
Cam
🛈 Info:
? Questions:
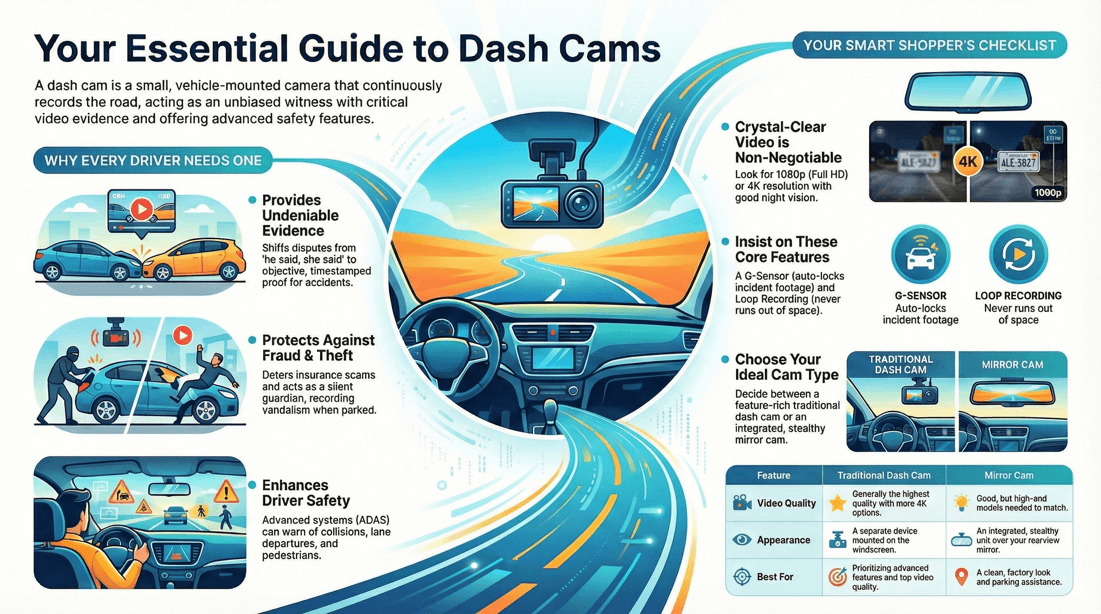
Advantages
Evidence in insurance claims, fraud or trial. Lower insurance premium. Deters theft. Record vandalism. Record of journeys. Alert emergency services. Lane and parking guidance. GPS Maps.
Type
DashCam: Mounted on dashboard. Simpler installation. MirrorCam: Mounted on mirror. Hidden from view of thieves. Smart Phone: Install cam app. Not as convenient to use as a dedicated car cam. Not as feature rich.
Features
Power:
Auto start - On and off when car is started or switched off. Hard wired to car, not cigarette lighter.
Storage:
Cloud. >64GB.
Connectivity:
3/4G. Blue Tooth. Wi-Fi. IP Address technology.
Camera:
Recording angle > 70 ° . 360 ° . Rear camera activated when reversing. HD: 4K. Low/Night lighting.
Screen:
Touchscreen. Size: 12 inch. Resolution: 1140px HD quality.
Display:
Front. Rear. Front and rear. Adjust view. Adjust brightness.
Metadata
Timestamp. GPS Coordinates. Speed. Vehicle identification. Lane lines.
Recording
Dual: Front and Rear. 30 fps. Bitrate: 18 000 kbps. CPL Filter: Filters sunlight reflections. Loop recording: Won't run out of space. G-Sensor: Mark current footage. Time lapse mode: Takes stills at preset intervals. Lock video clip: Prevents accidental deletion. Parking guard: Capture vandalism.
Features:
Speech recognition.
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System)
FCW (Forward Collision Warning) – warn you of an impending collision by detecting stopped or slowly moved vehicles ahead of your vehicle. PCW (Pedestrian Collision Warning) – warn you of an imminent collision with a pedestrian or cyclist ahead of your vehicle, allowing you time to react. LDW (Lane Departure Warning) – help you avoid crashes due to drifting or departing your lane by detecting lane markers. HMW (Headway Monitoring Warning) – warn you of an unsafe distance by constantly monitoring the distance to the vehicle ahead. FMW (Forward Movement Warning) – constantly monitors the distance and speed of the vehicle ahead. If it is monitored to start, an alert is issued.
🛈 Dash Cam vs Mirror Cam
Dash Cam
Mounting : Mounted on the dashboard or windshield. Recording : Typically records the road ahead, with some models offering dual-camera setups to record the interior or rear view. Display : Usually has a built-in screen for live viewing and playback. GPS : Often includes GPS for tracking speed and location. G-sensor : Detects impacts and saves recordings of incidents. Parking Mode : Records when the car is parked and detects motion or impacts.
Variety : A wide range of models and features to choose from. Placement Flexibility : Can be positioned to avoid obstructing the driver’s view. Specialized Functions : Advanced features like lane departure warnings and collision alerts. Clear Video : High-quality video resolution options, including 4K.
Space : Takes up space on the windshield or dashboard. Wiring : May require visible cables unless hardwired. Obstruction : Can potentially obstruct the driver’s view if not mounted correctly.
Mirror Cam
Mounting : Attaches over the existing rearview mirror. Recording : Typically records both front and rear views. Display : Integrated into the mirror, providing a live view and playback without an additional screen. Touchscreen : Many models feature a touchscreen for easy control. Rearview Assistance : Functions as a rearview camera, aiding in reversing and parking.
Space-Saving : Does not take up additional space on the windshield or dashboard. Stealthy : Less conspicuous and blends with the car's interior. Dual Function : Acts as both a rearview mirror and a dash cam, offering a seamless experience. Easy Installation : Simple to install over the existing mirror.
Limited Models : Fewer options compared to traditional dash cams. Screen Glare : The integrated display can cause glare or reflections. Mirror Size : May be bulkier than the original rearview mirror. Rear Camera Installation : The rear camera might require additional installation effort and wiring.
Comparison
Dash Cam : Generally offers higher video quality and better night vision. Mirror Cam : Video quality can vary, but high-end models provide comparable quality to dash cams.
Dash Cam : Installation varies; some require professional help for hardwiring. Mirror Cam : Usually easier to install, but the rear camera can be more complex.
Dash Cam : Often has more specialized features. Mirror Cam : Combines multiple functionalities, reducing the need for separate devices.
Dash Cam : Wide price range depending on features. Mirror Cam : Prices are generally competitive but can be higher for models with more features.
Conclusion
Choose a Dash Cam if you want the best video quality, more advanced features, and don't mind the additional space and installation effort. Choose a Mirror Cam if you prefer a more integrated, space-saving solution that combines the functions of a rearview mirror and a dash cam. This is particularly useful if you need assistance with reversing and parking.
? What is a Dash Cam?
Key Features of a Dash Cam:
Continuous Recording: Dash cams typically start recording automatically when the vehicle is turned on and continue recording until the vehicle is turned off. They often use a loop recording system, where the oldest footage is overwritten by the newest when the storage is full. G-Sensor: Many dash cams are equipped with a G-sensor, which detects sudden movements or impacts. If the sensor detects an incident, such as a collision, it automatically saves the footage from before, during, and after the event, preventing it from being overwritten. GPS Functionality: Some dash cams come with GPS functionality, which can record the vehicle's speed and location alongside the video footage. This data can be useful in case of an accident or dispute. Night Vision: To ensure clear recording in low light conditions, many dash cams feature infrared or other night vision technologies. Parking Mode: In parking mode, the dash cam can continue to monitor the surroundings of the vehicle even when it is parked and the engine is off. If it detects motion or an impact, it will start recording. Dual Cameras: Some dash cams have dual lenses, allowing them to record both the front and rear of the vehicle simultaneously.
Uses of a Dash Cam:
Accident Evidence: Dash cams provide video evidence in case of accidents, which can be useful for insurance claims or legal disputes. Protection Against Fraud: Dash cams can protect against fraudulent claims, such as staged accidents or false accusations. Monitoring Driving Habits: Some drivers use dash cams to monitor and improve their driving habits or to keep an eye on young or inexperienced drivers. Security: Dash cams can serve as a security device, capturing footage of break-ins, vandalism, or hit-and-run incidents when the vehicle is unattended. Recording Road Trips: Dash cams can also be used to record scenic drives or road trips, capturing memories and experiences.
Types of Dash Cams:
Single-Channel Dash Cam: Records only the front view of the vehicle. Dual-Channel Dash Cam: Records both the front and rear views. Triple-Channel Dash Cam: Some advanced models record the front, rear, and interior of the vehicle.
Legal Considerations:
? How does a Dash Cam work?
Power Source:
Connection: Dash cams are typically powered by plugging into the vehicle's 12V power socket (cigarette lighter socket) or through hardwiring directly into the vehicle's electrical system. Some dash cams have built-in batteries, but these usually only provide short-term power when the vehicle is off. Automatic Start: When the vehicle is started, the dash cam powers on automatically and begins recording. It usually turns off when the vehicle is turned off, unless it has a parking mode feature.
Recording Video:
Continuous Loop Recording: The dash cam records video in a continuous loop, meaning it overwrites the oldest footage with new footage once the memory card is full. This ensures that the camera is always recording the most recent events. Resolution and Frame Rate: Most dash cams offer various video resolutions, such as 1080p Full HD or 4K, and different frame rates (e.g., 30 fps, 60 fps). Higher resolution and frame rate provide clearer, smoother video but use more storage space.
Storage:
Memory Card: Dash cams store recorded video on a microSD card, typically ranging from 16GB to 128GB or more. The size of the card determines how much footage can be stored before being overwritten. File Segments: Video is usually saved in small segments (e.g., 1 minute, 3 minutes, 5 minutes), making it easier to find and review specific events.
Sensors and Features:
G-Sensor (Accelerometer): The G-sensor detects sudden changes in motion, such as a sharp turn, sudden braking, or a collision. When this occurs, the dash cam automatically locks and saves the current video segment to prevent it from being overwritten. GPS (Optional): Some dash cams are equipped with GPS modules that record the vehicle's speed, location, and route. This data is synced with the video footage and can be useful for reviewing travel history or in case of an accident . Night Vision: Dash cams with night vision use infrared lights or other technology to improve video quality in low-light conditions. Parking Mode: In parking mode, the dash cam can remain active when the vehicle is off, recording footage if it detects motion or impact near the vehicle. This is useful for capturing events like hit-and-runs or vandalism while parked.
Viewing and Managing Footage:
Screen: Some dash cams have a built-in screen for viewing live footage or playback directly on the device. Mobile App: Many dash cams have Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, allowing you to view and download footage on your smartphone via a dedicated app. Computer Transfer: Footage can be transferred to a computer by removing the memory card or using a USB cable. This allows for easier viewing, sharing, or saving of important clips.
Additional Features:
Voice Control: Some dash cams support voice commands for hands-free operation, such as starting or stopping recording. Driver Assistance: Advanced dash cams may include features like lane departure warning, forward collision warning, and other driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Privacy: While dash cams are legal in many places, there are laws regarding where they can be mounted, how they can be used, and what can be recorded. It's important to ensure your dash cam use complies with local regulations, especially regarding audio recording and privacy.
? Is a car camera legal?
Recording Public Roads
General Legality : In most places, it is legal to record video on public roads since there is no reasonable expectation of privacy in public spaces. Audio Recording : Some jurisdictions have stricter laws regarding audio recording. Many places require the consent of all parties involved when recording audio, so be aware of the local laws regarding this.
Placement and Visibility
Obstruction of View : Most jurisdictions have laws requiring that dash cams should not obstruct the driver’s view of the road. It’s essential to mount the camera in a way that complies with these regulations, often behind the rearview mirror. Size and Position : Ensure the dash cam is of a size and positioned in a way that doesn’t interfere with the vehicle’s safety features, such as airbags.
Privacy Concerns
Inside the Vehicle : Recording inside the vehicle may have privacy implications, especially if passengers are unaware they are being recorded. It is good practice to inform passengers if your dash cam records audio or video inside the car. Third-Party Privacy : Be cautious about recording individuals who have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as in private driveways or homes visible from the car.
Data Protection and Use
Storage and Security : Some regions have data protection laws that govern how recorded footage must be stored and protected. Ensure that your recordings are stored securely and that access is limited to authorized individuals. Usage of Footage : Using footage for purposes other than personal use, such as sharing publicly or for commercial use, may require additional consent or may be restricted by local laws.
Legal Implications
Evidence in Court : Dash cam footage is often admissible as evidence in court cases involving traffic violations, accidents , or disputes. However, its admissibility can depend on the jurisdiction and how the footage was obtained. Law Enforcement Requests : In some cases, law enforcement may request or subpoena dash cam footage as part of an investigation.
Country-Specific Regulations
United States : Generally legal, but regulations vary by state regarding windshield obstructions and audio recording. United Kingdom : Legal, but must not obstruct the driver's view. Audio recording is subject to privacy laws. Canada : Legal, but rules vary by province regarding windshield obstructions. European Union : Varies by country, with some countries having stricter privacy laws and regulations on data usage and recording in public spaces.
Best Practices for Using a Dash Cam Legally
Inform Passengers : Always inform passengers if the dash cam records audio or video inside the vehicle. Proper Installation : Mount the dash cam in a way that does not obstruct your view of the road. Review Local Laws : Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations regarding dash cam use in your jurisdiction. Secure Storage : Ensure that recorded footage is stored securely and used responsibly. Respect Privacy : Avoid recording private properties or individuals in situations where they have a reasonable expectation of privacy.
? Can Dash Cam footage be used in court?
Admissibility of Evidence:
Relevance: The footage must be relevant to the case at hand. For example, it can be used to show what happened during a traffic accident , confirm the behavior of drivers or pedestrians, or provide a timeline of events. Authenticity: The footage must be authenticated, meaning it must be shown that the footage is accurate and has not been tampered with. This may involve proving that the dash cam was functioning properly and that the video has not been edited or manipulated. Chain of Custody: The party presenting the footage may need to establish a clear chain of custody, showing how the footage was handled from the time it was recorded until it was presented in court.
Legal Considerations:
Privacy Laws: In some jurisdictions, recording audio or video without consent might violate privacy laws, particularly if the recording includes conversations. Footage recorded in public spaces is generally admissible, but laws vary by location, so it's important to know local regulations. State and Local Laws: The rules for using dash cam footage in court can vary widely depending on local laws. Some states or countries may have specific rules about how dash cam footage can be used as evidence.
Impact in Court:
Supporting Evidence: Dash cam footage can be compelling evidence, providing a visual and sometimes audio record of the events. It can help support or contradict witness testimony, clarify the sequence of events, or show conditions at the time of an incident (e.g., weather, traffic). Dispute Resolution: In traffic accident cases, dash cam footage can be crucial in determining fault, especially in situations where it's one driver's word against another’s. Criminal Cases: Dash cam footage can be used in criminal cases, such as hit-and-run incidents, road rage incidents, or other criminal activities that occur in or around the vehicle.
Challenges:
Quality of Footage: Poor video quality, unclear views, or technical issues with the footage may reduce its usefulness or credibility in court. Partial Footage: If the footage only captures part of the incident, it may not provide a complete picture, which could lead to questions about what occurred before or after the recorded event. Interpretation: Even clear footage may be subject to interpretation, and different parties may argue about what the video shows or does not show.
Presentation in Court:
Format: The footage must be presented in a format that the court can view. It may need to be transferred to a standard digital format if it was recorded in a proprietary format. Expert Testimony: In some cases, expert testimony may be needed to explain the footage, especially if it involves technical aspects like speed calculations, time stamps, or GPS data.
? Can a Dash Cam record while the car is parked?
Types of Parking Mode:
Motion Detection: The dash cam starts recording when it detects movement near the vehicle. This is useful for capturing footage of people or vehicles that come close to your car while it’s parked. Impact Detection (G-Sensor): The dash cam records when it detects a physical impact, such as someone hitting your car. This mode is particularly useful for capturing incidents like hit-and-runs. Time-Lapse Recording: The dash cam records continuously at a lower frame rate, creating a time-lapse video. This allows the dash cam to capture longer periods of time without using too much storage space. Low-Bit Rate Recording: The dash cam records continuously but at a lower quality to save storage space and batter y life. This ensures that you have footage of the entire time the car is parked, though the video may not be as clear as regular recordings.
Power Supply:
Hardwiring: For parking mode to function effectively, the dash cam often needs to be hardwired to your car’s battery . This setup allows the dash cam to draw power even when the car is turned off. Some hardwire kits come with a low-voltage cutoff feature to prevent the car battery from being drained completely. Battery Pack: Another option is to use an external battery pack specifically designed for dash cams. This allows the camera to operate in parking mode without drawing power from the car battery , thus preventing any risk of draining the car’s battery. Internal Battery: Some dash cams have built-in batteries that allow short bursts of recording while the car is off, but these typically only last for a few minutes and may not be suitable for extended parking mode usage.
Considerations:
Storage: Continuous or frequent recording in parking mode can fill up the memory card quickly, so it’s important to use a high-capacity memory card and ensure the dash cam supports loop recording (overwriting the oldest footage when the card is full). Sensitivity Settings: You can usually adjust the sensitivity of the motion or impact detection to avoid unnecessary recordings, such as from light breezes or minor vibrations. Temperature: If your vehicle is parked in extreme temperatures, ensure that the dash cam is designed to operate in those conditions, as heat can affect the performance of the camera and battery.
Legal and Privacy Considerations:
Local Laws: Be aware of local laws regarding surveillance and recording. In some places, recording audio without consent may be illegal, or there may be restrictions on where and how video recording can be conducted. Privacy: Consider privacy issues, particularly if the dash cam records in public spaces. It’s important to be mindful of where your dash cam is pointing and what it’s recording.
? Do Dash Cams record audio?
Default Setting:
Enabled by Default: Many dash cams come with audio recording enabled by default, meaning they will capture any sounds inside the vehicle, including conversations, music, and other noises. Toggle On/Off: Most dash cams offer the option to disable audio recording if you prefer not to record sound. This can usually be done through the dash cam’s settings menu or by pressing a dedicated button on the device.
Legal Considerations:
Consent Laws: In some regions, recording audio without the consent of all parties involved may be illegal. These are known as "two-party consent" or "all-party consent" laws. It’s important to be aware of the specific regulations in your area regarding audio recording. Privacy Concerns: Recording audio can raise privacy concerns, particularly if other passengers in the vehicle are unaware they are being recorded. It’s a good practice to inform passengers if your dash cam is recording audio.
Use Cases:
Evidence Collection: Audio recordings can be valuable in providing context to an incident, such as capturing conversations or sounds that may explain what happened before or during an event (e.g., an accident or an altercation). In-Car Conversations: Audio can also record conversations in the car, which could be useful for personal review or documentation purposes, but again, consider the legal implications.
Audio Quality:
Microphone Sensitivity: The quality of audio recording can vary depending on the microphone quality in the dash cam. Some dash cams may pick up background noise or may not clearly capture distant sounds. Noise Reduction: Some advanced dash cams include noise reduction features to improve audio quality by filtering out wind noise, engine noise, or other ambient sounds.
Situational Use:
Mute for Privacy: If you’re in a situation where you don’t want to record audio, such as during private conversations, you can mute the microphone. Some dash cams have a quick-access button to mute/unmute audio. Automatic Recording: In some models, audio recording is automatically tied to video recording. When the dash cam starts recording video (e.g., when the car is started), it also records audio unless manually disabled.
? How long does Dash Cam footage last?
Memory Card Size:
Larger Capacity, Longer Recording: The size of the memory card (typically measured in gigabytes, GB) directly affects how much footage the dash cam can store. Common sizes are 32GB, 64GB, 128GB, and 256GB. Estimated Storage Time: As a rough estimate: 32GB : About 4 to 6 hours of footage at 1080p resolution. 64GB : About 8 to 12 hours of footage at 1080p resolution. 128GB : About 16 to 24 hours of footage at 1080p resolution. 256GB : About 32 to 48 hours of footage at 1080p resolution. Higher Resolution = Less Time: Higher resolutions (e.g., 1440p or 4K) use more storage space, so the recording time will be shorter compared to 1080p.
Recording Mode:
Loop Recording: Most dash cams use loop recording, where the oldest footage is automatically overwritten by new footage once the memory card is full. This means that the dash cam can continuously record without running out of storage. Event Recording: Many dash cams are equipped with G-sensors that detect sudden movements or impacts (e.g., in an accident ). When an event is detected, the dash cam will save that particular segment of footage in a protected folder that is not overwritten by loop recording. This can reduce the overall storage available for continuous recording. Parking Mode: If the dash cam has a parking mode, it can record when the vehicle is parked. This footage may also be stored separately and may reduce the available recording time for driving footage.
Video Quality Settings:
Lower Quality, More Storage: Lowering the video quality (e.g., reducing resolution or frame rate) will allow more footage to be stored on the memory card. Compression: Some dash cams use advanced video compression technologies (like H.265/HEVC) to reduce file sizes without significantly compromising video quality. This allows more footage to be stored on the same memory card.
File Management:
Automatic Deletion: Dash cams will automatically delete or overwrite old footage to free up space, ensuring continuous recording. Important clips can usually be locked to prevent them from being overwritten. Manual Deletion: Users can manually delete footage from the memory card via the dash cam interface or by removing the memory card and managing files on a computer.
External Storage and Cloud Backup:
Cloud Storage: Some advanced dash cams offer cloud storage options where footage can be uploaded and stored online, allowing for potentially unlimited storage, depending on the subscription plan. External Hard Drives: Some dash cams can be connected to external hard drives for additional storage, though this is less common.
Summary:
? How do I retrieve and save Dash Cam footage?
Turn Off the Dash Cam:
Before removing the memory card or connecting the dash cam to a computer, make sure the dash cam is turned off to prevent any potential data corruption.
Remove the Memory Card:
Locate the memory card slot on your dash cam, usually a microSD card. Gently push the card inwards until it clicks, then release it. The card will pop out slightly, allowing you to remove it.
Insert the Memory Card into a Card Reader:
Use a microSD card adapter or a USB card reader if your computer doesn’t have a built-in card reader. Insert the memory card into the adapter or card reader, and then connect it to your computer.
Access the Dash Cam Files on Your Computer:
On your computer, open the file explorer or finder, and locate the memory card under "Devices" or "Drives." The dash cam footage is usually stored in folders organized by date and time, often labeled with the camera’s make or model.
Copy and Save the Footage:
Browse through the folders to find the footage you want to save. Video files are typically in formats like MP4, AVI, or MOV. Select the files you wish to save and copy them to your computer by right-clicking and selecting "Copy," then pasting them into a folder on your computer. Consider renaming the files with a date or description to make them easier to find later.
Alternative: Connect the Dash Cam Directly to the Computer:
Some dash cams allow you to connect directly to a computer via a USB cable. If your dash cam has this feature: Turn off the dash cam and connect it to your computer using a USB cable. Turn the dash cam back on. It should appear as an external drive on your computer. Follow the same steps as above to access, copy, and save the files.
Using Dash Cam Software or Mobile Apps:
Some dash cams come with dedicated software or mobile apps that allow you to view, download, and manage footage. PC Software: Install the dash cam’s software on your computer, then connect the dash cam or memory card. The software will guide you through accessing and saving the footage. Mobile App: If your dash cam has Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, you may be able to connect it to a mobile app on your smartphone. The app will allow you to download and save footage directly to your phone.
Backup the Footage:
Once you’ve saved the footage to your computer, consider creating a backup. You can store it on an external hard drive, USB drive, cloud storage, or another secure location.
Eject the Memory Card Safely:
If you’re using a memory card reader, be sure to safely eject the memory card from your computer before removing it to avoid any potential data loss. Reinsert the memory card into the dash cam if you plan to continue using it.
Review and Share the Footage:
Open the saved video files on your computer to review the footage. You can share the footage via email, social media, or upload it to cloud storage if needed.
Important Tips:
Check File Integrity: After copying, ensure the files are playing correctly without any corruption. Maintain Privacy: Be mindful of privacy laws and the sensitive nature of the footage if sharing with others. Regularly Transfer Footage: Regularly transfer and save important footage to prevent it from being overwritten, especially if your dash cam uses loop recording.
? Do I need a Dash Cam with GPS?
Benefits of a Dash Cam with GPS:
Accurate Location Data: A dash cam with GPS records the exact location where the footage was captured. This can be crucial in providing evidence for insurance claims or legal matters, as it shows where an incident occurred. Speed Monitoring: GPS-equipped dash cams can track your speed and display it alongside the video footage. This can be helpful in proving that you were driving within the speed limit if there’s a dispute. Route Tracking: The GPS function allows the dash cam to track your entire route. This can be useful for retracing your journey, checking the route taken by others using your vehicle, or reviewing your driving habits. Enhanced Evidence in Case of an Accident : The combination of video, location, and speed data can provide a more comprehensive picture of an event, making it easier to establish fault or defend against false claims. Time and Date Stamping: GPS-enabled dash cams automatically synchronize the time and date, ensuring that the footage is accurately timestamped without needing manual adjustment.
When You Might Not Need GPS:
Simple Documentation: If your primary goal is to record video footage for simple documentation or personal review, you might not need GPS functionality. A basic dash cam without GPS could suffice. Privacy Concerns: Some users prefer not to have their location and speed tracked for privacy reasons. If this is a concern for you, a non-GPS dash cam might be a better choice. Budget Considerations: Dash cams with GPS are generally more expensive than those without. If you’re on a tight budget and don’t need the additional features, you might opt for a more affordable model without GPS. Urban Driving: In densely populated urban areas, GPS signals can sometimes be inconsistent due to tall buildings or tunnels, which might make the GPS data less reliable. If you mostly drive in such areas, the benefits of GPS might be reduced.
Conclusion:
Choose a Dash Cam with GPS If: You want comprehensive evidence for legal or insurance purposes, drive in varied environments where location tracking could be beneficial, or need to monitor speed and routes for safety or record-keeping purposes. Skip GPS If: You’re mainly interested in basic video recording, want to save on costs, or have privacy concerns about being tracked.
? Can I install a Dash Cam myself?
Tools and Materials Needed:
Dash Cam Kit: Includes the dash cam, mount, power cable, and sometimes a trim tool. MicroSD Card: For storing footage. Power Source: Typically the 12V cigarette lighter socket or a hardwiring kit. Trim Tool (optional): Helps tuck the cable behind panels. Cable Clips (optional): To secure the cable along the windshield or dashboard.
Step-by-Step Installation:
The best place to mount a dash cam is usually behind the rearview mirror, where it won’t obstruct your view but still captures the road ahead.
Attach the Mount: Clean the windshield area where the mount will be attached. Peel off the adhesive backing or use the suction mount to secure it to the windshield. Attach the Dash Cam: Slide the dash cam onto the mount and adjust its angle to ensure it’s capturing the desired field of view.
Tuck the Cable: Starting from the dash cam, run the power cable along the edge of the windshield. Use the trim tool to tuck the cable behind the headliner, A-pillar, and down to the dashboard. Route to Power Source: Continue routing the cable to the power source, typically the 12V cigarette lighter socket. If you prefer a cleaner look, you can use a hardwiring kit to connect the dash cam directly to the car’s fuse box.
Plug the power cable into the dash cam and the other end into the power source (cigarette lighter or fuse box).
Insert the MicroSD card into the dash cam’s card slot, making sure it’s properly formatted if necessary.
Turn on your vehicle, and the dash cam should power up automatically. Check the video feed to ensure the camera angle is correct and that it’s recording properly.
If needed, use cable clips to secure any loose parts of the power cable along the windshield or dashboard.
Access the dash cam’s menu to adjust settings like resolution, loop recording, date/time, and GPS (if applicable).
