
DANGERS > PEDESTRIANS > BIZARRE
Bizarre
☠️ Alert:
? Questions :
⮟ How can drivers safely navigate around pedestrians exhibiting bizarre behavior? ⮟ What role do mental health issues play in bizarre pedestrian behavior? ⮟ How should bystanders react to bizarre pedestrian behavior? ⮟ Are there legal implications for pedestrians displaying bizarre behavior? ⮟ How can communities address and mitigate bizarre pedestrian behavior? ⮟ What are the best practices for emergency responders dealing with bizarre pedestrian behavior? ⮟ How does technology help in managing bizarre pedestrian behavior?
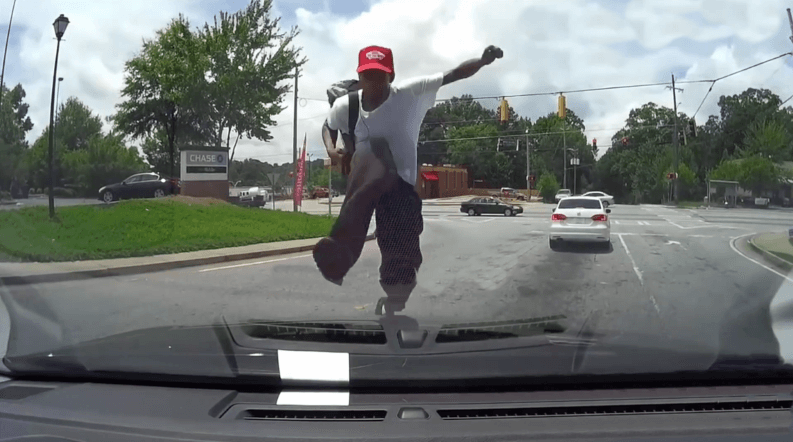

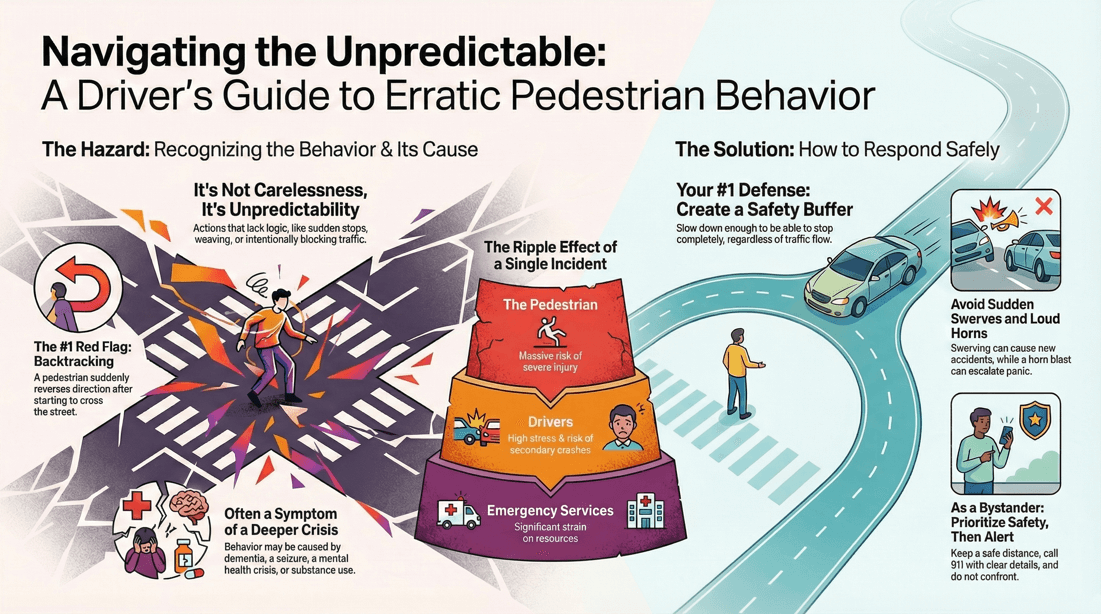
☠️ Dangers regarding bizarre pedestrian behavior
Increased Risk of Accidents
Erratic Pathways: Pedestrians behaving erratically may cross streets unpredictably, making it difficult for drivers to anticipate their movements and avoid collisions. Sudden Actions: Sudden or unexpected actions, such as running into traffic or stopping abruptly, increase the likelihood of accidents.
Poor Awareness: Pedestrians exhibiting bizarre behavior might be less aware of their surroundings, including traffic conditions and vehicle approaches. Nighttime Hazards: Unusual behavior, especially in low-light conditions, can make pedestrians less visible and harder for drivers to see.
Increased Risk of Injury
Falls and Collisions: Pedestrians displaying unusual behavior are at higher risk of physical injuries from falls, collisions with vehicles, or accidental impacts with objects. Lack of Protective Gear: Bizarre behavior might lead pedestrians to neglect safety measures, such as wearing reflective clothing or using crosswalks.
Dangerous Situations: Pedestrians might put themselves in dangerous situations, such as wandering into high-traffic areas or unsafe locations, increasing the risk of severe injuries.
Impact on Drivers
Sudden Braking: Drivers may need to make sudden stops or evasive maneuvers to avoid hitting pedestrians behaving unusually, which can cause rear-end collisions or loss of vehicle control. Distraction: Dealing with unpredictable pedestrian behavior can distract drivers from their primary task of safely navigating the road.
Driver Anxiety: Encountering pedestrians with bizarre behavior can increase driver stress and anxiety, affecting their overall driving performance and decision-making.
Legal and Liability Issues
Liability Disputes: Determining fault in accidents involving pedestrians with unusual behavior can be complex, potentially leading to legal disputes over liability and compensation. Insurance Complications: Insurance claims may be complicated by the presence of unusual pedestrian behavior, affecting settlements and coverage.
Traffic Violations: In some jurisdictions, pedestrians engaging in bizarre behavior might face legal consequences or fines, especially if their actions violate traffic laws.
Public Safety Concerns
Higher Accident Rates: Areas with frequent occurrences of bizarre pedestrian behavior might experience higher rates of accidents and injuries, affecting overall community safety. Emergency Services: Increased incidents related to bizarre pedestrian behavior can strain emergency services and resources.
Public Perception: Persistent issues with pedestrian safety can impact public perception of traffic safety and community well-being, leading to increased calls for intervention and policy changes.
Mental Health and Social Issues
Underlying Issues: Bizarre pedestrian behavior may indicate underlying mental health crises or substance abuse problems, posing additional challenges for support and intervention. Social Stigma: The visibility of such behavior can contribute to social stigma and misunderstanding about mental health issues.
Intervention: Individuals displaying bizarre behavior may require support from mental health professionals or social services, highlighting the need for effective intervention strategies.
Summary
? What constitutes bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Erratic Movements
Random Walking: Moving in an erratic or random manner, such as suddenly changing direction or pace without warning. Crossing Unpredictably: Crossing streets at unexpected points or suddenly entering the roadway without regard for traffic signals.
Abrupt Stops: Stopping abruptly in the middle of the road or walkway. Quick Movements: Making sudden, quick movements that are hard for drivers and other pedestrians to anticipate.
Disregard for Traffic Rules
Ignoring Crosswalks: Crossing streets away from designated crosswalks or pedestrian signals. Disregarding Signals: Failing to observe or obey traffic signals and signs.
Multiple Lanes: Attempting to cross multi-lane roads or highways without proper planning or safety measures. Backtracking: Walking back and forth across a street or road repeatedly.
Inappropriate or Hazardous Behavior
Intoxication: Exhibiting signs of impairment due to alcohol or drugs, leading to erratic or unsafe behavior. Disorientation: Showing signs of disorientation or confusion, which may affect their ability to navigate safely.
Obstructing Traffic: Blocking traffic lanes or walkways in a manner that impedes the flow of traffic. Dangerous Interactions: Engaging in behaviors that involve interacting with vehicles or road infrastructure in unsafe ways.
Mental Health or Cognitive Issues
Unusual Speech or Actions: Exhibiting speech or actions that are significantly out of the ordinary, potentially indicating a mental health crisis. Erratic Physical Actions: Engaging in physically unusual actions, such as walking in circles or performing repetitive motions.
Ignoring Surroundings: Demonstrating a lack of awareness of their surroundings, including traffic, other pedestrians, or environmental hazards. Unusual Reactions: Reacting inappropriately to normal traffic or environmental stimuli.
Safety Negligence
Dark Clothing: Wearing clothing that does not provide adequate visibility, especially in low-light conditions or bad weather. No Reflective Gear: Failing to use safety gear such as reflective vests or lights when required.
Walking on Highways: Walking on highways or roads where pedestrians are not allowed or where it is unsafe. Ignoring Safety Measures: Ignoring safety measures such as pedestrian barriers, signs, and signals.
Social or Behavioral Anomalies
Unusual Social Behavior: Exhibiting behavior that is markedly different from normal social interactions, potentially indicating distress or a crisis. Public Disturbances: Creating disturbances or engaging in behavior that attracts undue attention and disrupts normal traffic flow.
Summary
? What causes bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Medical Conditions
Psychiatric Disorders: Conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or severe depression can lead to unusual or erratic behavior. Cognitive Impairments: Dementia, Alzheimer's disease, or other cognitive disorders can affect judgment and spatial awareness.
Seizures: Individuals experiencing seizures might exhibit unusual movements or disorientation. Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis can affect motor control and coordination.
Substance Use
Impaired Judgment: Alcohol can impair cognitive functions and decision-making, leading to erratic or risky behavior. Coordination Issues: Alcohol impairs physical coordination, increasing the likelihood of stumbling or unsafe actions.
Recreational Drugs: Use of recreational drugs can cause hallucinations, confusion, and unpredictable behavior. Medications: Some prescription medications can have side effects that affect behavior, such as dizziness or drowsiness.
Environmental Factors
Low Light Conditions: Insufficient lighting can impair a pedestrian’s ability to see and be seen, leading to unusual or unsafe behavior. Weather Conditions: Adverse weather, such as fog, rain, or snow, can reduce visibility and affect movement.
Obstacles: Physical obstacles like construction zones or poorly maintained sidewalks can cause confusion or lead to erratic movements. Road Layout: Unfamiliar or complex road layouts might contribute to disorientation and unusual behavior.
Situational Factors
Emotional Distress: High levels of stress or personal crisis can impact behavior, leading to erratic or irrational actions. Emergency Situations: In emergencies, individuals may act unpredictably due to panic or urgent needs.
Peer Influence: Social pressures or group behavior can lead to unusual pedestrian actions, especially among younger individuals. Cultural Practices: Certain cultural practices or traditions might involve behaviors that are perceived as unusual in different contexts.
Cognitive and Developmental Factors
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Individuals with autism may exhibit behaviors that are perceived as unusual due to differences in sensory processing or social interaction. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD can lead to impulsive or inattentive behavior, affecting how a person navigates their environment.
Children: Young children may exhibit bizarre behavior due to lack of experience or understanding of road safety. Elderly: Older adults may experience cognitive decline affecting their ability to navigate safely.
Lack of Awareness or Education
Traffic Rules: Lack of understanding of traffic rules and pedestrian safety can lead to risky behavior. Safety Practices: Inadequate awareness of safety practices, such as using crosswalks or wearing visible clothing, can contribute to unusual actions.
Electronic Devices: Use of mobile phones or other devices can distract pedestrians and lead to unsafe behavior. Inattentiveness: General inattention to surroundings can result in erratic movements or poor decision-making.
Psychological and Emotional Factors
Exhaustion: Physical or mental fatigue can impair judgment and coordination, leading to unusual pedestrian behavior. Overstimulation: Being overwhelmed by sensory input or stress can affect how an individual navigates their environment.
Psychotic Episodes: Individuals experiencing psychotic episodes might exhibit bizarre behavior due to altered perceptions or thoughts.
Summary
? How can drivers safely navigate around pedestrians exhibiting bizarre behavior?
Stay Alert and Observant
Anticipate Unpredictability: Expect the unexpected and remain vigilant, especially in areas where pedestrians might display unusual behavior. Scan Regularly: Continuously scan the road and sidewalks for any signs of unusual or erratic pedestrian activity.
Behavior Indicators: Look for signs of bizarre behavior, such as unpredictable movements, disorientation, or erratic walking patterns. Environmental Cues: Be mindful of environmental factors that might contribute to pedestrian behavior, such as poor lighting or road conditions.
Adjust Driving Speed
In Uncertain Areas: Slow down in areas where pedestrian behavior is unpredictable or where visibility is limited. React Quickly: Reducing speed gives you more time to react to sudden movements or unexpected actions by pedestrians.
Increase Distance: Keep a greater distance from pedestrians and other vehicles to allow more time for emergency maneuvers if needed.
Use Defensive Driving Techniques
Anticipate Stops: Be ready to make sudden stops if a pedestrian suddenly enters your path or behaves unpredictably. Maintain Control: Ensure you have control of your vehicle and are prepared to react safely to unexpected situations.
Smooth Adjustments: Make gradual changes to speed and direction to avoid startling pedestrians or losing control of the vehicle. Use Signals: Signal your intentions well in advance if you need to change lanes or make turns near pedestrians.
Implement Safe Driving Practices
Observe Traffic Controls: Adhere to traffic signals, signs, and pedestrian crossings to ensure safe interactions with pedestrians. Yield to Pedestrians: Yield the right of way to pedestrians at crosswalks and designated crossing points.
Stay Focused: Minimize distractions, such as using mobile phones or adjusting controls, to maintain full attention on the road. Engage with the Environment: Be mindful of road conditions and pedestrian activity to anticipate and respond effectively.
Enhance Visibility and Communication
Headlights and Taillights: Ensure your headlights and taillights are functioning properly to increase your visibility to pedestrians, especially in low-light conditions. Turn Signals: Use turn signals to clearly communicate your intentions to pedestrians and other drivers.
Check for Awareness: When approaching pedestrians, make eye contact if possible to ensure they are aware of your presence. Communicate Intentions: Use your horn sparingly to alert pedestrians if they are in immediate danger or to signal your approach.
Be Mindful of Special Situations
Follow Instructions: If emergency responders or law enforcement are present, follow their instructions and adjust your driving accordingly. Clear Pathways: Ensure that you do not obstruct emergency vehicles or personnel attending to a pedestrian in distress.
Adapt to Weather: Adjust your driving according to weather conditions, such as rain or fog, which may affect pedestrian visibility and behavior. Watch for Road Hazards: Be aware of road conditions that could contribute to unusual pedestrian behavior, such as construction zones or damaged sidewalks.
Educate Yourself and Others
Know Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local traffic laws and regulations regarding pedestrian interactions and behavior. Stay Informed: Stay updated on safety practices and guidelines for interacting with pedestrians.
Community Engagement: Participate in or support community awareness programs that address pedestrian safety and behavior. Share Knowledge: Educate others about safe driving practices and the importance of being cautious around pedestrians.
Summary
? How can pedestrians avoid engaging in bizarre behavior?
Maintain Awareness and Focus
Avoid Distractions: Keep your attention on your surroundings. Avoid using mobile phones, listening to loud music, or engaging in activities that distract from your environment. Be Mindful of Traffic: Always be aware of approaching vehicles, traffic signals, and pedestrian crossings.
Act Purposefully: Move in a clear, deliberate manner. Avoid sudden or erratic movements that could confuse drivers or other pedestrians. Plan Your Route: Know your path and follow it without unnecessary deviations.
Follow Traffic Rules and Safety Practices
Cross Safely: Always use designated crosswalks and follow pedestrian signals at intersections. Wait for the Signal: Wait for the walk signal before crossing and only cross when it’s safe.
Respect Signs: Adhere to all traffic signs and signals intended for pedestrians, such as “Don’t Walk” or “No Crossing” signs. Be Patient: Follow posted guidelines and wait for safe conditions before crossing.
Stay Visible and Wear Appropriate Clothing
Enhance Visibility: Wear reflective clothing or accessories, especially in low-light conditions or poor weather. Carry Lights: Use a flashlight or wear a headlamp if walking in dark or dimly lit areas.
Choose Bright Colors: Opt for bright or high-visibility clothing to make yourself more noticeable to drivers.
Avoid Risky Behavior and Situations
Limit Substance Use: Avoid walking while under the influence of alcohol or drugs, which can impair judgment and coordination. Seek Alternatives: Use transportation services if you’re impaired or need to travel a long distance.
Stay on Sidewalks: Stick to sidewalks or designated walking paths. Avoid walking on highways or busy roads where pedestrians are not allowed. Be Cautious in Construction Zones: Navigate around construction areas or obstacles carefully, following any posted detours or instructions.
Manage Stress and Health
Seek Support: If experiencing emotional or psychological stress, seek professional help or support from friends and family. Practice Self-Care: Engage in activities that reduce stress and promote well-being, which can help maintain focus and stability.
Stay Fit: Regular physical activity helps improve balance, coordination, and overall health, reducing the likelihood of unusual behavior. Stay Hydrated and Rested: Ensure you’re well-hydrated and rested to maintain optimal cognitive and physical function.
Educate Yourself and Others
Understand Pedestrian Rules: Familiarize yourself with pedestrian safety rules and best practices for crossing streets. Stay Informed: Keep updated on local traffic regulations and safety tips.
Share Knowledge: Educate friends and family about pedestrian safety and the importance of following road rules. Participate in Programs: Engage in community programs or campaigns that focus on pedestrian safety and behavior.
Plan Ahead for Safe Navigation
Choose Safe Paths: Plan your routes to include safe crossings and well-lit areas. Avoid High-Traffic Times: If possible, avoid walking during peak traffic hours or in areas with heavy vehicle congestion.
Notify Others: If walking with others, communicate your intentions and ensure everyone follows safety practices. Seek Help if Needed: If you’re feeling unwell or unsure, ask for assistance from someone you trust.
Summary
? What role do mental health issues play in bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Cognitive Impairments
Disorientation: Individuals may become disoriented or confused about their surroundings, leading to unsafe or unpredictable movements. Memory Issues: Difficulty recalling familiar routes or understanding road safety rules can result in erratic behavior.
Impaired Judgment: TBI can affect decision-making and impulse control, leading to risky or unusual behavior. Coordination Problems: Reduced motor skills and coordination can cause stumbling or difficulty navigating.
Psychiatric Disorders
Hallucinations and Delusions: Individuals might experience visual or auditory hallucinations that affect their perception of reality, leading to erratic movements or unsafe actions. Disorganized Behavior: Symptoms may include disorganized thinking and behavior, impacting the ability to follow traffic rules.
Manic Episodes: During manic phases, individuals may engage in impulsive or risky behavior, such as crossing streets unpredictably or ignoring safety signals. Depressive Episodes: Depression can lead to low energy and decreased attention, potentially increasing the risk of accidents.
Anxiety Disorders
Panic Attacks: Sudden panic attacks can lead to irrational behavior or hasty decisions, such as running into the street without regard for traffic. Avoidance Behavior: Anxiety might cause individuals to avoid certain areas or move erratically due to fear.
Excessive Worry: Persistent worry about potential dangers can lead to over-cautious or unusual behavior, such as hesitating excessively before crossing the street.
Mood Disorders
Reduced Motivation: Individuals may exhibit low motivation or energy, affecting their ability to follow safety practices and navigate effectively. Self-Neglect: Symptoms such as neglecting personal safety and hygiene can increase vulnerability to accidents.
Seasonal Impact: Changes in mood related to seasonal variations may affect behavior and cognitive function, influencing pedestrian actions.
Developmental Disorders
Sensory Sensitivities: Sensory processing differences can affect how individuals respond to their environment, potentially leading to unusual reactions or movements. Social Interaction Challenges: Difficulties with understanding social cues can result in behavior that might seem out of place or unpredictable.
Impulsivity: Impulsive behavior can lead to unsafe actions, such as darting into traffic or making sudden movements. Inattention: Difficulty maintaining focus can cause problems with awareness and following traffic signals.
Substance-Related Disorders
Impaired Judgment: Intoxication can lead to impaired judgment and decision-making, resulting in risky pedestrian behavior. Coordination Issues: Substance use can affect motor skills and coordination, increasing the likelihood of stumbling or erratic movement.
Psychotic Disorders
Altered Perceptions: Experiences of delusions or hallucinations can impact a person’s ability to safely navigate their environment. Disorganized Actions: Behavior may become disorganized or unpredictable, affecting their interactions with traffic and pedestrians.
Strategies for Safety
Educate Individuals: Increase awareness and understanding of how mental health issues can affect pedestrian behavior. Provide Support: Offer support services and resources for individuals with mental health conditions to help them navigate safely.
Implement Safety Programs: Develop community programs that address pedestrian safety, particularly for those with mental health challenges. Enhance Environmental Design: Design public spaces with features that improve safety for all pedestrians, including those with mental health issues.
Summary
? How should bystanders react to bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Assess the Situation
Evaluate Behavior: Observe if the pedestrian’s behavior poses an immediate risk to themselves or others, such as walking into traffic or stumbling in dangerous areas. Check for Signs of Distress: Look for signs that the pedestrian might be in distress or experiencing a medical emergency.
Stay Safe: Maintain a safe distance from the pedestrian, especially if their behavior seems unpredictable or potentially dangerous. Avoid Confrontation: Approach the situation calmly and avoid actions that might escalate any potential conflict.
Alert Appropriate Authorities
Call for Help: If the pedestrian’s behavior poses a significant risk or if they appear to be in a medical emergency, call emergency services (911 or the local emergency number). Provide Details: Give a clear description of the situation, including the location, behavior of the pedestrian, and any potential hazards.
Report Dangerous Behavior: If the pedestrian is engaging in behavior that could endanger themselves or others (e.g., walking in traffic), contact local law enforcement to assist in managing the situation.
Offer Assistance If Safe
Be Non-Threatening: If it is safe and you feel comfortable, approach the pedestrian calmly and speak in a non-threatening manner. Ask if They Need Help: Offer assistance by asking if they need help or if there’s someone they can contact.
Guide Them Safely: If the pedestrian is disoriented or confused, offer to guide them to a safer location, such as a sidewalk or a nearby safe area. Help with Transportation: If appropriate and if the person is receptive, help them contact a ride service or arrange for transportation.
Promote Awareness and Safety
Raise Awareness: Engage in or support community awareness programs that educate the public on how to handle unusual pedestrian behavior safely. Share Knowledge: Inform friends and family about appropriate responses to bizarre pedestrian behavior and the importance of alerting authorities when necessary.
Support Safety Initiatives: Advocate for improvements in public spaces, such as better lighting, signage, and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, to reduce the risks associated with bizarre behavior.
Document the Situation
Record Details: If it’s safe to do so, take note of the pedestrian’s behavior, location, and any relevant details. This information can be useful when reporting to authorities. Avoid Recording Videos: Be cautious with recording videos or taking photos, as this might be perceived as intrusive or aggravating.
Provide Supportive Resources
Offer Resource Information: If the pedestrian seems receptive, provide information about local support services, mental health resources, or emergency shelters. Connect with Care: Encourage them to seek help from community resources or mental health services if appropriate.
Summary
? Are there legal implications for pedestrians displaying bizarre behavior?
Public Safety and Disorderly Conduct
Definition: Bizarre behavior that disrupts public peace or safety, such as aggressive behavior, loud disturbances, or erratic actions, can be classified as disorderly conduct. Legal Consequences: Individuals charged with disorderly conduct may face fines, community service, or even arrest. The specific penalties depend on local laws and the severity of the behavior.
Definition: If bizarre behavior is due to intoxication, it may be considered public intoxication or drunkenness, which is illegal in many places. Legal Consequences: Penalties can include fines, mandatory alcohol education programs, or even arrest. Some jurisdictions may offer diversion programs for first-time offenders.
Endangerment and Safety Violations
Definition: Behavior that puts others at risk, such as wandering into traffic or blocking roadways, may be considered endangerment. Legal Consequences: Charges could be filed if the behavior results in harm to others or causes significant disruption. Penalties may include fines or mandatory safety courses.
Definition: If bizarre behavior affects traffic flow or safety, such as walking in traffic lanes or causing accidents, it may lead to traffic-related legal issues. Legal Consequences: Individuals might face fines or be held liable for any resulting accidents or damages. Law enforcement may issue citations or orders to appear in court.
Mental Health and Medical Interventions
Definition: In some jurisdictions, individuals displaying bizarre behavior may be subject to mental health evaluations or interventions under mental health laws. Legal Consequences: Authorities may detain individuals for psychiatric evaluation or treatment if they are deemed a danger to themselves or others. These actions are typically guided by mental health statutes and require adherence to legal procedures.
Definition: If bizarre behavior indicates a severe mental health crisis, individuals may be involuntarily committed for evaluation and treatment. Legal Consequences: Involuntary commitment usually involves a legal process and may require court orders. Individuals have rights to legal representation and can challenge the commitment if they believe it is unjustified.
Criminal Charges
Definition: If bizarre behavior involves criminal activities, such as vandalism, assault, or theft, individuals may face criminal charges. Legal Consequences: Penalties vary based on the nature and severity of the offense, ranging from fines to imprisonment. Criminal charges are handled through the judicial system and may involve legal proceedings.
Definition: Individuals exhibiting bizarre behavior that involves illegal actions may be arrested and detained by law enforcement. Legal Consequences: Arrests lead to legal processes, including potential court appearances and criminal records, depending on the outcome of the case.
Civil Liabilities
Definition: If bizarre behavior causes property damage or personal injury, individuals may be held civilly liable for the damages. Legal Consequences: Civil lawsuits may be filed by affected parties seeking compensation for damages. The outcome depends on the specifics of the incident and the legal proceedings.
Summary
? How can communities address and mitigate bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Increase Public Awareness and Education
Conduct Awareness Programs: Implement public awareness campaigns about pedestrian safety, focusing on the impact of mental health and substance use on pedestrian behavior. Educational Workshops: Offer workshops and seminars to educate community members, including pedestrians and drivers, on recognizing and responding to unusual behavior.
Integrate Safety Education: Incorporate pedestrian safety and mental health awareness into school curricula and community education programs. Promote Safe Practices: Encourage safe pedestrian practices through community outreach and local events.
Enhance Environmental Design
Design Safe Spaces: Ensure that sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian areas are well-maintained and free from obstructions that could contribute to stumbling or erratic behavior. Improve Lighting: Enhance street and sidewalk lighting to increase visibility, especially in areas where unusual behavior might occur.
Implement Alerts: Use electronic warning systems or signs to alert drivers of pedestrian crossings and potential hazards. Add Reflective Markings: Use reflective paint or materials to improve visibility of pedestrian crossings and pathways.
Support Mental Health and Substance Use Services
Provide Support Services: Ensure access to mental health and substance use treatment services for individuals who may be at risk of engaging in bizarre behavior. Promote Community Resources: Make information about local mental health resources and support services readily available to the community.
Collaborate with Professionals: Work with healthcare providers to address the needs of individuals displaying unusual behavior and ensure they receive appropriate care.
Implement Community Policing and Support
Train Officers: Train law enforcement and community patrol officers to recognize and respond to unusual pedestrian behavior appropriately. Foster Relationships: Build strong relationships between law enforcement and community organizations to better address public safety concerns.
Establish Support Groups: Develop community support groups or networks that provide assistance and resources for individuals struggling with mental health or substance use issues. Promote Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between community organizations, local government, and social services to address underlying issues.
Improve Traffic Management and Safety Measures
Reduce Speed Limits: Lower speed limits in areas with high pedestrian traffic to reduce the risk of accidents. Enhance Crossings: Use pedestrian refuge islands, raised crosswalks, and other traffic calming measures to improve safety at crossings.
Analyze Data: Collect and analyze data on pedestrian behavior and traffic incidents to identify patterns and areas needing improvement. Adjust Policies: Use data to inform and adjust traffic management policies and safety measures.
Foster Community Engagement and Support
Organize Events: Host community events that promote pedestrian safety and mental health awareness. Support Local Initiatives: Support local initiatives and programs aimed at improving public safety and addressing mental health concerns.
Engage Volunteers: Create opportunities for community members to volunteer in roles that support pedestrian safety and assist those in need.
Develop and Promote Effective Policies
Support Legislation: Advocate for policies and legislation that address pedestrian safety, mental health support, and substance use treatment. Enforce Regulations: Ensure that existing safety regulations and standards are enforced effectively.
Develop Community Plans: Develop and implement community safety plans that address pedestrian behavior and provide guidelines for managing unusual behavior. Review and Update: Regularly review and update safety plans based on community needs and emerging issues.
Summary
? What are the best practices for emergency responders dealing with bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Assess the Situation
Assess Risk: Determine if the pedestrian’s behavior poses a risk to themselves or others, such as walking into traffic or showing signs of distress. Secure the Scene: Ensure the area is safe for both the pedestrian and emergency responders, and if necessary, control traffic or use barriers.
Monitor Actions: Pay attention to the pedestrian’s behavior, demeanor, and any potential signs of medical or psychological issues. Identify Needs: Determine if the pedestrian requires medical attention, psychological support, or both.
Approach with Caution and Empathy
Maintain Calmness: Approach the pedestrian in a calm, non-threatening manner to avoid escalating the situation. Speak Clearly: Use clear and simple language when communicating with the pedestrian.
Understand Their Perspective: Approach with understanding and empathy, recognizing that the pedestrian may be experiencing distress or confusion. Offer Reassurance: Provide reassurance and support to help them feel safe and understood.
Ensure Personal and Public Safety
Position Safely: Guide the pedestrian to a safe location away from traffic or hazardous areas if necessary. Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE to protect yourself and the pedestrian.
Control Traffic Flow: If the pedestrian is in a dangerous location, use traffic control measures such as setting up roadblocks or using warning lights. Coordinate with Other Responders: Work with law enforcement or traffic management to ensure safety and manage the situation effectively.
Provide Appropriate Assistance
Assess Health: Conduct a quick health assessment to check for any immediate medical needs or injuries. Provide First Aid: Administer first aid if needed and arrange for further medical evaluation if necessary.
Offer Support: If the pedestrian appears to be experiencing a mental health crisis, provide support and calm them down. Contact Mental Health Professionals: Arrange for mental health professionals or crisis intervention teams to provide appropriate care if required.
Use Communication and Coordination
Gather Information: Ask the pedestrian simple questions to gather information about their condition and needs. Explain Actions: Clearly explain what actions you are taking and why, to help reduce confusion or anxiety.
Involve Relevant Agencies: Coordinate with relevant agencies such as mental health services, social workers, or specialized crisis teams. Follow Protocols: Adhere to established protocols and procedures for handling unusual or bizarre behavior.
Document and Report
Document the Situation: Keep detailed records of the pedestrian’s behavior, actions taken, and any interactions with other responders. Report Findings: Provide a clear report to relevant agencies or follow-up services to ensure appropriate ongoing care.
Conduct Debriefings: After the situation is resolved, conduct debriefings to review what occurred and identify any areas for improvement. Update Procedures: Use feedback to update procedures and training for handling similar situations in the future.
Engage in Follow-Up
Check on Well-being: Follow up to ensure that the pedestrian receives the necessary care and support. Provide Resources: Offer information about support services or resources that may be helpful for their situation.
Coordinate Care: Work with community resources to provide ongoing support and assistance to the pedestrian if needed.
Summary
? How does technology help in managing bizarre pedestrian behavior?
Surveillance and Detection
Real-Time Monitoring: CCTV cameras can monitor pedestrian behavior in real-time, allowing authorities to detect unusual or hazardous activities promptly. Pattern Recognition: Advanced video analytics can identify patterns and anomalies in pedestrian behavior, triggering alerts for potential issues.
Behavioral Analysis: Sensors embedded in infrastructure can detect abnormal pedestrian movements or behaviors, such as stumbling or erratic walking. Environmental Monitoring: Sensors can also monitor environmental conditions (e.g., road conditions, weather) that might contribute to unusual behavior.
Communication and Alerts
Automated Alerts: Automated systems can send alerts to emergency services when unusual pedestrian behavior is detected, speeding up the response time. Public Alerts: Systems can also alert the public through signs, notifications, or mobile apps about potential hazards or disruptions.
Crowdsourced Information: Apps and platforms allow bystanders to report unusual pedestrian behavior quickly, providing valuable information to responders. Real-Time Updates: Responders can receive real-time updates and location information to manage incidents more effectively.
Traffic Management
Adaptive Control: Traffic lights can adjust in response to real-time pedestrian behavior, such as delaying signals to accommodate pedestrians displaying erratic behavior. Crossing Assistance: Enhanced pedestrian signal systems can provide additional guidance or warnings based on observed behaviors.
Safety Alerts: Vehicles equipped with V2I technology can receive alerts about pedestrians in unusual positions or exhibiting bizarre behavior, improving driver awareness and safety.
Data Analysis and Predictive Modeling
Pattern Detection: Analyzing data from surveillance cameras and sensors helps identify trends and recurring issues related to pedestrian behavior. Predictive Models: Predictive analytics can forecast potential problem areas and times when bizarre behavior is likely, allowing for proactive measures.
Data Integration: Integrated systems can compile data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of pedestrian behavior and incidents. Resource Allocation: Data-driven insights help allocate resources effectively and improve response strategies.
Mobile Technology and Apps
Personal Safety: Apps designed for personal safety can help pedestrians stay alert and avoid dangerous situations, providing real-time alerts and emergency contact options. Navigation Assistance: Apps with enhanced navigation features can assist pedestrians in finding safe routes and avoiding hazardous areas.
Emergency Services Integration: Apps can facilitate communication between pedestrians, emergency services, and responders, providing essential information and coordination.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Enhanced Awareness: AR applications can overlay safety information and guidance on the pedestrian’s view, helping them navigate safely and avoid potential hazards. Real-Time Assistance: AR can provide real-time feedback and warnings based on the pedestrian’s behavior and surroundings.
Simulation Training: VR can be used for training emergency responders and pedestrians on how to handle and respond to unusual behaviors effectively. Scenario Planning: VR simulations can help prepare for various scenarios involving bizarre pedestrian behavior and improve response strategies.
Health Monitoring Technology
Health Tracking: Wearable devices can monitor vital signs and health indicators, providing data that can help identify individuals who may be experiencing medical issues affecting their behavior. Emergency Alerts: Wearables can send alerts to emergency contacts or services if abnormal health patterns are detected.
Data Sharing: Health data from wearables can be shared with emergency responders to provide more accurate information about the pedestrian’s condition.