
Aggressive
Brake checking: ⮟ 📹 Goes Wrong ⮟ 📹 Irritant ⮟ 📹 Truck ⮟ 📹 Cutting-off ⮟ 📹 Impatience ⮟ 📹 Tailgating ⮟ 📹 Lane changing ⮟ 📹 Side swiping Striking: ⮟ 📹 Pedestrians ⮟ 📹 Vehicles ⮟ 📹 Throwing ⮟ 📹 Fleeing
🛈 Info:
💡 Tips:
? Questions:

📹 Truck
📹 Cutting-Off
📹 Impatience
📹 Tailgating
📹 Lane Changing
📹 Side Swiping
📹 Striking
Pedestrians
📹 Throwing
📹 Fleeing
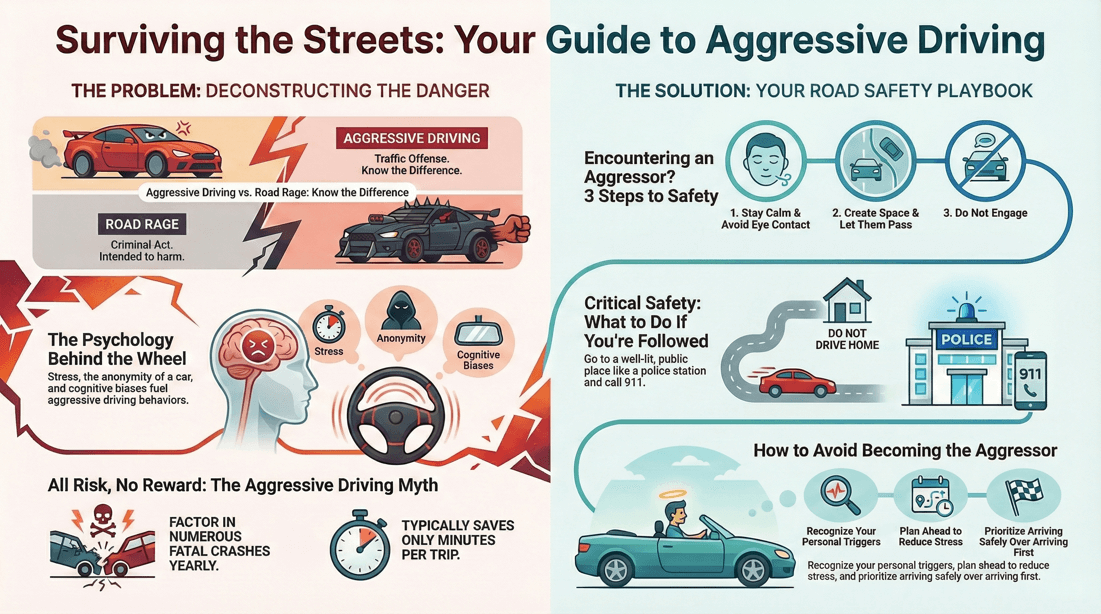
🛈 Aggressive driving vs. road rage
Aggressive Driving
Speeding excessively Frequent and abrupt lane changes without signaling Running red lights or stop signs Cutting off other drivers Blocking other cars from changing lanes
Road Rage
Deliberately cutting off another vehicle Physically confronting another driver Verbal abuse, including yelling and obscene gestures Intentionally ramming or sideswiping another vehicle Brandishing or using a weapon
Key Differences
Aggressive Driving: Typically involves actions that are dangerous but not directly confrontational. Road Rage: Involves direct confrontation and aggressive, violent behavior towards another driver.
Aggressive Driving: Generally less severe but still dangerous and illegal. Road Rage: More severe, involving intentional harm or threats.
Aggressive Driving: Often unintentional in the sense that the driver is reacting to frustration rather than seeking to harm others. Road Rage: Intentional, with a focus on confronting or harming another driver.
Prevention Tips
Stay calm and patient , even in heavy traffic or when delayed. Avoid engaging with aggressive drivers; do not make eye contact or respond to their actions. Use techniques like deep breathing or listening to calming music to manage stress .
Implement stricter enforcement of traffic laws related to aggressive driving. Educate the public about the dangers of aggressive driving and road rage through campaigns. Provide anger management resources for drivers who exhibit frequent aggressive driving behaviors.
🛈 Psychology of aggressive driving
Emotional Factors
Anger and Frustration: These are primary emotional drivers of aggressive driving. Situations like traffic congestion , being cut off , or perceived slights can trigger anger, leading some drivers to express this anger through aggressive driving behaviors. Stress : High levels of stress, whether related to driving conditions or external life pressures, can decrease patience and increase irritability, contributing to aggressive driving. Impulse Control: Individuals with lower impulse control may be more likely to engage in aggressive driving behaviors as a spontaneous reaction to road incidents.
Cognitive Factors
Risk Perception: Aggressive drivers often have a distorted perception of risk, underestimating the dangers associated with their driving behaviors. Attribution Bias: Aggressive drivers may attribute other drivers' behavior to personal flaws or hostile intentions, rather than to external factors, leading to anger and aggression. Dehumanization: Aggressive drivers may view other drivers less as people with their own needs and more as obstacles to their goals, making it easier to justify aggressive actions against them.
Personality Traits
Aggression and Hostility: Individuals with generally aggressive or hostile personality traits are more likely to engage in aggressive driving. Sensation Seeking: Those who seek high levels of stimulation and excitement may find aggressive driving to be a source of thrill. Narcissism: Narcissistic traits, such as a sense of entitlement and superiority, can lead to aggressive driving behaviors, as these individuals may believe traffic rules are less applicable to them.
Social and Environmental Influences
Cultural Norms: In some cultures or communities, aggressive driving may be more socially accepted or even encouraged, influencing individual behavior. Modeling: Observing and mimicking aggressive driving behaviors from parents, peers, or media can normalize these actions. Anonymity: The anonymity of being in one's vehicle can embolden individuals to act out aggressively, believing they are less likely to face consequences.
Mitigating Aggressive Driving
Educational Programs : Teaching drivers about the dangers of aggressive driving and strategies for managing anger and stress on the road. Law Enforcement: Implementing and enforcing laws to penalize aggressive driving behaviors, thereby increasing perceived risks of such actions. Mental Health Support: Offering resources for individuals to address underlying issues such as anger management, stress, and impulse control. Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about the consequences of aggressive driving and promoting a culture of patience and respect on the roads.
🛈 Aggressive driving and road safety
Impact on Road Safety
Increased Accident Risk: Aggressive driving behaviors, such as speeding , tailgating , and erratic lane changes , significantly increase the risk of collisions. These behaviors can lead to loss of vehicle control, reduced reaction time to avoid hazards, and increased severity of crashes. Intimidation and Stress for Other Drivers: Aggressive drivers can intimidate other road users, causing stress, confusion, or panic, which may lead to unsafe reactions or accidents. Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety: Aggressive drivers are less likely to yield to pedestrians and cyclists or give them the necessary space, leading to higher risks of accidents involving vulnerable road users. Chain Reactions: One aggressive driver can trigger aggressive responses from others, leading to a chain reaction of unsafe driving behaviors across multiple drivers.
Strategies for Mitigation
Law Enforcement and Penalties: Strong enforcement of traffic laws, including the use of speed cameras, increased patrols, and hefty penalties for aggressive driving offenses, can deter aggressive behaviors. Education and Awareness: Educational programs that highlight the dangers of aggressive driving and teach emotional regulation, stress management, and defensive driving techniques can help reduce aggressive driving. Road Design: Implementing road designs that reduce congestion and frustration among drivers, such as adding more lanes, improving traffic flow, or creating separate lanes for bicycles, can help mitigate aggressive driving behaviors. Technology: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) such as adaptive cruise control , lane-keeping assist , and collision avoidance systems can help prevent accidents caused by aggressive driving. Cultural Change: Promoting a culture of patience and respect on the roads through public awareness campaigns and community initiatives can lead to more courteous driving behaviors. Reporting Systems: Encouraging the reporting of aggressive drivers to authorities with mechanisms such as hotline numbers or online platforms can help in identifying and penalizing such drivers.
Conclusion
💡 Tips when you encounter aggressive drivers
Stay Calm
Keep Your Cool: Take deep breaths and remain calm. Don't let another driver's aggression provoke you into responding aggressively. Avoid Eye Contact: Aggressive drivers may see eye contact as a challenge. Focus on the road instead.
Give Them Space
Let Them Pass: If it's safe, move over and let the aggressive driver pass. Don't try to block or impede their progress. Increase Following Distance : Maintain a safe distance between your car and the aggressive driver's vehicle to reduce the risk of a collision.
Avoid Engagement
Don't Respond: Avoid making gestures, honking excessively, or shouting. Any form of retaliation can escalate the situation. Stay Out of Conflict: If the aggressive driver is trying to engage with you, ignore them and continue driving safely.
Use Your Defensive Driving Skills
Stay Aware : Keep an eye on the road and be aware of your surroundings. Anticipate possible hazards created by the aggressive driver. Plan an Escape Route : Always have an escape route in mind in case you need to avoid a dangerous situation quickly.
Report Dangerous Behavior
Call for Help: If the aggressive driver is putting others in danger, pull over safely and call the police. Provide as much information as possible, such as the vehicle's make, model, color, and license plate number.
Avoid Stopping
Don't Stop: If the aggressive driver is following you, do not stop or get out of your car. Continue driving to a public place or the nearest police station.
Stay Visible and Safe
Use Your Lights: Keep your headlights on, especially at night or in bad weather , to remain visible. Lock Your Doors: Ensure your doors are locked in case the aggressive driver tries to confront you physically.
Practice Patience
Be Patient: Understand that some drivers may be stressed or in a hurry. Patience and understanding can help de-escalate the situation.
Avoid High-Risk Areas
Stay on Main Roads: Avoid secluded or poorly lit areas where it's harder to get help if needed. Use Well-Traveled Routes: Stick to well-known and busy roads where there is more traffic and potential witnesses.
Seek Help if Harassed
Drive to a Safe Place: If you feel threatened, drive to a police station, fire station, or a well-lit public area with people around. Use Your Horn: If necessary, use your horn to attract attention and signal for help.
💡 Tips when you encounter an aggressive driver tailgating you
Stay Calm
Keep Your Cool: It's crucial to remain calm and composed. Don't let the tailgater's behavior affect your driving.
Avoid Confrontation
Don't React: Avoid making gestures, brake checking , or engaging with the tailgater in any way. Stay Focused: Keep your attention on the road and your surroundings.
Safely Move Over
Signal and Change Lanes: If it's safe to do so, signal and move to the right lane to let the tailgater pass. Find a Safe Spot: If you're on a single-lane road, look for a safe place to pull over and let them go around you.
Maintain a Safe Speed
Follow Speed Limits: Maintain a safe and consistent speed, adhering to the speed limit. Don't speed up just to get away from the tailgater. Don't Slow Down Suddenly: Avoid slowing down abruptly, as this could cause an accident.
Increase Your Following Distance
Create Space Ahead: Increase the distance between your car and the vehicle in front of you to give yourself more reaction time and reduce the risk of a collision.
Use Your Signals
Signal Early: Use your turn signals well in advance to indicate your intentions. This gives the tailgater more time to react.
Stay in the Right Lane
Keep to the Right: On multi-lane roads, stay in the right lane and use the left lane for passing only.
Don't Escalate the Situation
Avoid Eye Contact: Eye contact can be seen as confrontational. Keep your focus on the road. Stay Calm: Take deep breaths and remind yourself that your safety is the priority.
Report Dangerous Behavior
Call for Help: If the tailgater is driving dangerously or you feel threatened, pull over safely and call the police. Provide details such as the vehicle's make, model, color, and license plate number.
Seek a Safe Place
Drive to a Public Area: If you can't shake the tailgater, drive to a busy public area, police station, or gas station where there are people around.
Use Your Hazard Lights
Signal a Problem: Briefly turning on your hazard lights can signal to the tailgater that there might be an issue, prompting them to back off. Use this sparingly and only if you feel it might help.
Avoid Unfamiliar Routes
Stick to Familiar Roads: Stay on familiar and well-traveled routes where you feel more comfortable and safe.
? How can I avoid becoming an aggressive driver?
Self- Awareness
Recognize Triggers : Identify what situations or behaviors by other drivers trigger your aggression. Stay Calm : Practice deep breathing or other relaxation techniques when you start to feel stressed.
Planning and Preparation
Leave Early : Give yourself plenty of time to reach your destination so you're not rushed. Plan Your Route : Avoid known congested areas and high-traffic times if possible.
Positive Attitude
Be Courteous : Treat other drivers with respect and courtesy, even if they are not doing the same. Empathize with Others : Consider that other drivers might be having a bad day or could be dealing with emergencies.
Safe Driving Habits
Obey Traffic Laws : Follow speed limits and other traffic regulations. Use Signals : Always use turn signals to communicate your intentions to other drivers. Maintain Distance : Keep a safe following distance to avoid tailgating.
Stress Management
Stay Relaxed : Listen to calming music or audiobooks to keep yourself relaxed. Take Breaks : If you are on a long trip , take regular breaks to stretch and relax.
Avoid Competitive Driving
Let Others Pass : If someone wants to overtake, let them. It's not a competition. Don’t Engage : If another driver is aggressive, avoid making eye contact and do not respond with aggression.
Focus on Safety
Prioritize Safety : Remember that getting to your destination safely is more important than getting there quickly. Mind Your Speed : Keep an eye on your speed and adjust according to road conditions.
Dealing with Aggressive Drivers
Avoid Confrontation : Do not engage or retaliate against aggressive drivers. Report Dangerous Drivers : If you encounter an extremely aggressive driver, report them to the authorities if it's safe to do so.
? Is there a psychological component to aggressive driving?
Stress and Anxiety
High Stress Levels : Stress from work, personal life, or other sources can manifest as aggressive driving. Time Pressure : Feeling rushed or late can increase anxiety and lead to aggressive behaviors.
Personality Traits
Type A Personality : Individuals with Type A personalities, characterized by competitiveness and impatience, are more prone to aggressive driving. Impulsivity : People who are more impulsive may react aggressively to perceived slights or delays on the road.
Perception of Anonymity
Deindividuation : Drivers often feel a sense of anonymity in their vehicles, which can reduce their inhibition and lead to more aggressive behaviors. Lack of Accountability : The belief that they will not be held accountable for their actions can embolden drivers to act aggressively.
Cognitive Factors
Attribution Errors : Drivers may attribute negative intentions to other drivers’ actions, such as believing someone cut them off intentionally. Overestimation of Abilities : Some drivers may overestimate their driving skills and take unnecessary risks.
Emotional States
Anger and Frustration : Situations on the road can trigger anger and frustration, leading to aggressive responses. Mood Swings : Emotional instability or mood swings can influence how a driver reacts to traffic situations.
Social and Environmental Factors
Cultural Norms : In some cultures, aggressive driving may be more accepted or seen as a sign of assertiveness. Environmental Stressors : Heavy traffic, poor road conditions, and adverse weather can contribute to driver frustration and aggression.
Learning and Reinforcement
Modeling Behavior : Drivers may learn aggressive driving behaviors from observing others, including parents , peers, or media representations. Reinforcement : If aggressive driving leads to perceived positive outcomes, such as getting ahead in traffic, it can reinforce the behavior.
Control and Power Dynamics
Control Issues : Some drivers may use their vehicle as a means to exert control or dominance over others on the road. Power Struggles : Aggressive driving can be a way for some individuals to engage in power struggles with other drivers.
Prevention and Mitigation
Stress Management : Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing , and taking breaks can help reduce stress. Education and Awareness : Educating drivers about the dangers and consequences of aggressive driving can promote safer behaviors. Therapeutic Interventions : Cognitive-behavioral therapy and other psychological interventions can help address underlying issues contributing to aggressive driving.
? Can aggressive driving lead to accidents?
Types of Aggressive Driving Behaviors
Driving above the speed limit reduces the driver’s ability to react to sudden changes in traffic conditions. Higher speeds increase the severity of crashes.
Following too closely reduces the time available to react if the vehicle in front suddenly stops. Tailgating often leads to rear-end collisions.
Abrupt lane changes without signaling can surprise other drivers and cause accidents. This behavior increases the risk of side-impact collisions.
Ignoring traffic signals and signs can lead to collisions at intersections, which are often severe.
Blocking intersections can lead to gridlock and increased chances of accidents as drivers try to maneuver around the obstruction.
Failing to yield can cause collisions, particularly at intersections or merge points.
Engaging in road rage can distract the driver and escalate the situation, leading to dangerous maneuvers and potential accidents.
Speeding or tailgating in rain , snow, or fog increases the risk of losing control and causing accidents.
Statistics on Aggressive Driving and Accidents
Studies have shown that aggressive driving behaviors are involved in a significant percentage of traffic accidents . The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) attributes aggressive driving as a factor in a substantial number of fatal crashes.
Accidents caused by aggressive driving tend to be more severe due to the higher speeds and reckless nature of the driving.
Aggressive driving often leads to multi-vehicle pile-ups , especially on highways, due to sudden braking and lane changes .
Consequences of Aggressive Driving Accidents
Accidents caused by aggressive driving can result in serious injuries or death to drivers, passengers, and pedestrians .
Aggressive drivers may face legal penalties, including fines, license suspension, and imprisonment. Increased insurance premiums and financial liability for damages and injuries.
Victims of aggressive driving accidents may suffer from long-term emotional and psychological trauma.
Prevention
Raising awareness about the dangers of aggressive driving through public safety campaigns. Promoting defensive driving courses that teach safe driving practices.
Increased police presence and enforcement of traffic laws to deter aggressive driving. Use of traffic cameras and other technologies to monitor and penalize aggressive driving behaviors.
Encouraging drivers to manage stress and emotions while driving. Promoting courteous and patient driving habits to reduce road rage and aggressive behaviors.
? What should I do if an aggressive driver follows me?
Steps to Take When Followed by an Aggressive Driver
Keep your emotions in check and avoid making eye contact or gesturing at the aggressive driver. This can prevent escalating the situation.
Refrain from responding to the aggressive driver’s behavior. Avoid speeding up, slowing down, or making sudden maneuvers to retaliate or provoke them.
If possible, increase the distance between you and the aggressive driver by changing lanes safely. Allow them to pass if they are tailgating.
Avoid leading the aggressive driver to your home or a familiar location. Instead, drive to a public place with plenty of people around, such as a shopping center, police station, or busy street.
Call 911 if you feel threatened or believe the aggressive driver poses a danger to you or others. Provide the dispatcher with as much information as possible, including your location, the aggressive driver’s behavior, and the make, model, and license plate number of their vehicle.
Continue driving on well-lit and busy roads where there are other cars and witnesses. This can deter the aggressive driver from continuing their behavior.
Avoid stopping your car unless absolutely necessary. If you need to stop, choose a safe and public location where you can get help if needed.
If you are close to a police station, drive there. The presence of law enforcement can often deter the aggressive driver.
If you have passengers, ask them to alert other drivers by using hand signals or flashing your lights to attract attention and get help.
If it is safe to do so, take note of details about the aggressive driver and their vehicle. If you have a dash cam , it can record valuable evidence.
After the Incident
Even if the situation resolves without immediate danger, report the aggressive driver to the police. Provide them with the details of the incident and any evidence you have.
Review the incident to understand what happened and how you can avoid or handle similar situations in the future.
? What are some common myths about aggressive driving?
Myth 1: Aggressive Driving is Just Speeding
Reality: Aggressive driving encompasses a wide range of behaviors beyond speeding, including tailgating , weaving in and out of traffic , running red lights , and road rage . It's a pattern of unsafe driving practices that endanger others on the road.
Myth 2: Aggressive Driving Only Happens in Bad Traffic
Reality: While aggressive driving can be more common in congested traffic , it can occur at any time and in any traffic condition. Drivers can become aggressive on empty roads, during long commutes, or even in residential areas.
Myth 3: Aggressive Drivers Are Always Young Males
Reality: Aggressive driving is not limited to a specific demographic. Drivers of all ages, genders, and backgrounds can exhibit aggressive driving behaviors.
Myth 4: It's Safe to Confront an Aggressive Driver
Reality: Confronting an aggressive driver can escalate the situation and increase the risk of a dangerous encounter. It's safer to avoid engaging and take steps to protect yourself by staying calm and finding a safe place.
Myth 5: Honking or Gesturing Will Teach Them a Lesson
Reality: Honking or making gestures at an aggressive driver often exacerbates the situation. It's unlikely to change their behavior and can provoke further aggression.
Myth 6: You Can Spot Aggressive Drivers Easily
Reality: While some aggressive driving behaviors are overt, others can be subtle. Drivers may not always notice when someone is engaging in unsafe practices, especially if they're distracted.
Myth 7: Aggressive Driving is Only a Problem for Other Drivers
Reality: Aggressive driving poses a risk to everyone on the road, including pedestrians , cyclists , and the aggressive driver themselves. It increases the likelihood of accidents and injuries for all road users.
Myth 8: Aggressive Driving is a Quick Way to Get There Faster
Reality: While aggressive driving may seem like it saves time, it often results in minimal time savings and significantly increases the risk of accidents , traffic violations, and legal consequences.
Myth 9: Aggressive Driving Can’t Be Controlled
Reality: Drivers can control their aggressive tendencies by adopting safe driving practices, managing stress , and being courteous on the road. Defensive driving courses and stress management techniques can help.
Myth 10: Everyone Drives Aggressively Sometimes
Reality: While many drivers may experience frustration on the road, not everyone engages in aggressive driving. It's important to distinguish between occasional frustration and habitual aggressive driving behaviors.
? Can medication or substance abuse contribute to aggressive driving?
Impact of Medication :
Certain medications, especially those that affect the central nervous system, can cause side effects such as irritability, agitation, or aggression. These side effects can influence driving behavior, making a person more prone to aggressive driving.
Mixing medications with other substances, such as alcohol, can exacerbate side effects and lead to unpredictable behavior, including increased aggression.
Misusing or overusing prescription drugs can lead to heightened emotions and impaired judgment, contributing to aggressive driving behaviors.
Impact of Substance Abuse:
Alcohol and drugs impair cognitive functions, making it difficult for drivers to assess situations accurately and respond appropriately. This impairment can lead to risky and aggressive driving behaviors.
Substance abuse often lowers inhibitions and increases the likelihood of taking risks, such as speeding , tailgating , or engaging in road rage.
Many substances can alter mood, causing heightened anger or frustration, which can translate into aggressive actions on the road.
Substances that impair physical coordination can lead to erratic driving, which other drivers might perceive as aggressive.
Statistics and Studies:
Studies have shown that drivers under the influence of alcohol or drugs are significantly more likely to engage in aggressive driving behaviors compared to sober drivers. Research indicates that certain psychiatric medications can influence aggression and driving behavior, depending on the individual's reaction to the medication.
Preventive Measures:
Educating drivers about the potential effects of medications and substances on driving behavior can help them make informed decisions.
Healthcare providers should monitor patients for side effects and advise them on safe driving practices when prescribing medications with known side effects that could affect driving.
Implementing and promoting substance abuse prevention and treatment programs can reduce the incidence of impaired and aggressive driving.
What to Do:
If you are taking medication, consult with your healthcare provider about how it might affect your driving.
Never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Use alternative transportation options if you have consumed substances that impair your ability to drive safely.
Stay informed about the potential side effects of any medications you are taking and how they might interact with other substances.
? What role does culture play in aggressive driving?
Driving Norms and Behaviors:
Regional Driving Habits: In some cultures, aggressive driving behaviors such as tailgating , speeding , and frequent lane changes may be more common and socially accepted. Traffic Laws and Enforcement: The strictness of traffic laws and the rigor with which they are enforced can influence driving behaviors. In cultures with lax enforcement, aggressive driving may be more prevalent.
Societal Attitudes:
Attitudes Toward Aggression: Societal norms regarding aggression can influence driving behavior. In cultures where aggressive behavior is more accepted or even encouraged in daily life, this can translate into more aggressive driving styles. Perception of Driving Skills: Some cultures place a high value on demonstrating driving skills and control, which can lead to risky behaviors and aggressive driving as a way to showcase these skills.
Stress and Time Pressure:
Urbanization and Traffic Congestion: In highly urbanized and congested areas , drivers may experience more stress and frustration, leading to aggressive driving. Cultural attitudes toward time and punctuality can exacerbate this stress. Economic Factors: In regions with economic pressures, people might be more likely to engage in aggressive driving to save time or meet tight schedules.
Education and Awareness :
Driver Education Programs: The presence and quality of driver education programs can vary. In cultures where driver education is thorough and emphasizes safe driving practices, aggressive driving may be less common. Public Awareness Campaigns: Campaigns that raise awareness about the dangers of aggressive driving can influence public attitudes and behaviors. Cultures with proactive road safety campaigns may see lower rates of aggressive driving.
Influence of Media:
Media Representation: How driving is portrayed in media and entertainment can shape people's attitudes toward aggressive driving. Cultures that glorify high-speed chases and aggressive driving in movies and TV shows might see more of these behaviors on the road. Social Media: Social media can both positively and negatively influence driving behavior. While it can spread awareness about safe driving practices, it can also encourage risky behaviors through viral videos of aggressive driving stunts.
Collective vs. Individualistic Cultures:
Collectivist Cultures: In collectivist cultures, where the welfare of the group is emphasized over individual desires, drivers might be more considerate and less likely to engage in aggressive driving. Individualistic Cultures: In individualistic cultures, where personal freedom and self-expression are prioritized, there may be more instances of aggressive driving as individuals assert their dominance on the road.
Examples of Cultural Influence:
Japan: Known for its polite and orderly driving culture, aggressive driving is less common. Respect for others and adherence to rules are deeply ingrained in Japanese culture. Italy: In some parts of Italy, driving can be more chaotic, with frequent lane changes and tailgating . The cultural acceptance of assertive driving behaviors can lead to more aggressive driving. United States: Driving behaviors can vary widely, but in some urban areas, aggressive driving is more prevalent due to high stress and congestion.