip and wear out faster.
Worn or Faulty Clutch Components
What It Is : Parts like the release bearing, pressure plate, or flywheel may become worn or damaged over time. Effect : Worn components can cause the clutch to engage unevenly or with insufficient force, leading to premature wear.
Improper Clutch Adjustment
What It Is : The clutch pedal or hydraulic system is not adjusted correctly, causing improper engagement or disengagement. Effect : An improperly adjusted clutch can cause slipping or incomplete engagement, both of which lead to faster wear.
Summary:
? What can I do if the clutch fails?
Immediate Actions
Stay Calm : Maintaining composure is crucial. Panicking can impair decision-making. Assess the Situation : Quickly assess the severity of the clutch failure. Determine if the clutch pedal feels different (e.g., stuck to the floor) or if there’s unusual noise or lack of engagement when shifting gears. Engage Emergency Brake : If the clutch fails while driving, immediately engage the emergency brake (handbrake) to bring the vehicle to a controlled stop. This brake is usually independent of the clutch system and can help slow down the vehicle safely.
Techniques to Manage Clutch Failure
If you are stationary, make sure the engine is switched off. Put the car in first gear. Switch the engine on, holding the ignition until the engine takes. The car will hop until the engine starts propelling it smoothly. When needing to change gears (whether up or down), move the gear to 'neutral' by taking your foot off the accelerator and put pressure on the gear lever until it slides out of gear. Then rev the engine and then take your foot off the gas pedal. Hold the gear lever with a slight pressure (not too hard), against the gear that you want to change to and keep the pressure there. When the engine revs drop to the correct RPM, you will find that the gear lever easily slides into gear. Repeat for each gear change. Before stopping, make sure the gear is in neutral. If possible, coast the vehicle to a safe location off the road or onto the shoulder. Reduce speed gradually using engine braking and the emergency brake.
Safety Precautions
Signal and Communicate : Use hazard lights to signal to other drivers that there’s an issue. If needed, use your horn intermittently to alert nearby drivers of your situation. Steer Safely : Maintain control of the steering wheel while slowing down. Avoid sudden or sharp maneuvers that could lead to loss of control.
After Stopping
Secure the Vehicle : Once safely stopped, engage the parking brake and shift the transmission to neutral (if possible). Turn off the engine to prevent any further issues with the clutch or transmission. Seek Assistance : Contact roadside assistance or a qualified mechanic to tow the vehicle to a repair facility. Attempting to drive with a failed clutch can cause further damage to the transmission or other components.
Preventative Measures
Regular Maintenance : Ensure your vehicle receives regular inspections and maintenance, including checking clutch fluid levels and replacing worn clutch components as recommended by the manufacturer. Learn Basic Techniques : Familiarize yourself with techniques such as engine braking and emergency braking, which can be invaluable in situations like clutch failure. Emergency Preparedness : Keep a roadside emergency kit in your vehicle with essentials such as reflective triangles, flashlight, and contact numbers for roadside assistance or towing services.
? Can you drive a car with a bad clutch?
Risks of Driving with a Bad Clutch:
Complete Clutch Failure : A severely worn or damaged clutch can fail entirely, leaving you unable to change gears or move the vehicle. Damage to the Transmission : Continuing to drive with a bad clutch can cause further damage to the transmission, flywheel, pressure plate, and other related components, leading to more costly repairs. Reduced Control : A malfunctioning clutch can make it difficult to control the vehicle, especially when starting from a stop, shifting gears, or climbing hills. This can increase the risk of accidents. Stalling : The car may stall frequently, especially in stop-and-go traffic or on inclines, making it unsafe to drive. Increased Wear and Tear : Driving with a bad clutch puts additional stress on other components of the drivetrain, potentially leading to more extensive damage.
Temporary Measures:
Avoid Heavy Traffic : Try to avoid situations where you need to stop and start frequently, as this will put more strain on the clutch. Use Low Gears : Stick to lower gears and avoid shifting as much as possible. You may need to start the car in second gear if first gear is unusable. Drive Smoothly : Accelerate and decelerate gently to reduce the load on the clutch. Plan Your Route : Choose a route with fewer stops, hills, or challenging driving conditions.
Summary:
? How can I make my clutch last longer?
Avoid Riding the Clutch
What to Do : Keep your foot off the clutch pedal when you're not shifting gears. Resting your foot on the clutch pedal can cause the clutch to partially engage, leading to unnecessary wear. Why It Helps : Prevents constant friction between the clutch disc and flywheel, reducing wear.
Use the Clutch Only When Necessary
What to Do : Only press the clutch pedal when you need to change gears or start/stop the vehicle. Avoid using the clutch to control speed or hold the vehicle on an incline. Why It Helps : Minimizes clutch engagement, reducing wear and tear.
Shift Gears Smoothly
What to Do : Engage the clutch fully before shifting gears, and release it smoothly after the shift. Avoid rapid gear changes or harsh shifts. Why It Helps : Reduces stress on the clutch components, leading to less wear.
Avoid Holding the Clutch at the Bite Point
What to Do : When waiting at traffic lights or in stop-and-go traffic, put the car in neutral instead of holding the clutch at the biting point. Why It Helps : Prevents excessive heat and wear from continuous clutch engagement.
Don't Use the Clutch to Control Speed
What to Do : Use your brakes to slow down instead of partially engaging the clutch. Downshift properly when necessary. Why It Helps : Reduces unnecessary friction and heat that can wear out the clutch.
Avoid Overloading Your Vehicle
What to Do : Stay within the recommended weight limits for your vehicle, especially when towing or carrying heavy loads. Why It Helps : Reduces the strain on the clutch, especially during acceleration and hill starts.
Use the Handbrake on Inclines
What to Do : When starting on a hill, use the handbrake to hold the vehicle in place rather than balancing the clutch and throttle. Why It Helps : Prevents clutch slipping and reduces wear during hill starts.
Don't Rush the Clutch Release
What to Do : When engaging the clutch, release it smoothly and at the right speed for the gear you're in. Avoid letting the clutch out too quickly, especially in low gears. Why It Helps : Ensures the clutch engages properly without unnecessary slippage.
Avoid Aggressive Driving
What to Do : Drive at moderate speeds, avoid unnecessary hard acceleration, and shift gears at the appropriate RPM. Why It Helps : Reduces the stress on the clutch and prolongs its life.
Maintain Your Vehicle Regularly
What to Do : Regularly check the clutch system, including the hydraulic fluid levels (if applicable), and address any issues like leaks or unusual noises promptly. Why It Helps : Ensures the clutch system is functioning properly and prevents small problems from becoming bigger, more expensive issues.
Learn Proper Clutch Control
What to Do : Practice good clutch control techniques, such as fully depressing the clutch pedal when shifting and avoiding unnecessary clutch use in traffic. Why It Helps : Reduces the likelihood of premature wear due to improper use.
Summary:
? What is clutch slipping?
How Clutch Slipping Happens:
Signs of Clutch Slipping:
Symptom : You press the accelerator, but the vehicle doesn’t accelerate as expected, or there’s a noticeable delay. Cause : The clutch isn’t fully engaging, so the power isn’t being transferred effectively to the wheels.
Symptom : The engine revs higher than normal when you try to accelerate, but the vehicle’s speed doesn’t increase proportionally. Cause : The clutch is slipping, allowing the engine to spin faster without transferring that power to the wheels.
Symptom : A strong, acrid smell, similar to burning rubber or burnt toast, coming from the engine area, especially after heavy use. Cause : The clutch disc is overheating due to excessive slipping and friction.
Symptom : The car struggles to move or maintain speed when towing a trailer or driving up a hill. Cause : The clutch slips under heavy load, reducing the vehicle’s ability to transmit power efficiently.
Symptom : Grinding, squealing, or other unusual noises when the clutch is engaged or disengaged. Cause : Worn clutch components can cause noise as they fail to engage properly.
Causes of Clutch Slipping:
Worn Clutch Disc : Over time, the friction material on the clutch disc wears down, reducing its ability to grip the flywheel effectively. Oil or Fluid Contamination : Leaks from the engine or transmission can contaminate the clutch disc, causing it to slip. Overheating : Repeated clutch slipping or aggressive driving can cause the clutch to overheat, leading to glazing of the clutch disc and reduced friction. Faulty Pressure Plate : A weakened or damaged pressure plate may not apply enough force to keep the clutch disc engaged with the flywheel. Misadjusted Clutch Pedal : If the clutch pedal is not adjusted correctly, it may not allow the clutch to fully engage or disengage, leading to slipping.
Consequences of Clutch Slipping:
Reduced Performance : The vehicle will feel underpowered and unresponsive, particularly during acceleration or when climbing hills. Increased Wear and Tear : Continuous slipping generates excessive heat and wear on the clutch components, leading to premature failure. Potential for Complete Clutch Failure : If left unaddressed, clutch slipping can worsen, eventually leading to complete clutch failure, where the vehicle can no longer move under its own power.
What to Do If Your Clutch Is Slipping:
Get a Professional Inspection : If you notice signs of clutch slipping, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible. Avoid Heavy Loads : If possible, avoid towing or carrying heavy loads until the clutch issue is resolved. Minimize Driving : Limit driving to reduce further damage to the clutch and transmission.
Summary:
? What should I do if my clutch is slipping?
Confirm the Symptoms
What to Do : Pay close attention to the signs of clutch slipping, such as loss of acceleration, high engine RPMs without corresponding speed increase, a burning smell, or difficulty driving uphill. Why It Helps : Accurately identifying the symptoms helps you determine whether the clutch is indeed slipping or if there might be another issue with your vehicle.
Avoid Heavy Loads
What to Do : If possible, avoid towing, carrying heavy loads, or driving up steep hills until the issue is resolved. Why It Helps : Reduces strain on the clutch, preventing it from slipping further and potentially worsening the problem.
Drive Carefully
What to Do : Drive conservatively to minimize clutch usage. Shift gears gently and try to avoid stop-and-go traffic where you would need to use the clutch frequently. Why It Helps : Minimizes further wear and tear on the clutch components.
Check Clutch Pedal Adjustment
What to Do : If you’re comfortable with basic car maintenance, check the clutch pedal’s free play. If it’s too tight or too loose, the clutch may not be fully engaging or disengaging. Why It Helps : Ensures that the clutch pedal is correctly adjusted, which might alleviate minor slipping issues.
Schedule a Professional Inspection
What to Do : Contact a trusted mechanic or auto repair shop to schedule an inspection of the clutch system. Why It Helps : A professional can accurately diagnose the issue and recommend the necessary repairs. They will check the clutch disc, pressure plate, flywheel, and other components for wear or damage.
Plan for Repairs
What to Do : Depending on the diagnosis, you may need to have the clutch replaced or repaired. This could involve replacing the clutch disc, pressure plate, release bearing, or even resurfacing the flywheel. Why It Helps : Timely repairs will restore your vehicle’s performance and prevent further damage to the transmission and drivetrain.
Consider Towing If Necessary
What to Do : If the clutch slipping is severe, or you’re unsure if the car is safe to drive, consider having your vehicle towed to the repair shop rather than driving it. Why It Helps : Prevents further damage and ensures your safety, especially if the clutch could fail completely while driving.
Avoid DIY Repairs Unless Experienced
What to Do : If you’re not experienced with car repairs, it’s best to leave clutch repairs to professionals. Clutch systems are complex, and improper repairs can lead to more issues. Why It Helps : Ensures that the repair is done correctly and safely, extending the lifespan of the new or repaired clutch.
Monitor After Repair
What to Do : After the clutch is repaired or replaced, keep an eye on its performance. Drive gently for the first few hundred miles to allow the new clutch components to settle in. Why It Helps : Ensures the new clutch operates smoothly and helps prevent early wear.
Summary:
? What is clutch drag?
How Clutch Drag Happens:
Symptoms of Clutch Drag:
Symptom : Gears may grind or be hard to engage, especially when shifting from one gear to another. Cause : The clutch disc is still partially engaged, making it difficult for the gears to mesh smoothly.
Symptom : The engine may stall when you attempt to start moving from a stop. Cause : The partial engagement of the clutch prevents a proper power transfer, causing the engine to struggle.
Symptom : You may hear unusual noises such as grinding or whining when the clutch is pressed. Cause : The clutch disc and flywheel are not fully separated, causing friction and noise.
Symptom : The vehicle may feel sluggish or unresponsive when accelerating. Cause : The clutch drag affects the power transfer from the engine to the transmission.
Causes of Clutch Drag:
Cause : The clutch pedal or linkage may be incorrectly adjusted, preventing the clutch from fully disengaging. Effect : Leads to partial engagement of the clutch disc.
Cause : Worn clutch disc, pressure plate, or release bearing can cause incomplete disengagement. Effect : The clutch disc may not separate completely from the flywheel.
Cause : Problems with the clutch master cylinder, slave cylinder, or hydraulic fluid can lead to insufficient clutch disengagement. Effect : Prevents the clutch from fully disengaging.
Cause : Oil, grease, or other contaminants on the clutch disc or flywheel. Effect : Reduces the friction required for proper disengagement.
Cause : Overheating due to excessive slipping or riding the clutch can cause the clutch disc to glaze, affecting its ability to disengage properly. Effect : Partial engagement of the clutch disc.
How to Address Clutch Drag:
What to Do : Ensure that the clutch pedal is properly adjusted according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Why It Helps : Ensures that the clutch fully disengages when the pedal is pressed.
What to Do : Have a mechanic inspect the clutch disc, pressure plate, and release bearing for wear and replace them if necessary. Why It Helps : Worn components can prevent proper disengagement.
What to Do : Inspect the clutch master and slave cylinders for leaks or issues, and ensure the hydraulic fluid is at the correct level. Why It Helps : Proper hydraulic function is crucial for clutch operation.
What to Do : Clean or replace any contaminated clutch components, such as the clutch disc or flywheel. Why It Helps : Ensures that the clutch can disengage properly without interference.
What to Do : Avoid aggressive driving or excessive clutch slipping that can cause overheating. Replace glazed components if necessary. Why It Helps : Reduces the risk of clutch drag due to overheating.
Summary:
? What is double-clutching?
How Double-Clutching Works:
Step 1 : Press the clutch pedal to disengage the current gear.
Step 2 : Move the gear lever to neutral.
Step 3 : Release the clutch pedal while in neutral, allowing the engine and transmission to equalize their speeds.
Step 4 : Briefly press the accelerator (throttle) to increase the engine speed to match the speed of the lower gear you will be engaging.
Step 5 : Press the clutch pedal again to re-engage the clutch.
Step 6 : Move the gear lever into the lower gear while the clutch pedal is still depressed.
Step 7 : Release the clutch pedal smoothly to engage the lower gear.
Benefits of Double-Clutching:
Benefit : Helps to synchronize the engine speed with the transmission speed, resulting in smoother gear transitions and less jerking or grinding.
Benefit : Reduces the stress on the gearbox, synchromesh, and other transmission components, potentially extending their lifespan.
Benefit : Helps maintain better control of the vehicle during downshifts, particularly in performance or high-speed driving situations.
Benefit : Particularly useful in older vehicles or those without modern synchronizers, where downshifting can be less smooth.
When to Use Double-Clutching:
Scenario : When you need to downshift to a lower gear while slowing down or preparing to accelerate.
Scenario : Particularly useful in vehicles with non-synchronized gearboxes or in classic cars.
Scenario : When driving aggressively on a track or during spirited driving, where smooth gear changes are crucial.
How Double-Clutching Differs from Heel-and-Toe:
Heel-and-Toe Technique : Often used in conjunction with double-clutching, where the driver uses the right foot to simultaneously brake and blip the throttle while downshifting. This helps maintain vehicle stability and balance during high-performance driving.
